Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

What does the year 2024 hold for us?
As the new year begins, we take a look at the trends and challenges ahead for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Most Popular This Week

Palestine
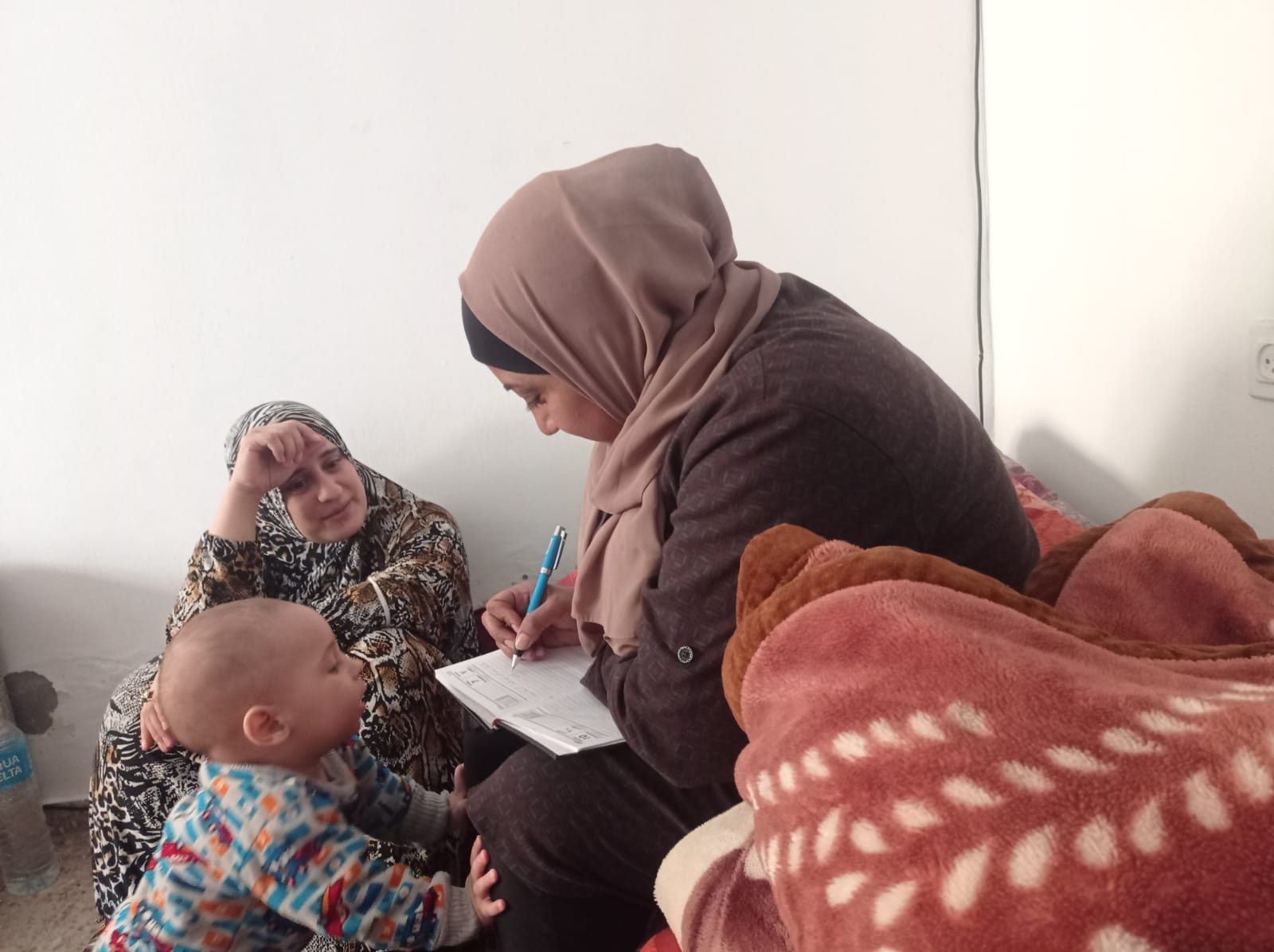

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
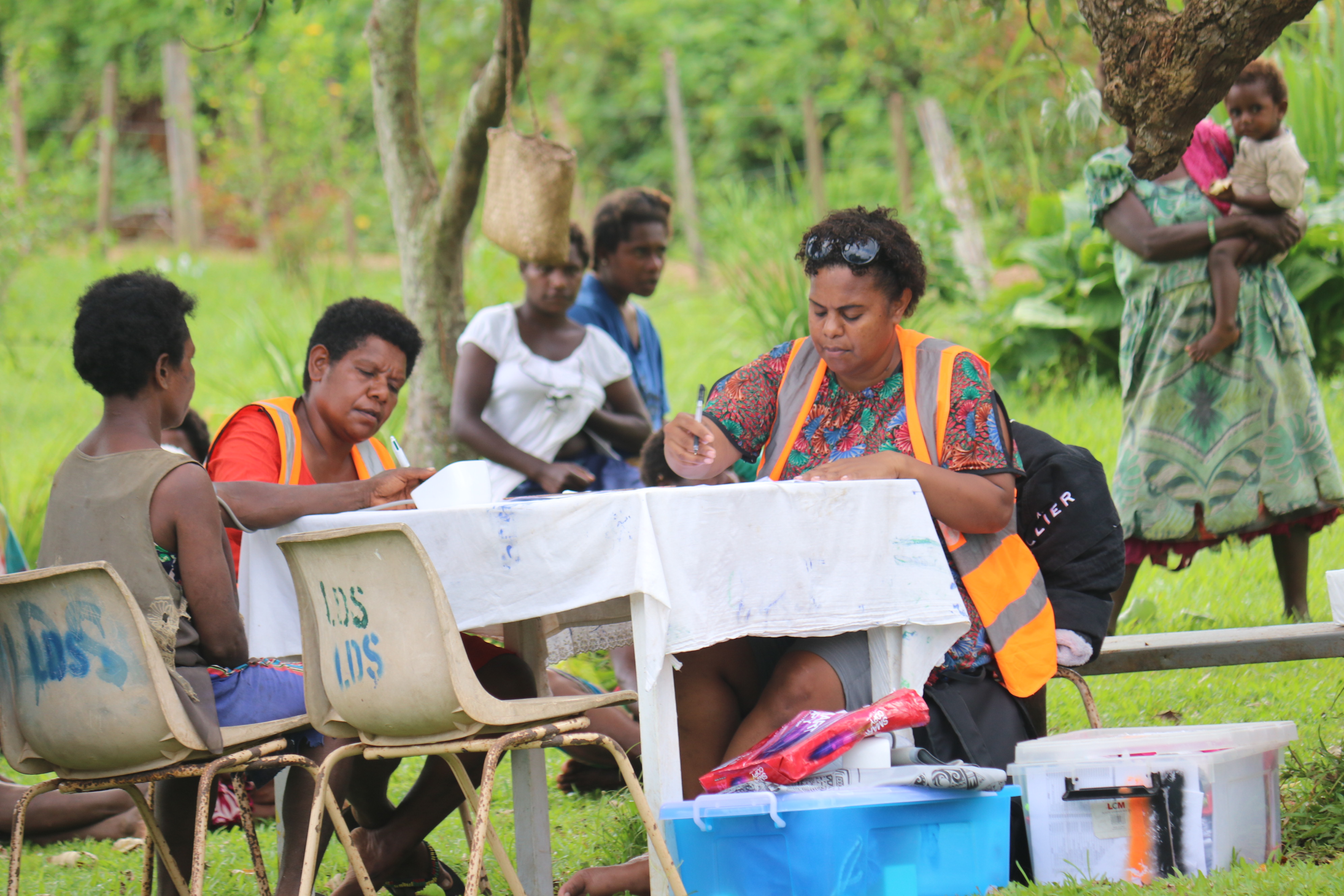

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
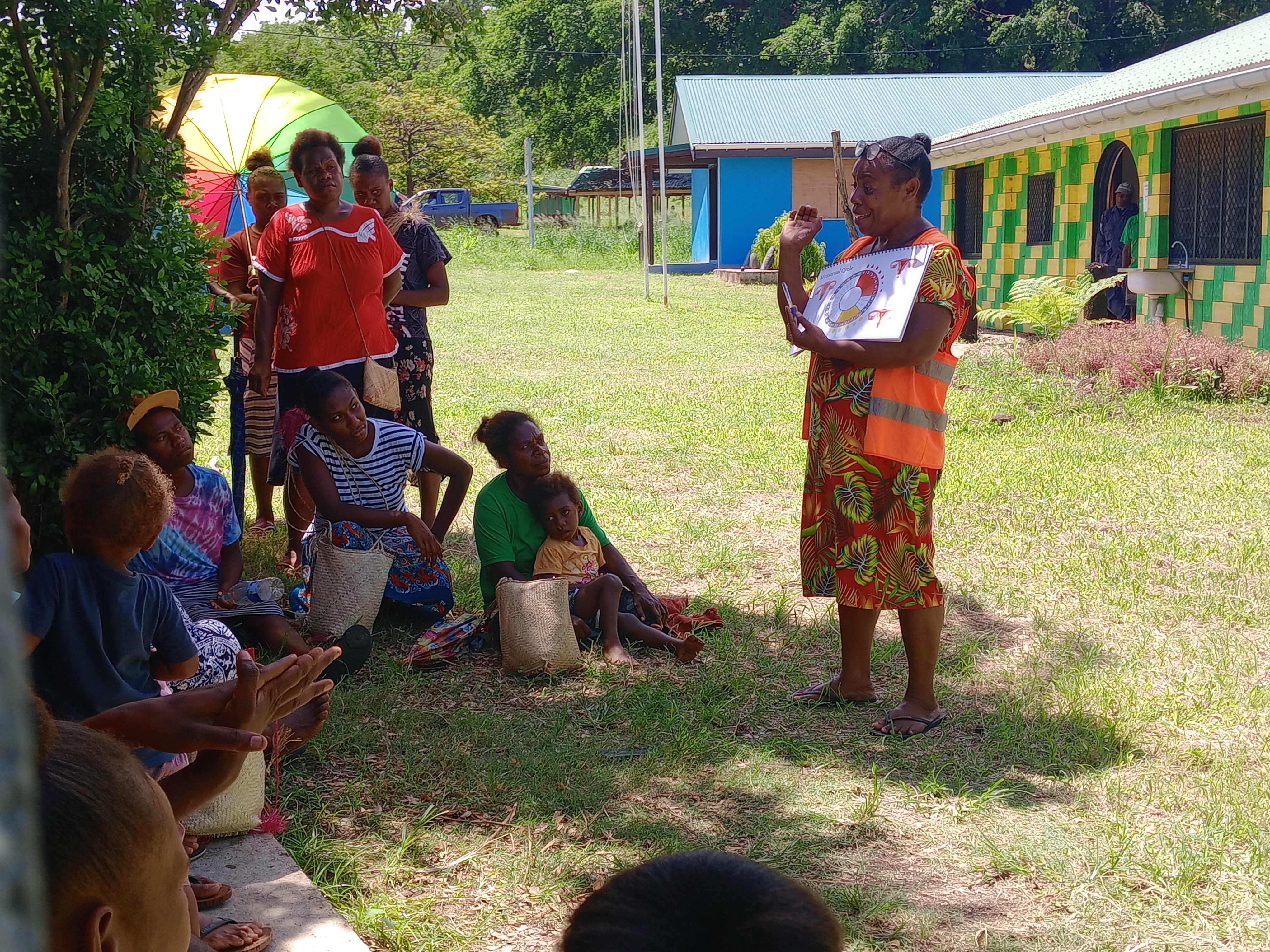

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Cook Islands

Dean and the Cook Islands Condom Car
On the island of Rarotonga, the main island of the Cook Islands in the South Pacific, a little white van makes its rounds on the palm-tree lined circular road.
