Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.
Most Popular This Week
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
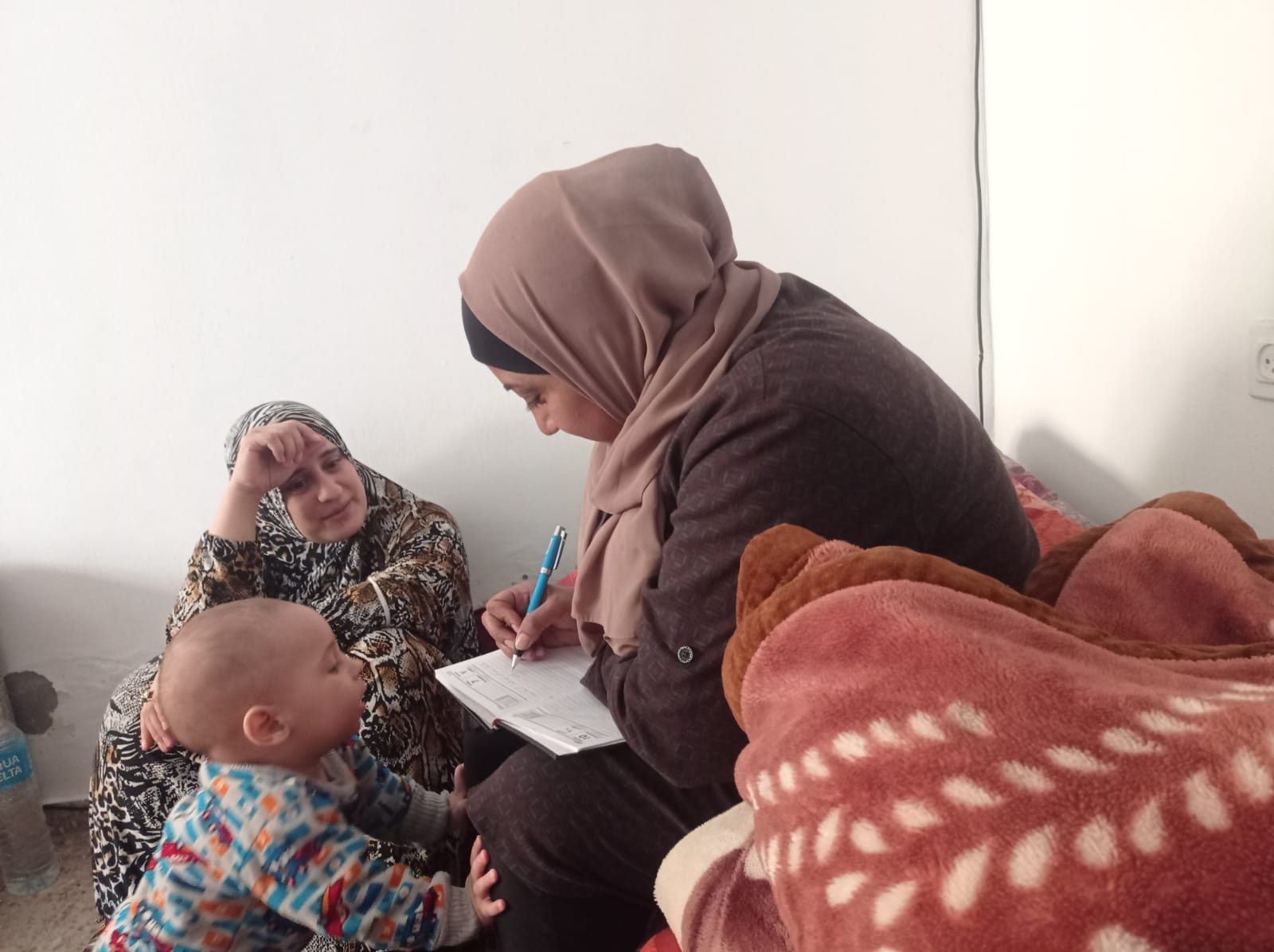

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
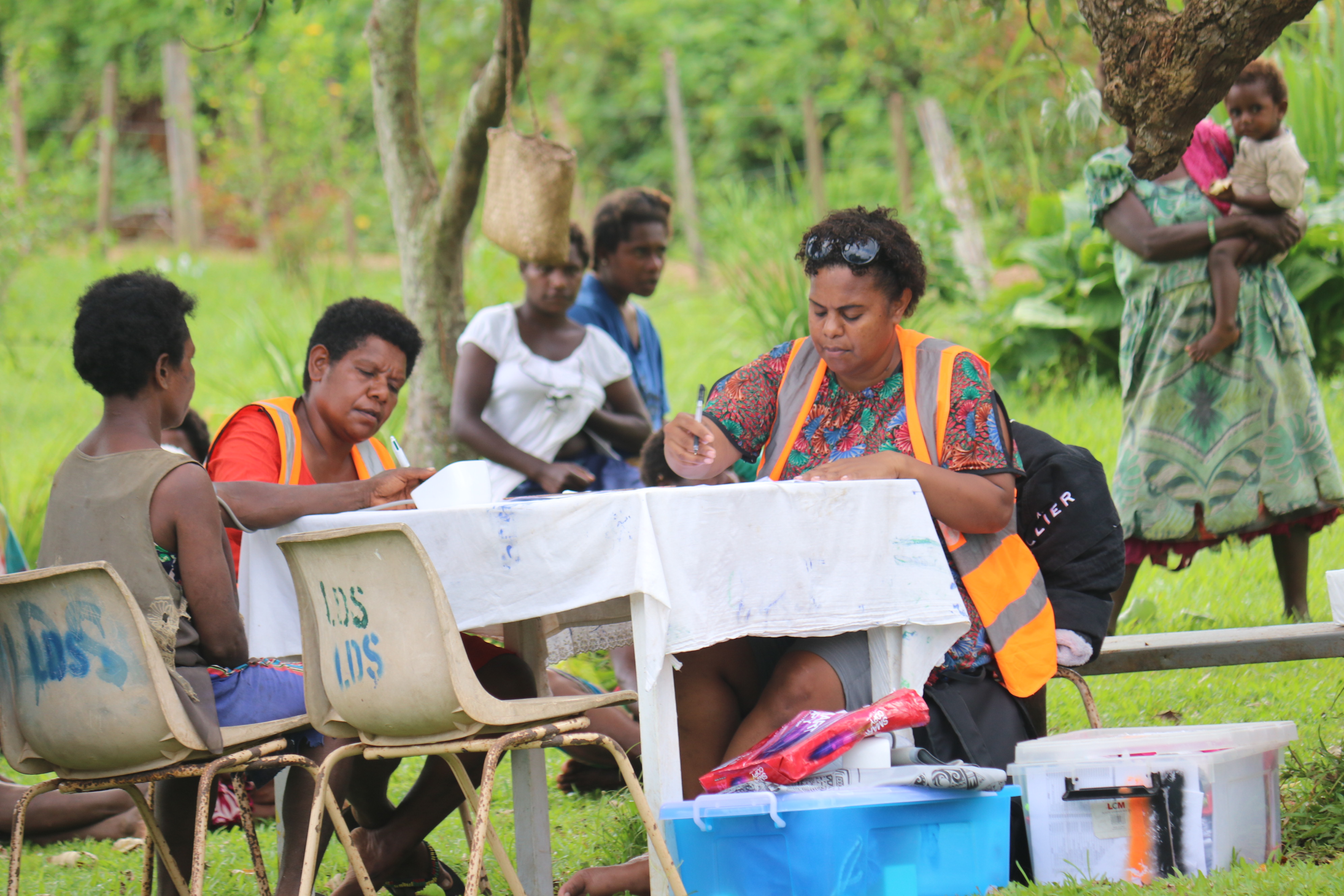

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
