Spotlight
A selection of resources from across the Federation

HIV Theory of Change
Our HIV Theory of Change is to clarify the goals and vision of IPPF’s HIV programme and to articulate the different pathways and strategies IPPF uses to contribute towards its HIV goals and vision.
Filter our resources by:


| 04 December 2018
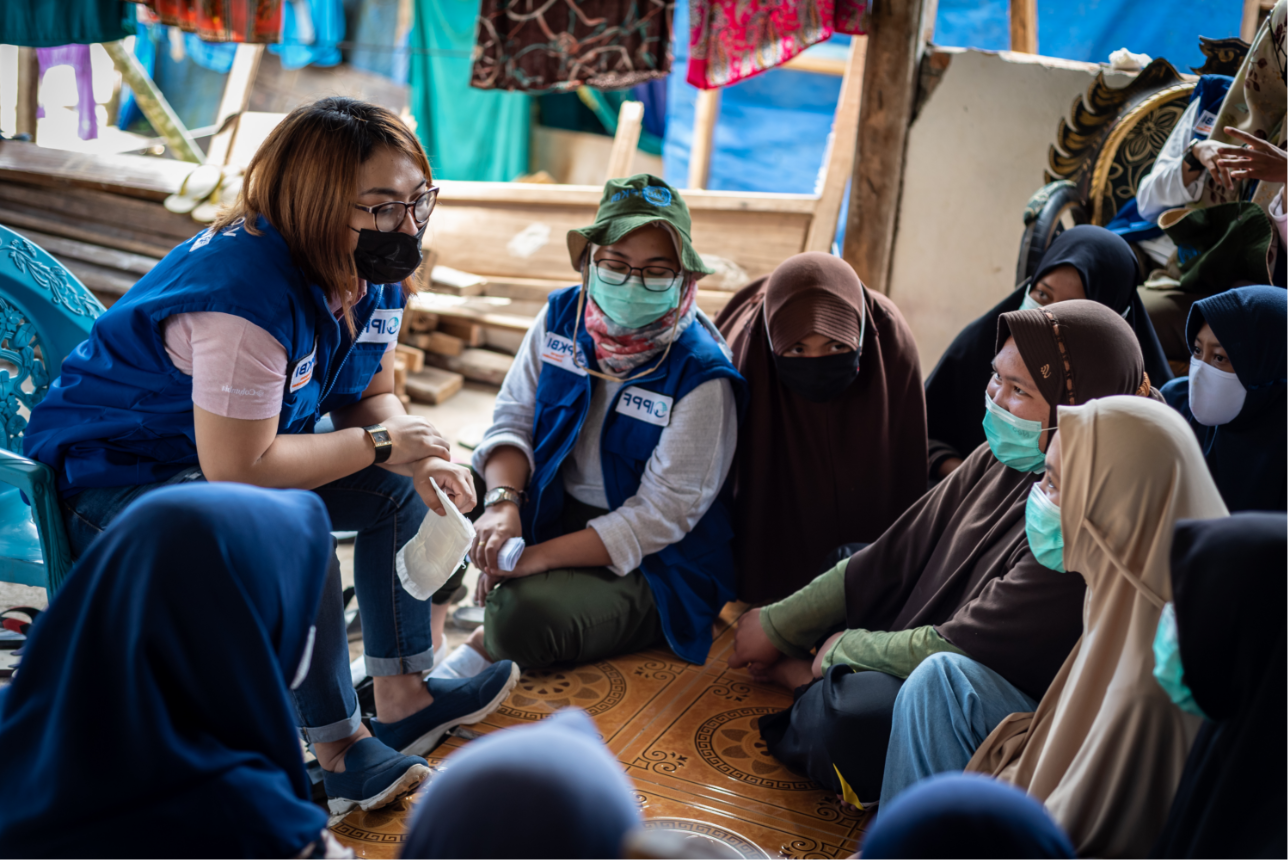
Leaving no one behind: Universal health coverage and sexual and reproductive health and rights
Universal health coverage means ensuring every person has access to quality, affordable health services and plays a pivotal role in achieving global development targets. Healthy populations can better contribute socially and economically, while poor health is a major driver of poverty. Universal access to sexual and reproductive health care services is identified in the Sustainable Development Goals as an essential contributor to ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages. IPPF, together with the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, undertook a literature review looking at progress to date in and challenges to achieving universal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights. The review, Leaving no one behind, is illustrated with case studies on Afghanistan, Cambodia, Kenya and Sudan. Supported by the Japan Trust Fund.