Filter our stories by:
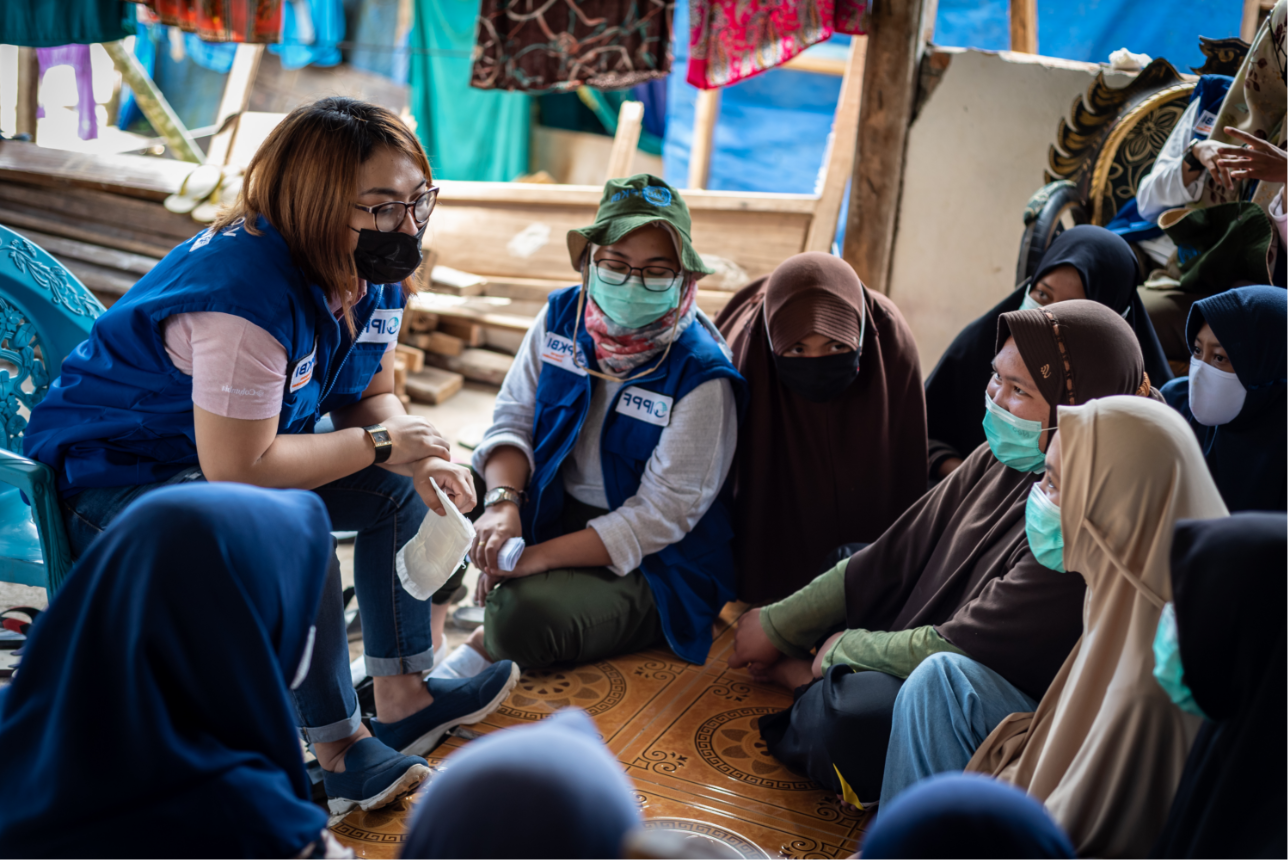


| 28 July 2020
"I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality"
Seventeen-year-old student Jumeya Mohammed Amin started educating other people about sexual and reproductive health when she was 14 years old. She trained as a ‘change agent’ for her community through the Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia’s south west office in Jimma, the capital of Oromia region. Amin comes from a small, conservative town about 20km outside the city. "I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality, because they [men in her community] start having sex with girls at a young age, even with girls as young as nine years old, because of a lack of education." "They suddenly had to act like grown-up women" "Before I started this training I saw the majority of students having sex early and getting pregnant because of a lack of information, and they would have to leave home and school. Boys would be disciplined and if they were seen doing things on campus, expelled. Girls younger than me at the time were married. The youngest was only nine. They would have to go back home and could not play anymore or go to school. They suddenly had to act like grown-up women, like old ladies. They never go back to school after marriage. My teacher chose me for this training and told me about the programme. I like the truth so I was not afraid. I heard about a lot of problems out there during my training and I told myself I had to be strong and go and fight this." "I have a brother and four sisters and I practiced my training on my family first. They were so shocked by what I was saying they were silent. Even on the second day, they said nothing. On the third day, I told them I was going to teach people in schools this, so I asked them why they had stayed silent. They told me that because of cultural and religious issues, people would not accept these ideas and stories, but they gave me permission to go and do it. Because of my efforts, people in my school have not started having sex early and the girls get free sanitary pads through the clubs so they no longer need to stay home during periods." Training hundreds of her peers "I know people in my community who have unplanned pregnancies consult traditional healers [for abortions] and take drugs and they suffer. I know one girl from 10th grade who was 15 years old and died from this in 2017. The healers sometimes use tree leaves in their concoctions. We tell them where they can go and get different [safe abortion] services. The first round of trainings I did was with 400 students over four months and eight sessions in 2017. Last year, I trained 600 people and this year in the first trimester of school I trained 400. When students finish the course, they want to do it again, and when we forget we have a session, they come and remind me. At school, they call me a teacher. I’d like to be a doctor and this training has really made me want to do that more."