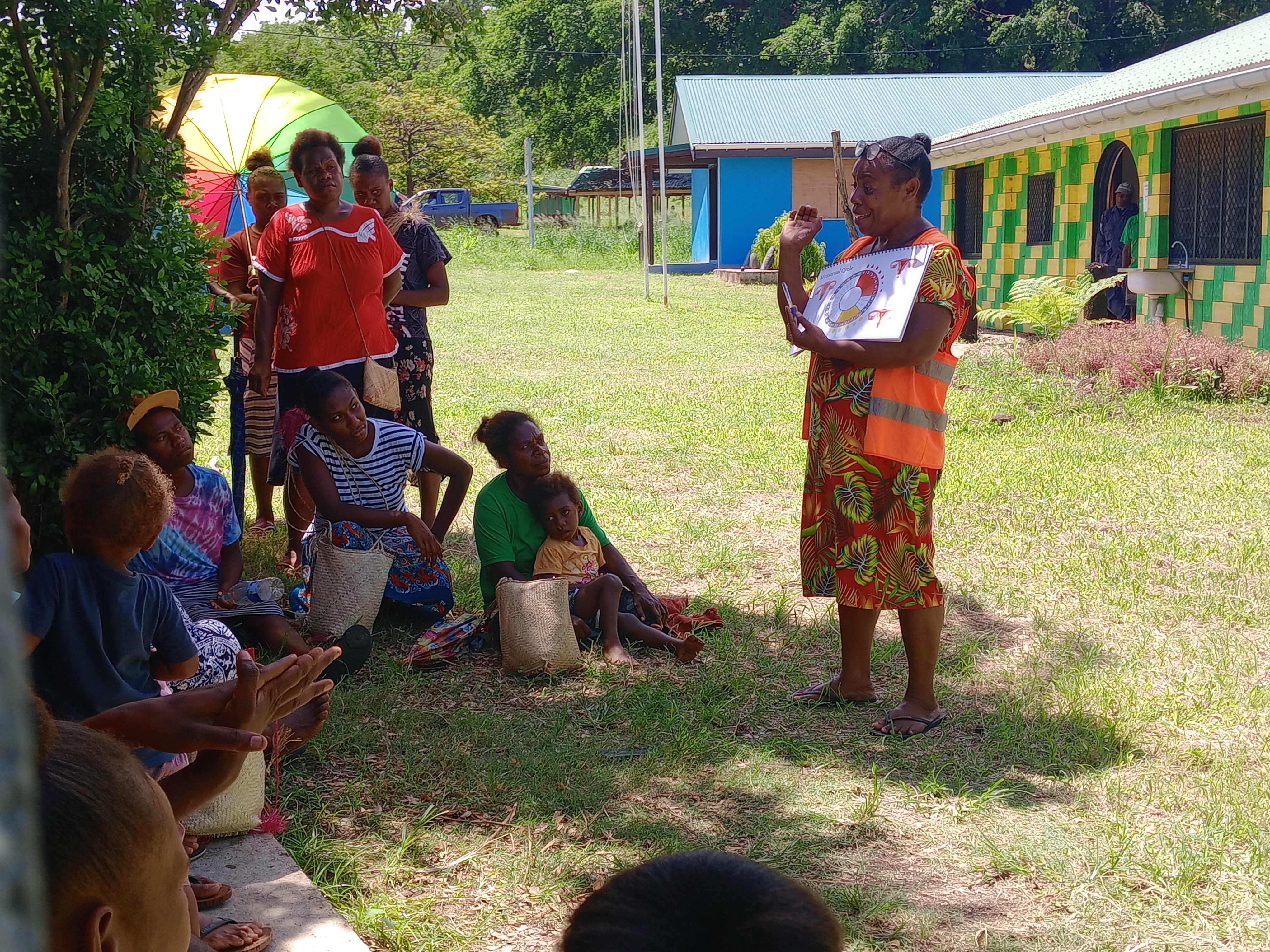

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Filter our stories by:
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Aruba
- Bangladesh
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- (-) Colombia
- Congo, Dem. Rep.