| 30 November 2018
Quiz: "Can I get HIV from kissing?"
World AIDS Day: “Can I get HIV from kissing?” and other questions answered1 December is World AIDS Day, an opportunity for us all to unite in the fight against HIV, to stand in solidarity with the 36.9 million people living with HIV around the world, and to commemorate those who have died from an AIDS-related illness. Over the past few decades, HIV and AIDS have been discussed a lot, but what do you really know about them? Find out in our quiz >> 1/10. True or false: HIV and AIDS are the same thing2/10. How might HIV be transmitted from one person to another?3/10. If both sexual partners have HIV, then they don’t need to worry about using condoms – true or false?4/10. There are 36.9 million people living with HIV globally. How many of them are not aware of their HIV status?5/10. Can people living with HIV safely have children?6/10. HIV only affects certain groups of people – true or false?7/10. Which of the following is the best way to prevent transmission of HIV and other STIs?8/10. True or false: If you have taken an HIV test already, then you don't need to do it again9/10. How long should you wait before going for an HIV test?10/10. What does being “undetectable” mean?Good try! If you learned something new today, scroll down to share this with friends :point_down:Pretty good! If you learned something new today, scroll down to share this with friends :point_down:Great work! If you learned something new today, scroll down to share this with friends :point_down:

| 17 September 2018
IMAP statement on sexual and reproductive health in Humanitarian settings
Today, unprecedented numbers of people are living in a state of crisis or emergency. In 2018, it is estimated that 135.7 million people are in need of humanitarian assistance, with conflict and natural disasters predicted to be the biggest drivers. Of those in need, approximately one-quarter is estimated to be women and girls of reproductive age (aged 15–49) and approximately 5 million will be pregnant. Globally, 60% of preventable maternal deaths take place in settings of conflict, fragility, displacement and natural disasters.

| 02 August 2018
Technical brief: Dolutegravir for women living with HIV of reproductive age
In May 2018, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a potential safety issue concerning dolutegravir (DTG), a common first-line antiretroviral treatment drug that is used to prevent and treat HIV infections. Preliminary findings from a study in Botswana found an increased risk of neural tube defects in infants born to women taking DTG at the time of conception. As a result of this study, WHO’s revised guidance on antiretroviral regimens for treating and preventing HIV infections, released in July 2018, include a caution on use of DTG by women and adolescent girls of childbearing potential. This brief aims to provide an overview of the research to date, current WHO guidance, and recommendations for IPPF.
| 19 June 2018
Humanitarian Strategy
IPPF’s Strategic Framework (SF) 2016-2022 commits the organisation to lead a locally-owned globally connected movement that provides and enables services, and champions sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) for all. Increasing numbers of people face crises or live in chronically insecure settings. In recent years we have scaled up the number of sexual and reproductive health services and information provided to people in emergencies from 1.3m in 2013 to 3.2m in 2016, but we can do much more. The goal of this strategy is to improve access to life-saving SRHR for crisis-affected people in all their diversity. As the situation normalises after a crisis, we aim to leave behind stronger MAs sustaining quality services to diverse populations. IPPF’s model for SRHR in crisis connects the key elements of humanitarian action (prevention and preparedness, response, recovery and resilience) with long-term, equitable development.
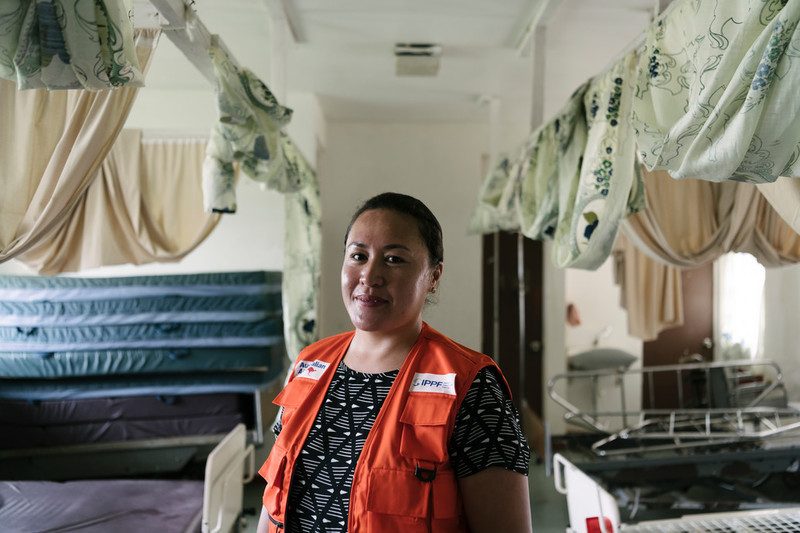

| 24 April 2018
Humanitarian disaster in Tonga brings opportunity through access to healthcare
Following the devastation wrecked by Tropical Cyclone Gita on the island of Kingdon of Tonga, the Tonga Family Health Association deployed an emergency response team. The team was able to bring vital sexual and reproductive health care to local communities. By taking services to the people, the team has been able to expand the types of care that many women would not readily access including pap smears and the opportunity to raise awareness around gender-based violence. Combining service delivery, as well as information, is part of our tailored approach to humanitarian crises; ensuring we meet need, wherever it is, whoever requires it, for as long as they want it. Photography © IPPF/Alana Holmberg