| 16 April 2024
"I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality"
Seventeen-year-old student Jumeya Mohammed Amin started educating other people about sexual and reproductive health when she was 14 years old. She trained as a ‘change agent’ for her community through the Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia’s south west office in Jimma, the capital of Oromia region. Amin comes from a small, conservative town about 20km outside the city. "I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality, because they [men in her community] start having sex with girls at a young age, even with girls as young as nine years old, because of a lack of education." "They suddenly had to act like grown-up women" "Before I started this training I saw the majority of students having sex early and getting pregnant because of a lack of information, and they would have to leave home and school. Boys would be disciplined and if they were seen doing things on campus, expelled. Girls younger than me at the time were married. The youngest was only nine. They would have to go back home and could not play anymore or go to school. They suddenly had to act like grown-up women, like old ladies. They never go back to school after marriage. My teacher chose me for this training and told me about the programme. I like the truth so I was not afraid. I heard about a lot of problems out there during my training and I told myself I had to be strong and go and fight this." "I have a brother and four sisters and I practiced my training on my family first. They were so shocked by what I was saying they were silent. Even on the second day, they said nothing. On the third day, I told them I was going to teach people in schools this, so I asked them why they had stayed silent. They told me that because of cultural and religious issues, people would not accept these ideas and stories, but they gave me permission to go and do it. Because of my efforts, people in my school have not started having sex early and the girls get free sanitary pads through the clubs so they no longer need to stay home during periods." Training hundreds of her peers "I know people in my community who have unplanned pregnancies consult traditional healers [for abortions] and take drugs and they suffer. I know one girl from 10th grade who was 15 years old and died from this in 2017. The healers sometimes use tree leaves in their concoctions. We tell them where