- Cook Islands
- El Salvador
- Ethiopia
- Fiji
- France
- Germany
- Ghana
- Guinea-Conakry
- India
- Ireland
- Jamaica
- Kenya
- Kiribati
- Lesotho
- (-) Malawi
- Mali
- Mozambique
- Nepal
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Palestine
- Poland
- Senegal
- Somaliland
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Thailand
- Togo
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vanuatu
- Zambia


| 09 September 2020
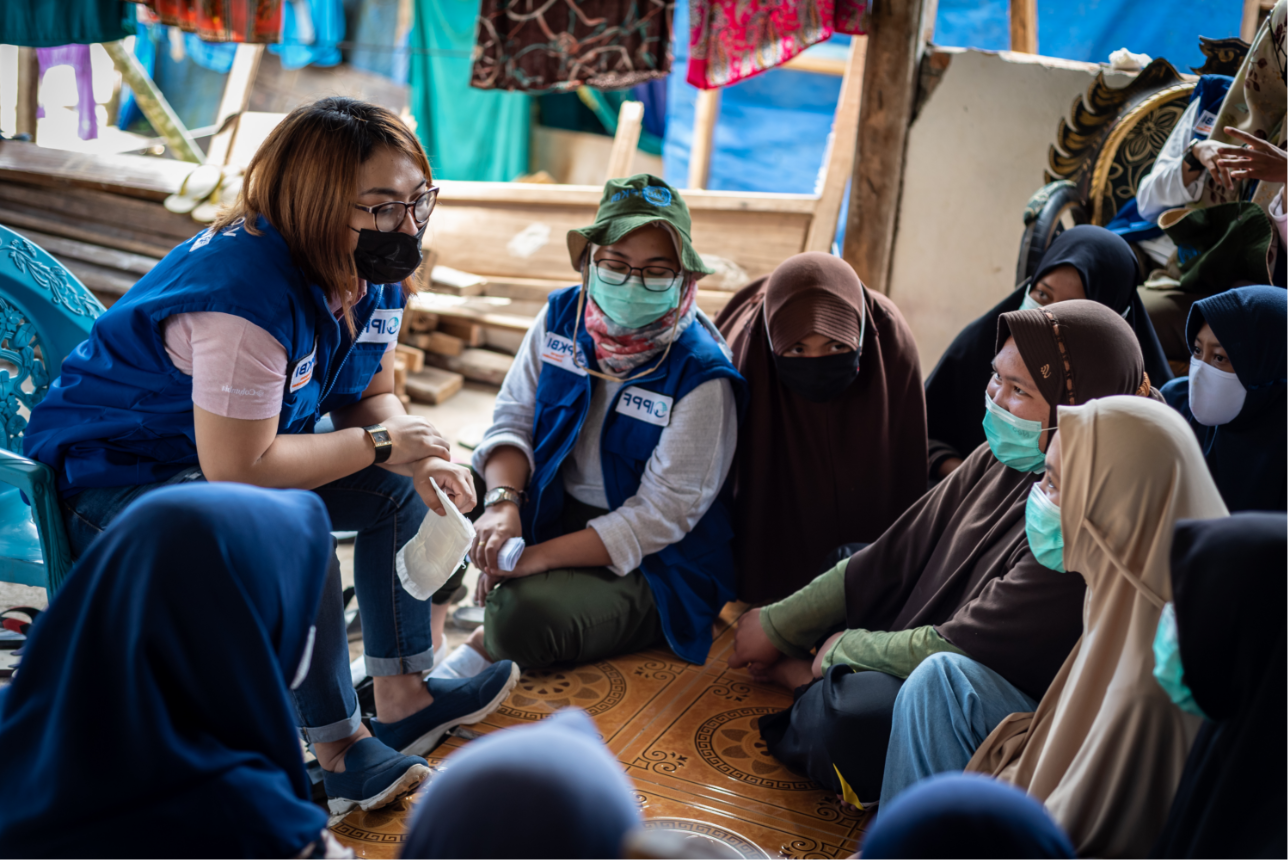
In pictures: Increasing contraceptive care to young people in Malawi
Our Member Association, Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM), is delivering healthcare through the support of WISH* in Lilongwe and Kasungu with a focus on young women and girls. A bespoke training programme supports community health workers on how to deliver youth-friendly healthcare through outreach to local communities, and especially young women. *The Women’s Integrated Sexual Health (WISH2Action) programme, is funded by the UK Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), under the strategy to ‘Leave No One Behind’. Photographs ©FPAM/Andrew Mkandawire/Malawi Barriers to contraceptive care Young people, particularly girls, face barriers to accessing sexual and reproductive healthcare and contraception due to societal perceptions that they have no need for them. Chiefs and parents in the Lilongwe and Kasungu districts have demonstrated that by working together they are able to meet this need and protect the health and wellbeing of young people in their communities. Their collective approach ensures elders advocate on behalf of the youth in their communities, encouraging them to feel confident in accessing healthcare provision and to counter myths and misconceptions about contraception. Their goal is to reduce the high number of unintended pregnancies and STIs among young people. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gogo Nakwenda Gogo Nakwenda is respected in her community as a go-to counsellor for young people, advising on sexuality and how to access healthcare. Now nearing her 80s, Nakwneda, talks about different contraception methods, saying that if she was 18 again, she would opt for the five-year implant to ensure her education and future work opportunities. “During our time we used traditional contraception, but I have learned that modern pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections prevention methods are very predictable and give no excuses to protection errors. One can comfortably plan when to have a child and when not to have child.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, volunteer and parent Lucy believes it is important to educate both parents and young people on the benefits of access to contraception. Lucy talks about how myths and misconceptions remain a barrier for young girls to be able to access contraception, mostly because of fears related to infertility. She is open about her own experiences with contraceptives. “I’m 38, I have used pills, injectables and now I’m now using the IUD and successfully I have given birth to three children and here I am in good health. Who else can lie about modern contraceptives? I usually encourage the young ones to be mindful of their future to avoid any mistake that could be prevented with available contraceptives they can comfortably demand from their community health workers.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Chiefs Sadulira and Chinoko Chiefs in Lilongwe and Kasungu districts are committed and supportive of the promotion of sexual and reproductive healthcare for the young people using the youth clubs they supervise. Chief Sadulira believes this is a crucial time for parents to understand the importance of being open with young people. Connecting them with community health workers who are experienced in counselling and provision of sexual and reproductive healthcare can help reduce unintended pregnancies. “I use community meeting sessions to advise parents who resist or misunderstand why youth should have access to contraceptives, because prevention is better than cure.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Matundu youth club In July 2020, FPAM visited the Lilongwe and Kasungu youth clubs to support sexual and reproductive health behaviour change communication interventions. “Our youth here access condoms from the chairman of Namangwe youth club who is linked to Chiwamba health center, located about 18km from Namangwe. He does all this as a volunteer because the area does not have any community-based distribution agents. And the fact that FPAM is finally here, we are assured that access to cervical cancer screening and contraception services are guaranteed,” says Chief Chinoko. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ngwangwa Ngwangwa applauded FPAM for bringing youth-targeted outreach clinics to their remote area and requested to increase the frequency of the clinics to reach more youth living in hard-to-reach communities. “My area is big yet is leaning more like an island without a health facility nearby. It takes youth to walk 17km to get to Dzenza hospital, 15km to reach Ngoni health center, and 35km to get to Kabudula community hospital. This gap requires frequent mobile clinics.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ruth, youth leader Radio and youth clubs are major sources of information on contraception as well as through community discussions and groups. “I first heard about contraception in 2016, when I was 15, from Zodiak and MBC radios. I accessed the Implanon implant that protects for three years from one of the FPAM outreach clinics. In my family we are three girls and all my elder sisters fell pregnant in their teens. I never wanted to get disturbed to complete my secondary school education. And hearing from radios about the benefits of contraception like the ability to complete education made me generate confidence to have an implant to avoid unintended pregnancy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Banda, vice chair, Youth Action Movement (YAM) The teams of youth leaders have successfully advocated for sexual and reproductive health and rights, creating demand specifically for contraceptive care in their communities. “I engage in contraception discussions slowly by starting with a little probe if girls and young women have ever heard or used contraception before. Later I extend the discussion to give in that the unwanted pregnancy I got was total negligence because access to contraception services was available. I encourage them not to fall into unwanted pregnancy trap when they have all the support and preventative measures around." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, youth leader Lucy chose a long-acting method of contraception through the FPAM mobile outreach clinic. “My friends discouraged me a lot because they feared a rumor that the IUD drops into the uterus and causes cancer. I gathered courage because I needed a solution that would enable me not to conceive again until my family's economic status improves, and I got the IUD fitted. I feel no problem. This evidence is now a tool I use to teach many girls and women about the benefits of contraception. We are really glad to have FPAM bring a youth-friendly mobile clinic which will support our ground efforts to advocate for youth access to all sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 25 April 2024
In pictures: Increasing contraceptive care to young people in Malawi
Our Member Association, Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM), is delivering healthcare through the support of WISH* in Lilongwe and Kasungu with a focus on young women and girls. A bespoke training programme supports community health workers on how to deliver youth-friendly healthcare through outreach to local communities, and especially young women. *The Women’s Integrated Sexual Health (WISH2Action) programme, is funded by the UK Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), under the strategy to ‘Leave No One Behind’. Photographs ©FPAM/Andrew Mkandawire/Malawi Barriers to contraceptive care Young people, particularly girls, face barriers to accessing sexual and reproductive healthcare and contraception due to societal perceptions that they have no need for them. Chiefs and parents in the Lilongwe and Kasungu districts have demonstrated that by working together they are able to meet this need and protect the health and wellbeing of young people in their communities. Their collective approach ensures elders advocate on behalf of the youth in their communities, encouraging them to feel confident in accessing healthcare provision and to counter myths and misconceptions about contraception. Their goal is to reduce the high number of unintended pregnancies and STIs among young people. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gogo Nakwenda Gogo Nakwenda is respected in her community as a go-to counsellor for young people, advising on sexuality and how to access healthcare. Now nearing her 80s, Nakwneda, talks about different contraception methods, saying that if she was 18 again, she would opt for the five-year implant to ensure her education and future work opportunities. “During our time we used traditional contraception, but I have learned that modern pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections prevention methods are very predictable and give no excuses to protection errors. One can comfortably plan when to have a child and when not to have child.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, volunteer and parent Lucy believes it is important to educate both parents and young people on the benefits of access to contraception. Lucy talks about how myths and misconceptions remain a barrier for young girls to be able to access contraception, mostly because of fears related to infertility. She is open about her own experiences with contraceptives. “I’m 38, I have used pills, injectables and now I’m now using the IUD and successfully I have given birth to three children and here I am in good health. Who else can lie about modern contraceptives? I usually encourage the young ones to be mindful of their future to avoid any mistake that could be prevented with available contraceptives they can comfortably demand from their community health workers.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Chiefs Sadulira and Chinoko Chiefs in Lilongwe and Kasungu districts are committed and supportive of the promotion of sexual and reproductive healthcare for the young people using the youth clubs they supervise. Chief Sadulira believes this is a crucial time for parents to understand the importance of being open with young people. Connecting them with community health workers who are experienced in counselling and provision of sexual and reproductive healthcare can help reduce unintended pregnancies. “I use community meeting sessions to advise parents who resist or misunderstand why youth should have access to contraceptives, because prevention is better than cure.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Matundu youth club In July 2020, FPAM visited the Lilongwe and Kasungu youth clubs to support sexual and reproductive health behaviour change communication interventions. “Our youth here access condoms from the chairman of Namangwe youth club who is linked to Chiwamba health center, located about 18km from Namangwe. He does all this as a volunteer because the area does not have any community-based distribution agents. And the fact that FPAM is finally here, we are assured that access to cervical cancer screening and contraception services are guaranteed,” says Chief Chinoko. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ngwangwa Ngwangwa applauded FPAM for bringing youth-targeted outreach clinics to their remote area and requested to increase the frequency of the clinics to reach more youth living in hard-to-reach communities. “My area is big yet is leaning more like an island without a health facility nearby. It takes youth to walk 17km to get to Dzenza hospital, 15km to reach Ngoni health center, and 35km to get to Kabudula community hospital. This gap requires frequent mobile clinics.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ruth, youth leader Radio and youth clubs are major sources of information on contraception as well as through community discussions and groups. “I first heard about contraception in 2016, when I was 15, from Zodiak and MBC radios. I accessed the Implanon implant that protects for three years from one of the FPAM outreach clinics. In my family we are three girls and all my elder sisters fell pregnant in their teens. I never wanted to get disturbed to complete my secondary school education. And hearing from radios about the benefits of contraception like the ability to complete education made me generate confidence to have an implant to avoid unintended pregnancy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Banda, vice chair, Youth Action Movement (YAM) The teams of youth leaders have successfully advocated for sexual and reproductive health and rights, creating demand specifically for contraceptive care in their communities. “I engage in contraception discussions slowly by starting with a little probe if girls and young women have ever heard or used contraception before. Later I extend the discussion to give in that the unwanted pregnancy I got was total negligence because access to contraception services was available. I encourage them not to fall into unwanted pregnancy trap when they have all the support and preventative measures around." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, youth leader Lucy chose a long-acting method of contraception through the FPAM mobile outreach clinic. “My friends discouraged me a lot because they feared a rumor that the IUD drops into the uterus and causes cancer. I gathered courage because I needed a solution that would enable me not to conceive again until my family's economic status improves, and I got the IUD fitted. I feel no problem. This evidence is now a tool I use to teach many girls and women about the benefits of contraception. We are really glad to have FPAM bring a youth-friendly mobile clinic which will support our ground efforts to advocate for youth access to all sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
| 22 January 2018
“I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator.”
Amina is a peer educator trained by Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) Linkages project. “I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator,” she says. “I have 51 other sex workers in my care, I inform them on testing and treatment, also about STI treatment and condom use. I teach about the disadvantages of sharing ART (anti-retroviral therapy) and encourage them to go for tuberculosis testing if they are coughing.” Another educator called Cecilia adds: “I reached out to 60 female sex workers. We are all friends and they trust me. I refer them to services and we address abuse by the police. They rape us and steal our money but through the project, we can follow up since the project has access to the managers of the police.” Basic sexual health information Her colleague Florence says: “It also helped that the rogue and vagabond law was repealed.” The law was a permanent curfew, giving the police the power to round up, fine or jail anybody who was on the streets after eight o’clock at night. Lucy, also a peer educator, says part of the work is giving basic information. “I teach my friends on HIV and GBV (gender-based violence),” she explains. “And I teach how to use condoms and lubricants and how to persuade clients to use condoms. I also talk about family planning. Many female sex workers do not know they need it.” “The project helped me with condoms and I shared that with others,” says another client of the programme, Angela. “Through the project, I got tested for HIV and treated for STIs. I also encourage pregnant sex workers to go for pre-natal care so that they do not infect their babies. It is the first time that an organisation like FPAM worked with us. We got respected within the community because we are knowledgeable.” In the year the Linkages project ran, 627 female sex workers were supported in getting tested for HIV, the initiation of anti-retroviral treatment and therapy adherence. 2,700 women were referred to services and many more received information. The HIV prevalence rate among female sex workers went down from 77% to 62%. Global Gag Rule effects FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule. The effects are keenly felt amongst those who benefitted from the project: Amina says: “Many stopped taking medication. Healthcare facilities are not for us. I sing in a church choir, which is important to me. If they find out what I do, they will throw me out.” “My family thinks I work at a filling station at night,” says Lucy. Cecilia adds: “This project has to come back, please bring it back. If not, we will all die early.”
| 25 April 2024
“I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator.”