they can go and get different [safe abortion] services. The first round of trainings I did was with 400 students over four months and eight sessions in 2017. Last year, I trained 600 people and this year in the first trimester of school I trained 400. When students finish the course, they want to do it again, and when we forget we have a session, they come and remind me. At school, they call me a teacher. I’d like to be a doctor and this training has really made me want to do that more."
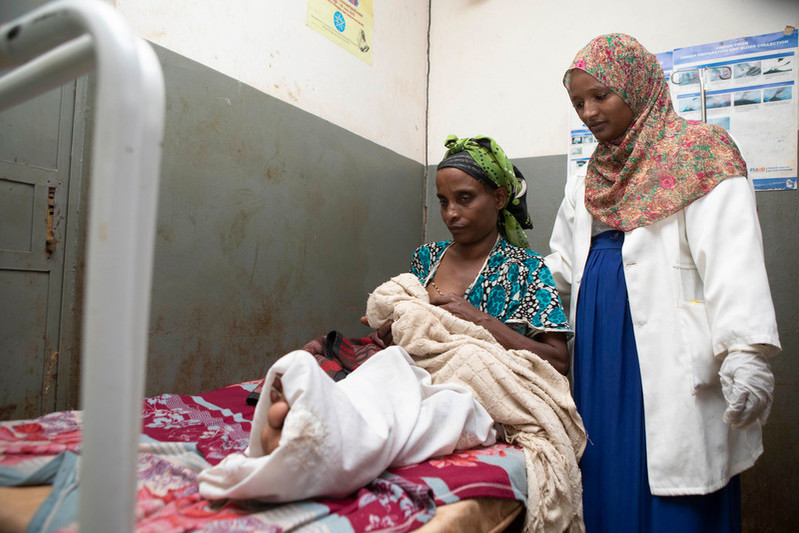

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 16 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
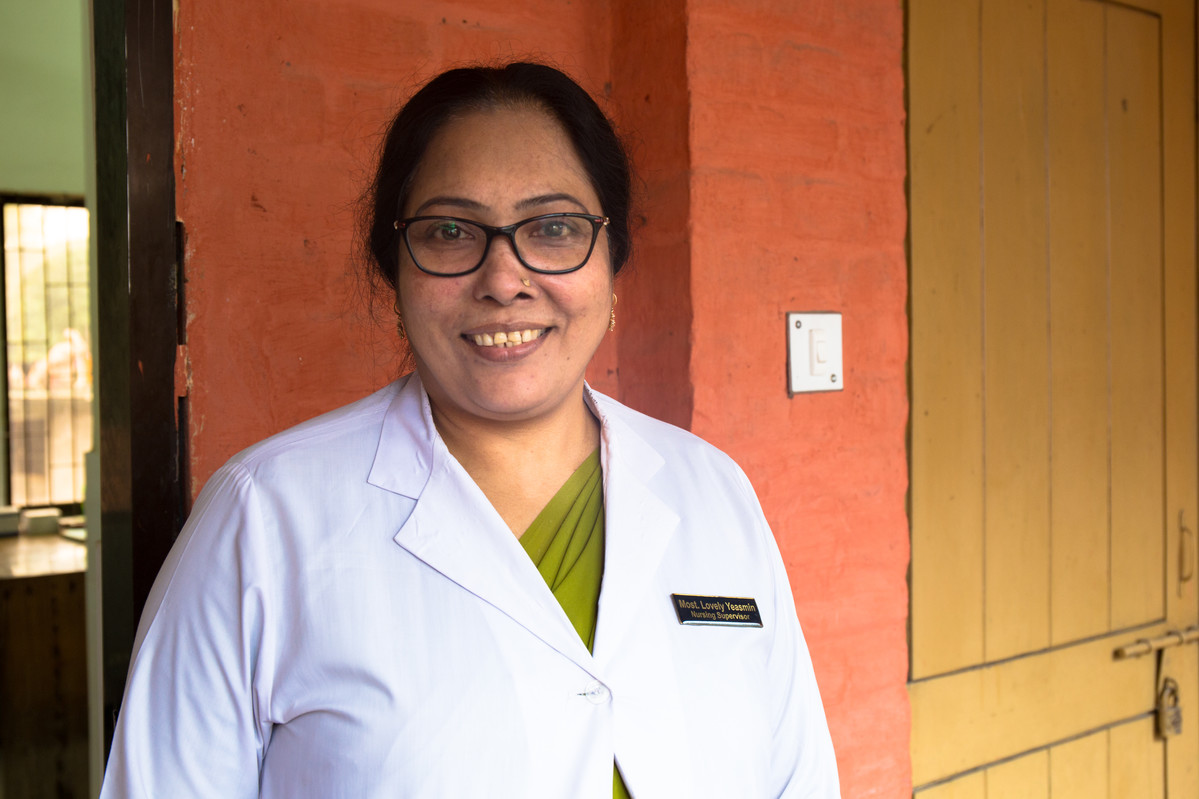

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 16 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”
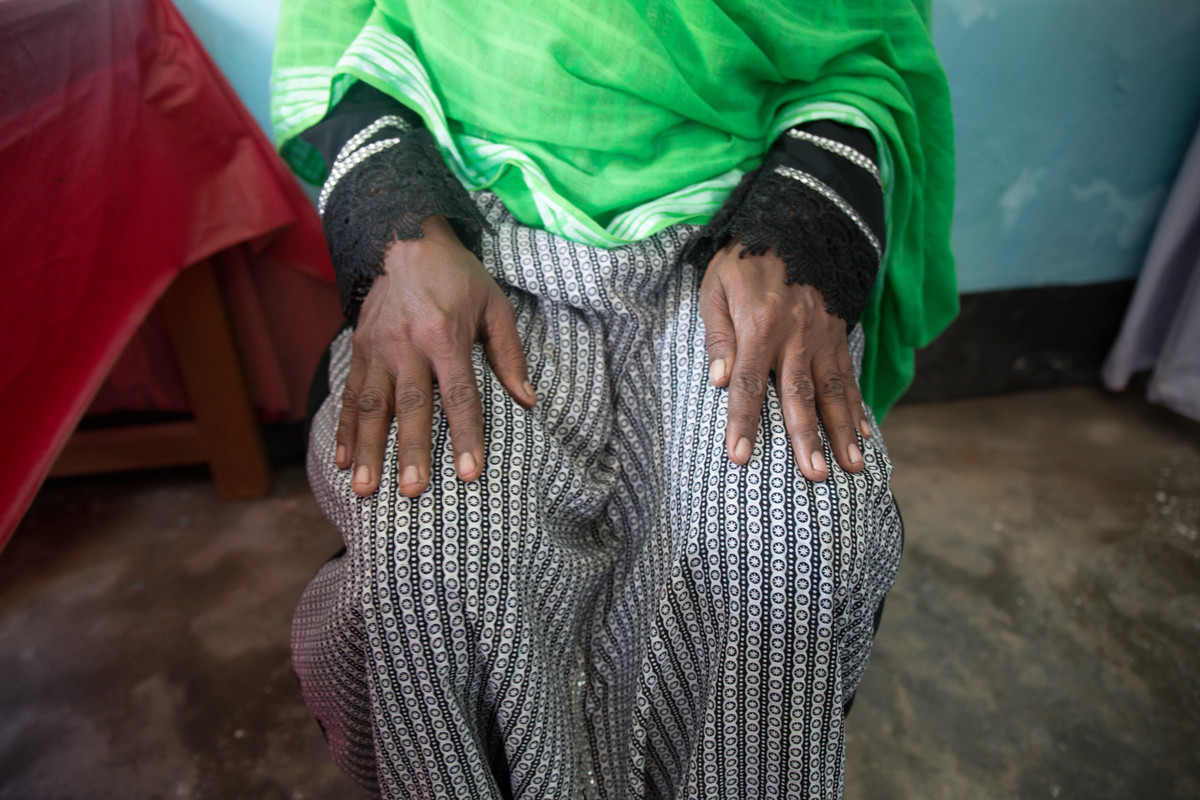
| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 16 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.
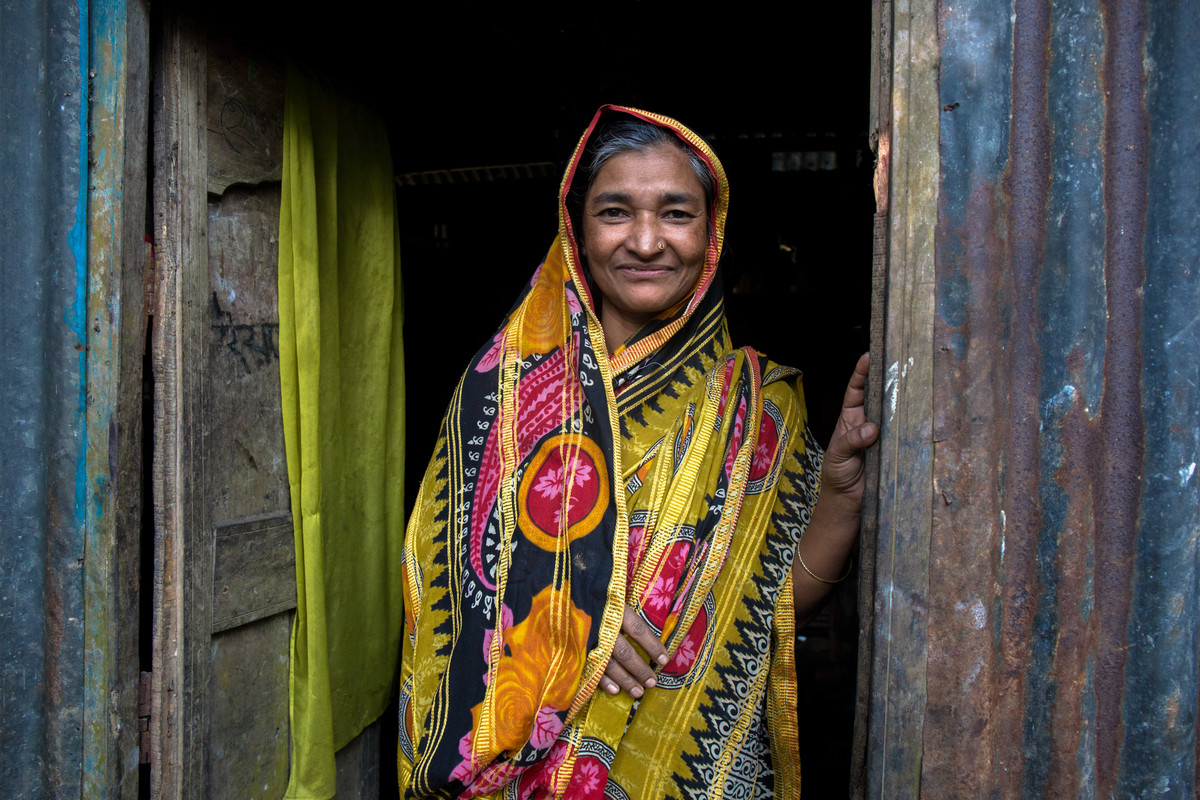

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 16 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 28 July 2020
"I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality"
Seventeen-year-old student Jumeya Mohammed Amin started educating other people about sexual and reproductive health when she was 14 years old. She trained as a ‘change agent’ for her community through the Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia’s south west office in Jimma, the capital of Oromia region. Amin comes from a small, conservative town about 20km outside the city. "I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality, because they [men in her community] start having sex with girls at a young age, even with girls as young as nine years old, because of a lack of education." "They suddenly had to act like grown-up women" "Before I started this training I saw the majority of students having sex early and getting pregnant because of a lack of information, and they would have to leave home and school. Boys would be disciplined and if they were seen doing things on campus, expelled. Girls younger than me at the time were married. The youngest was only nine. They would have to go back home and could not play anymore or go to school. They suddenly had to act like grown-up women, like old ladies. They never go back to school after marriage. My teacher chose me for this training and told me about the programme. I like the truth so I was