Amina is a peer educator trained by Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) Linkages project. “I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator,” she says. “I have 51 other sex workers in my care, I inform them on testing and treatment, also about STI treatment and condom use. I teach about the disadvantages of sharing ART (anti-retroviral therapy) and encourage them to go for tuberculosis testing if they are coughing.” Another educator called Cecilia adds: “I reached out to 60 female sex workers. We are all friends and they trust me. I refer them to services and we address abuse by the police. They rape us and steal our money but through the project, we can follow up since the project has access to the managers of the police.” Basic sexual health information Her colleague Florence says: “It also helped that the rogue and vagabond law was repealed.” The law was a permanent curfew, giving the police the power to round up, fine or jail anybody who was on the streets after eight o’clock at night. Lucy, also a peer educator, says part of the work is giving basic information. “I teach my friends on HIV and GBV (gender-based violence),” she explains. “And I teach how to use condoms and lubricants and how to persuade clients to use condoms. I also talk about family planning. Many female sex workers do not know they need it.” “The project helped me with condoms and I shared that with others,” says another client of the programme, Angela. “Through the project, I got tested for HIV and treated for STIs. I also encourage pregnant sex workers to go for pre-natal care so that they do not infect their babies. It is the first time that an organisation like FPAM worked with us. We got respected within the community because we are knowledgeable.” In the year the Linkages project ran, 627 female sex workers were supported in getting tested for HIV, the initiation of anti-retroviral treatment and therapy adherence. 2,700 women were referred to services and many more received information. The HIV prevalence rate among female sex workers went down from 77% to 62%. Global Gag Rule effects FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule. The effects are keenly felt amongst those who benefitted from the project: Amina says: “Many stopped taking medication. Healthcare facilities are not for us. I sing in a church choir, which is important to me. If they find out what I do, they will throw me out.” “My family thinks I work at a filling station at night,” says Lucy. Cecilia adds: “This project has to come back, please bring it back. If not, we will all die early.”

| 22 January 2018
"We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process."
It used to take Matilda Meke-Banda six hours on her motorbike along dirt roads to reach two remote districts and deliver sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services. In this part of southern Malawi, Machinga, family planning uptake is low, and the fertility rate, at 6.6, is the highest in the country. The Family Planning Association of Malawi, known as FPAM, runs a clinic in the town of Liwonde and it’s from here that Matilda travelled out six times a month. “We have established six watch groups, they are trained to address SRH issues in the community,” she explains. Luc Simon is the chair of one of those groups. “We teach about Family Planning,” he says. “We encourage parents and young people to go for HIV testing. We address forced early marriages, talk to parents and children to save a lot of young people.” And there are a lot of myths to dispel about family planning. Elizabeth Katunga is head of family planning in the district hospital in Machinga: “Family Planning is not very much accepted by the communities. Many women hide the use of contraceptives,” she says. “Injectables are most popular, easy to hide. We have cases here where husbands upon discovery of an implant take a knife and cut it out. It is not that people want big families per se but it is the misconceptions about contraceptives.” FPAM’s projects are based at the Youth Life clinic in Liwonde. The clinic offers integrated services: Family planning, HIV services, STI screening, cervical cancer screening and general healthcare (such as malaria). This joined-up approach has been effective says FPAM’s executive director Thoko Mbendera: “In government health facilities, you have different days, and long queues always, for family planning, for HIV, for general health, which is a challenge if the clinic is a 20 km walk away.There are privacy issues.” But now, FPAM’s services are being cut because of the Global Gag Rule (GGR), mobile clinics are grounded, and there are fears that much progress will be undone. Some of FPAM’s rural clients explain how the Watch Groups work in their community. “It starts with me as a man,” says group member George Mpemba. “We are examples on how to live with our wives. We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process. Our meetings are not hearings, but a normal chat, there is laughing and talking. After the discussion we evaluate together and make an action plan.” Katherine, went to the group for help: “There was violence in my marriage; my husband forced himself on me even if I was tired from working in the field. When I complained there was trouble. He did not provide even the bedding. “He is a fisherman and he makes a lot of cash which he used to buy beer but nothing for us.I overheard a watch group meeting once and I realised there was a solution. They talked to him and made him realise that what he was doing was violence and against the law. It was ignorance.Things are better now, he brings money home, sex is consensual and sometimes he helps with household chores.”

| 25 April 2024
"We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process."
It used to take Matilda Meke-Banda six hours on her motorbike along dirt roads to reach two remote districts and deliver sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services. In this part of southern Malawi, Machinga, family planning uptake is low, and the fertility rate, at 6.6, is the highest in the country. The Family Planning Association of Malawi, known as FPAM, runs a clinic in the town of Liwonde and it’s from here that Matilda travelled out six times a month. “We have established six watch groups, they are trained to address SRH issues in the community,” she explains. Luc Simon is the chair of one of those groups. “We teach about Family Planning,” he says. “We encourage parents and young people to go for HIV testing. We address forced early marriages, talk to parents and children to save a lot of young people.” And there are a lot of myths to dispel about family planning. Elizabeth Katunga is head of family planning in the district hospital in Machinga: “Family Planning is not very much accepted by the communities. Many women hide the use of contraceptives,” she says. “Injectables are most popular, easy to hide. We have cases here where husbands upon discovery of an implant take a knife and cut it out. It is not that people want big families per se but it is the misconceptions about contraceptives.” FPAM’s projects are based at the Youth Life clinic in Liwonde. The clinic offers integrated services: Family planning, HIV services, STI screening, cervical cancer screening and general healthcare (such as malaria). This joined-up approach has been effective says FPAM’s executive director Thoko Mbendera: “In government health facilities, you have different days, and long queues always, for family planning, for HIV, for general health, which is a challenge if the clinic is a 20 km walk away.There are privacy issues.” But now, FPAM’s services are being cut because of the Global Gag Rule (GGR), mobile clinics are grounded, and there are fears that much progress will be undone. Some of FPAM’s rural clients explain how the Watch Groups work in their community. “It starts with me as a man,” says group member George Mpemba. “We are examples on how to live with our wives. We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process. Our meetings are not hearings, but a normal chat, there is laughing and talking. After the discussion we evaluate together and make an action plan.” Katherine, went to the group for help: “There was violence in my marriage; my husband forced himself on me even if I was tired from working in the field. When I complained there was trouble. He did not provide even the bedding. “He is a fisherman and he makes a lot of cash which he used to buy beer but nothing for us.I overheard a watch group meeting once and I realised there was a solution. They talked to him and made him realise that what he was doing was violence and against the law. It was ignorance.Things are better now, he brings money home, sex is consensual and sometimes he helps with household chores.”

| 22 January 2018
"They are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.”