not afraid. I heard about a lot of problems out there during my training and I told myself I had to be strong and go and fight this." "I have a brother and four sisters and I practiced my training on my family first. They were so shocked by what I was saying they were silent. Even on the second day, they said nothing. On the third day, I told them I was going to teach people in schools this, so I asked them why they had stayed silent. They told me that because of cultural and religious issues, people would not accept these ideas and stories, but they gave me permission to go and do it. Because of my efforts, people in my school have not started having sex early and the girls get free sanitary pads through the clubs so they no longer need to stay home during periods." Training hundreds of her peers "I know people in my community who have unplanned pregnancies consult traditional healers [for abortions] and take drugs and they suffer. I know one girl from 10th grade who was 15 years old and died from this in 2017. The healers sometimes use tree leaves in their concoctions. We tell them where they can go and get different [safe abortion] services. The first round of trainings I did was with 400 students over four months and eight sessions in 2017. Last year, I trained 600 people and this year in the first trimester of school I trained 400. When students finish the course, they want to do it again, and when we forget we have a session, they come and remind me. At school, they call me a teacher. I’d like to be a doctor and this training has really made me want to do that more."

| 16 April 2024
"I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality"
Seventeen-year-old student Jumeya Mohammed Amin started educating other people about sexual and reproductive health when she was 14 years old. She trained as a ‘change agent’ for her community through the Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia’s south west office in Jimma, the capital of Oromia region. Amin comes from a small, conservative town about 20km outside the city. "I wanted to protect girls from violence – like early marriage – and I wanted to change people’s wrong perceptions about sex and sexuality, because they [men in her community] start having sex with girls at a young age, even with girls as young as nine years old, because of a lack of education." "They suddenly had to act like grown-up women" "Before I started this training I saw the majority of students having sex early and getting pregnant because of a lack of information, and they would have to leave home and school. Boys would be disciplined and if they were seen doing things on campus, expelled. Girls younger than me at the time were married. The youngest was only nine. They would have to go back home and could not play anymore or go to school. They suddenly had to act like grown-up women, like old ladies. They never go back to school after marriage. My teacher chose me for this training and told me about the programme. I like the truth so I was not afraid. I heard about a lot of problems out there during my training and I told myself I had to be strong and go and fight this." "I have a brother and four sisters and I practiced my training on my family first. They were so shocked by what I was saying they were silent. Even on the second day, they said nothing. On the third day, I told them I was going to teach people in schools this, so I asked them why they had stayed silent. They told me that because of cultural and religious issues, people would not accept these ideas and stories, but they gave me permission to go and do it. Because of my efforts, people in my school have not started having sex early and the girls get free sanitary pads through the clubs so they no longer need to stay home during periods." Training hundreds of her peers "I know people in my community who have unplanned pregnancies consult traditional healers [for abortions] and take drugs and they suffer. I know one girl from 10th grade who was 15 years old and died from this in 2017. The healers sometimes use tree leaves in their concoctions. We tell them where they can go and get different [safe abortion] services. The first round of trainings I did was with 400 students over four months and eight sessions in 2017. Last year, I trained 600 people and this year in the first trimester of school I trained 400. When students finish the course, they want to do it again, and when we forget we have a session, they come and remind me. At school, they call me a teacher. I’d like to be a doctor and this training has really made me want to do that more."

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 16 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 16 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 16 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 16 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”