It is 9.00pm in Lilongwe, the capital of Malawi , the fish market is one of the “hotspots” where the Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) opens its trailer doors to sex workers, a “key population” in the fight against HIV. Thoko Mbendera is the Executive Director of FPAM: “Key populations are groups whose needs you have to address if you ever want to bring down HIV prevalence in the general population. Sex workers clearly need help here: the HIV prevalence rate among them is 77% while among the general population it is 10.2%.” The clinic offers STI screening, family planning, HIV testing, tuberculosis (TBC) testing and cervical cancer screening. Outside, peer educators distribute condoms and talk to waiting clients. Thoko Mbendera says: “This group does not (have) access the public health sector, it is simple not an option for women who do not disclose what they do to anyone, so in the Linkages program we reach out to the hot spots at night.” Florence Mushani, is the coordinator of Linkages: “In the project we trained 63 peer educators. They are HIV positive; they approach their colleagues with information and advice. Our goal is the 90-90-90 target meaning 90% of sex workers know their status, 90% of HIV positive women are on anti-retroviral treatment (ART), and 90% of the women on ARTs will be virally suppressed. We also trained 21 peer navigators; they support others to adhere to therapy. We pay them a small stipend of 25 dollars a month, we expect a lot of them.” Tusekele Mwakasungula is FPAM’s Programs Manager: “The goal of the peer educators training is to build up the person,” he says. And it shows: these women are no shy victims of an unjust society, they are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.” FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule.

| 25 April 2024
"They are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.”
It is 9.00pm in Lilongwe, the capital of Malawi , the fish market is one of the “hotspots” where the Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) opens its trailer doors to sex workers, a “key population” in the fight against HIV. Thoko Mbendera is the Executive Director of FPAM: “Key populations are groups whose needs you have to address if you ever want to bring down HIV prevalence in the general population. Sex workers clearly need help here: the HIV prevalence rate among them is 77% while among the general population it is 10.2%.” The clinic offers STI screening, family planning, HIV testing, tuberculosis (TBC) testing and cervical cancer screening. Outside, peer educators distribute condoms and talk to waiting clients. Thoko Mbendera says: “This group does not (have) access the public health sector, it is simple not an option for women who do not disclose what they do to anyone, so in the Linkages program we reach out to the hot spots at night.” Florence Mushani, is the coordinator of Linkages: “In the project we trained 63 peer educators. They are HIV positive; they approach their colleagues with information and advice. Our goal is the 90-90-90 target meaning 90% of sex workers know their status, 90% of HIV positive women are on anti-retroviral treatment (ART), and 90% of the women on ARTs will be virally suppressed. We also trained 21 peer navigators; they support others to adhere to therapy. We pay them a small stipend of 25 dollars a month, we expect a lot of them.” Tusekele Mwakasungula is FPAM’s Programs Manager: “The goal of the peer educators training is to build up the person,” he says. And it shows: these women are no shy victims of an unjust society, they are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.” FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule.

| 09 September 2020
In pictures: Increasing contraceptive care to young people in Malawi
Our Member Association, Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM), is delivering healthcare through the support of WISH* in Lilongwe and Kasungu with a focus on young women and girls. A bespoke training programme supports community health workers on how to deliver youth-friendly healthcare through outreach to local communities, and especially young women. *The Women’s Integrated Sexual Health (WISH2Action) programme, is funded by the UK Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), under the strategy to ‘Leave No One Behind’. Photographs ©FPAM/Andrew Mkandawire/Malawi Barriers to contraceptive care Young people, particularly girls, face barriers to accessing sexual and reproductive healthcare and contraception due to societal perceptions that they have no need for them. Chiefs and parents in the Lilongwe and Kasungu districts have demonstrated that by working together they are able to meet this need and protect the health and wellbeing of young people in their communities. Their collective approach ensures elders advocate on behalf of the youth in their communities, encouraging them to feel confident in accessing healthcare provision and to counter myths and misconceptions about contraception. Their goal is to reduce the high number of unintended pregnancies and STIs among young people. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gogo Nakwenda Gogo Nakwenda is respected in her community as a go-to counsellor for young people, advising on sexuality and how to access healthcare. Now nearing her 80s, Nakwneda, talks about different contraception methods, saying that if she was 18 again, she would opt for the five-year implant to ensure her education and future work opportunities. “During our time we used traditional contraception, but I have learned that modern pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections prevention methods are very predictable and give no excuses to protection errors. One can comfortably plan when to have a child and when not to have child.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, volunteer and parent Lucy believes it is important to educate both parents and young people on the benefits of access to contraception. Lucy talks about how myths and misconceptions remain a barrier for young girls to be able to access contraception, mostly because of fears related to infertility. She is open about her own experiences with contraceptives. “I’m 38, I have used pills, injectables and now I’m now using the IUD and successfully I have given birth to three children and here I am in good health. Who else can lie about modern contraceptives? I usually encourage the young ones to be mindful of their future to avoid any mistake that could be prevented with available contraceptives they can comfortably demand from their community health workers.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Chiefs Sadulira and Chinoko Chiefs in Lilongwe and Kasungu districts are committed and supportive of the promotion of sexual and reproductive healthcare for the young people using the youth clubs they supervise. Chief Sadulira believes this is a crucial time for parents to understand the importance of being open with young people. Connecting them with community health workers who are experienced in counselling and provision of sexual and reproductive healthcare can help reduce unintended pregnancies. “I use community meeting sessions to advise parents who resist or misunderstand why youth should have access to contraceptives, because prevention is better than cure.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Matundu youth club In July 2020, FPAM visited the Lilongwe and Kasungu youth clubs to support sexual and reproductive health behaviour change communication interventions. “Our youth here access condoms from the chairman of Namangwe youth club who is linked to Chiwamba health center, located about 18km from Namangwe. He does all this as a volunteer because the area does not have any community-based distribution agents. And the fact that FPAM is finally here, we are assured that access to cervical cancer screening and contraception services are guaranteed,” says Chief Chinoko. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ngwangwa Ngwangwa applauded FPAM for bringing youth-targeted outreach clinics to their remote area and requested to increase the frequency of the clinics to reach more youth living in hard-to-reach communities. “My area is big yet is leaning more like an island without a health facility nearby. It takes youth to walk 17km to get to Dzenza hospital, 15km to reach Ngoni health center, and 35km to get to Kabudula community hospital. This gap requires frequent mobile clinics.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ruth, youth leader Radio and youth clubs are major sources of information on contraception as well as through community discussions and groups. “I first heard about contraception in 2016, when I was 15, from Zodiak and MBC radios. I accessed the Implanon implant that protects for three years from one of the FPAM outreach clinics. In my family we are three girls and all my elder sisters fell pregnant in their teens. I never wanted to get disturbed to complete my secondary school education. And hearing from radios about the benefits of contraception like the ability to complete education made me generate confidence to have an implant to avoid unintended pregnancy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Banda, vice chair, Youth Action Movement (YAM) The teams of youth leaders have successfully advocated for sexual and reproductive health and rights, creating demand specifically for contraceptive care in their communities. “I engage in contraception discussions slowly by starting with a little probe if girls and young women have ever heard or used contraception before. Later I extend the discussion to give in that the unwanted pregnancy I got was total negligence because access to contraception services was available. I encourage them not to fall into unwanted pregnancy trap when they have all the support and preventative measures around." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, youth leader Lucy chose a long-acting method of contraception through the FPAM mobile outreach clinic. “My friends discouraged me a lot because they feared a rumor that the IUD drops into the uterus and causes cancer. I gathered courage because I needed a solution that would enable me not to conceive again until my family's economic status improves, and I got the IUD fitted. I feel no problem. This evidence is now a tool I use to teach many girls and women about the benefits of contraception. We are really glad to have FPAM bring a youth-friendly mobile clinic which will support our ground efforts to advocate for youth access to all sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 25 April 2024
In pictures: Increasing contraceptive care to young people in Malawi
Our Member Association, Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM), is delivering healthcare through the support of WISH* in Lilongwe and Kasungu with a focus on young women and girls. A bespoke training programme supports community health workers on how to deliver youth-friendly healthcare through outreach to local communities, and especially young women. *The Women’s Integrated Sexual Health (WISH2Action) programme, is funded by the UK Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), under the strategy to ‘Leave No One Behind’. Photographs ©FPAM/Andrew Mkandawire/Malawi Barriers to contraceptive care Young people, particularly girls, face barriers to accessing sexual and reproductive healthcare and contraception due to societal perceptions that they have no need for them. Chiefs and parents in the Lilongwe and Kasungu districts have demonstrated that by working together they are able to meet this need and protect the health and wellbeing of young people in their communities. Their collective approach ensures elders advocate on behalf of the youth in their communities, encouraging them to feel confident in accessing healthcare provision and to counter myths and misconceptions about contraception. Their goal is to reduce the high number of unintended pregnancies and STIs among young people. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gogo Nakwenda Gogo Nakwenda is respected in her community as a go-to counsellor for young people, advising on sexuality and how to access healthcare. Now nearing her 80s, Nakwneda, talks about different contraception methods, saying that if she was 18 again, she would opt for the five-year implant to ensure her education and future work opportunities. “During our time we used traditional contraception, but I have learned that modern pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections prevention methods are very predictable and give no excuses to protection errors. One can comfortably plan when to have a child and when not to have child.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, volunteer and parent Lucy believes it is important to educate both parents and young people on the benefits of access to contraception. Lucy talks about how myths and misconceptions remain a barrier for young girls to be able to access contraception, mostly because of fears related to infertility. She is open about her own experiences with contraceptives. “I’m 38, I have used pills, injectables and now I’m now using the IUD and successfully I have given birth to three children and here I am in good health. Who else can lie about modern contraceptives? I usually encourage the young ones to be mindful of their future to avoid any mistake that could be prevented with available contraceptives they can comfortably demand from their community health workers.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Chiefs Sadulira and Chinoko Chiefs in Lilongwe and Kasungu districts are committed and supportive of the promotion of sexual and reproductive healthcare for the young people using the youth clubs they supervise. Chief Sadulira believes this is a crucial time for parents to understand the importance of being open with young people. Connecting them with community health workers who are experienced in counselling and provision of sexual and reproductive healthcare can help reduce unintended pregnancies. “I use community meeting sessions to advise parents who resist or misunderstand why youth should have access to contraceptives, because prevention is better than cure.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Matundu youth club In July 2020, FPAM visited the Lilongwe and Kasungu youth clubs to support sexual and reproductive health behaviour change communication interventions. “Our youth here access condoms from the chairman of Namangwe youth club who is linked to Chiwamba health center, located about 18km from Namangwe. He does all this as a volunteer because the area does not have any community-based distribution agents. And the fact that FPAM is finally here, we are assured that access to cervical cancer screening and contraception services are guaranteed,” says Chief Chinoko. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ngwangwa Ngwangwa applauded FPAM for bringing youth-targeted outreach clinics to their remote area and requested to increase the frequency of the clinics to reach more youth living in hard-to-reach communities. “My area is big yet is leaning more like an island without a health facility nearby. It takes youth to walk 17km to get to Dzenza hospital, 15km to reach Ngoni health center, and 35km to get to Kabudula community hospital. This gap requires frequent mobile clinics.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ruth, youth leader Radio and youth clubs are major sources of information on contraception as well as through community discussions and groups. “I first heard about contraception in 2016, when I was 15, from Zodiak and MBC radios. I accessed the Implanon implant that protects for three years from one of the FPAM outreach clinics. In my family we are three girls and all my elder sisters fell pregnant in their teens. I never wanted to get disturbed to complete my secondary school education. And hearing from radios about the benefits of contraception like the ability to complete education made me generate confidence to have an implant to avoid unintended pregnancy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Banda, vice chair, Youth Action Movement (YAM) The teams of youth leaders have successfully advocated for sexual and reproductive health and rights, creating demand specifically for contraceptive care in their communities. “I engage in contraception discussions slowly by starting with a little probe if girls and young women have ever heard or used contraception before. Later I extend the discussion to give in that the unwanted pregnancy I got was total negligence because access to contraception services was available. I encourage them not to fall into unwanted pregnancy trap when they have all the support and preventative measures around." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Lucy, youth leader Lucy chose a long-acting method of contraception through the FPAM mobile outreach clinic. “My friends discouraged me a lot because they feared a rumor that the IUD drops into the uterus and causes cancer. I gathered courage because I needed a solution that would enable me not to conceive again until my family's economic status improves, and I got the IUD fitted. I feel no problem. This evidence is now a tool I use to teach many girls and women about the benefits of contraception. We are really glad to have FPAM bring a youth-friendly mobile clinic which will support our ground efforts to advocate for youth access to all sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
| 22 January 2018
“I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator.”
Amina is a peer educator trained by Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) Linkages project. “I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator,” she says. “I have 51 other sex workers in my care, I inform them on testing and treatment, also about STI treatment and condom use. I teach about the disadvantages of sharing ART (anti-retroviral therapy) and encourage them to go for tuberculosis testing if they are coughing.” Another educator called Cecilia adds: “I reached out to 60 female sex workers. We are all friends and they trust me. I refer them to services and we address abuse by the police. They rape us and steal our money but through the project, we can follow up since the project has access to the managers of the police.” Basic sexual health information Her colleague Florence says: “It also helped that the rogue and vagabond law was repealed.” The law was a permanent curfew, giving the police the power to round up, fine or jail anybody who was on the streets after eight o’clock at night. Lucy, also a peer educator, says part of the work is giving basic information. “I teach my friends on HIV and GBV (gender-based violence),” she explains. “And I teach how to use condoms and lubricants and how to persuade clients to use condoms. I also talk about family planning. Many female sex workers do not know they need it.” “The project helped me with condoms and I shared that with others,” says another client of the programme, Angela. “Through the project, I got tested for HIV and treated for STIs. I also encourage pregnant sex workers to go for pre-natal care so that they do not infect their babies. It is the first time that an organisation like FPAM worked with us. We got respected within the community because we are knowledgeable.” In the year the Linkages project ran, 627 female sex workers were supported in getting tested for HIV, the initiation of anti-retroviral treatment and therapy adherence. 2,700 women were referred to services and many more received information. The HIV prevalence rate among female sex workers went down from 77% to 62%. Global Gag Rule effects FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule. The effects are keenly felt amongst those who benefitted from the project: Amina says: “Many stopped taking medication. Healthcare facilities are not for us. I sing in a church choir, which is important to me. If they find out what I do, they will throw me out.” “My family thinks I work at a filling station at night,” says Lucy. Cecilia adds: “This project has to come back, please bring it back. If not, we will all die early.”
| 25 April 2024
“I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator.”
Amina is a peer educator trained by Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) Linkages project. “I am a HIV positive sex worker and a peer educator,” she says. “I have 51 other sex workers in my care, I inform them on testing and treatment, also about STI treatment and condom use. I teach about the disadvantages of sharing ART (anti-retroviral therapy) and encourage them to go for tuberculosis testing if they are coughing.” Another educator called Cecilia adds: “I reached out to 60 female sex workers. We are all friends and they trust me. I refer them to services and we address abuse by the police. They rape us and steal our money but through the project, we can follow up since the project has access to the managers of the police.” Basic sexual health information Her colleague Florence says: “It also helped that the rogue and vagabond law was repealed.” The law was a permanent curfew, giving the police the power to round up, fine or jail anybody who was on the streets after eight o’clock at night. Lucy, also a peer educator, says part of the work is giving basic information. “I teach my friends on HIV and GBV (gender-based violence),” she explains. “And I teach how to use condoms and lubricants and how to persuade clients to use condoms. I also talk about family planning. Many female sex workers do not know they need it.” “The project helped me with condoms and I shared that with others,” says another client of the programme, Angela. “Through the project, I got tested for HIV and treated for STIs. I also encourage pregnant sex workers to go for pre-natal care so that they do not infect their babies. It is the first time that an organisation like FPAM worked with us. We got respected within the community because we are knowledgeable.” In the year the Linkages project ran, 627 female sex workers were supported in getting tested for HIV, the initiation of anti-retroviral treatment and therapy adherence. 2,700 women were referred to services and many more received information. The HIV prevalence rate among female sex workers went down from 77% to 62%. Global Gag Rule effects FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule. The effects are keenly felt amongst those who benefitted from the project: Amina says: “Many stopped taking medication. Healthcare facilities are not for us. I sing in a church choir, which is important to me. If they find out what I do, they will throw me out.” “My family thinks I work at a filling station at night,” says Lucy. Cecilia adds: “This project has to come back, please bring it back. If not, we will all die early.”

| 22 January 2018
"We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process."
It used to take Matilda Meke-Banda six hours on her motorbike along dirt roads to reach two remote districts and deliver sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services. In this part of southern Malawi, Machinga, family planning uptake is low, and the fertility rate, at 6.6, is the highest in the country. The Family Planning Association of Malawi, known as FPAM, runs a clinic in the town of Liwonde and it’s from here that Matilda travelled out six times a month. “We have established six watch groups, they are trained to address SRH issues in the community,” she explains. Luc Simon is the chair of one of those groups. “We teach about Family Planning,” he says. “We encourage parents and young people to go for HIV testing. We address forced early marriages, talk to parents and children to save a lot of young people.” And there are a lot of myths to dispel about family planning. Elizabeth Katunga is head of family planning in the district hospital in Machinga: “Family Planning is not very much accepted by the communities. Many women hide the use of contraceptives,” she says. “Injectables are most popular, easy to hide. We have cases here where husbands upon discovery of an implant take a knife and cut it out. It is not that people want big families per se but it is the misconceptions about contraceptives.” FPAM’s projects are based at the Youth Life clinic in Liwonde. The clinic offers integrated services: Family planning, HIV services, STI screening, cervical cancer screening and general healthcare (such as malaria). This joined-up approach has been effective says FPAM’s executive director Thoko Mbendera: “In government health facilities, you have different days, and long queues always, for family planning, for HIV, for general health, which is a challenge if the clinic is a 20 km walk away.There are privacy issues.” But now, FPAM’s services are being cut because of the Global Gag Rule (GGR), mobile clinics are grounded, and there are fears that much progress will be undone. Some of FPAM’s rural clients explain how the Watch Groups work in their community. “It starts with me as a man,” says group member George Mpemba. “We are examples on how to live with our wives. We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process. Our meetings are not hearings, but a normal chat, there is laughing and talking. After the discussion we evaluate together and make an action plan.” Katherine, went to the group for help: “There was violence in my marriage; my husband forced himself on me even if I was tired from working in the field. When I complained there was trouble. He did not provide even the bedding. “He is a fisherman and he makes a lot of cash which he used to buy beer but nothing for us.I overheard a watch group meeting once and I realised there was a solution. They talked to him and made him realise that what he was doing was violence and against the law. It was ignorance.Things are better now, he brings money home, sex is consensual and sometimes he helps with household chores.”

| 25 April 2024
"We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process."
It used to take Matilda Meke-Banda six hours on her motorbike along dirt roads to reach two remote districts and deliver sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services. In this part of southern Malawi, Machinga, family planning uptake is low, and the fertility rate, at 6.6, is the highest in the country. The Family Planning Association of Malawi, known as FPAM, runs a clinic in the town of Liwonde and it’s from here that Matilda travelled out six times a month. “We have established six watch groups, they are trained to address SRH issues in the community,” she explains. Luc Simon is the chair of one of those groups. “We teach about Family Planning,” he says. “We encourage parents and young people to go for HIV testing. We address forced early marriages, talk to parents and children to save a lot of young people.” And there are a lot of myths to dispel about family planning. Elizabeth Katunga is head of family planning in the district hospital in Machinga: “Family Planning is not very much accepted by the communities. Many women hide the use of contraceptives,” she says. “Injectables are most popular, easy to hide. We have cases here where husbands upon discovery of an implant take a knife and cut it out. It is not that people want big families per se but it is the misconceptions about contraceptives.” FPAM’s projects are based at the Youth Life clinic in Liwonde. The clinic offers integrated services: Family planning, HIV services, STI screening, cervical cancer screening and general healthcare (such as malaria). This joined-up approach has been effective says FPAM’s executive director Thoko Mbendera: “In government health facilities, you have different days, and long queues always, for family planning, for HIV, for general health, which is a challenge if the clinic is a 20 km walk away.There are privacy issues.” But now, FPAM’s services are being cut because of the Global Gag Rule (GGR), mobile clinics are grounded, and there are fears that much progress will be undone. Some of FPAM’s rural clients explain how the Watch Groups work in their community. “It starts with me as a man,” says group member George Mpemba. “We are examples on how to live with our wives. We are non-judgemental; we embark on a mutual learning process. Our meetings are not hearings, but a normal chat, there is laughing and talking. After the discussion we evaluate together and make an action plan.” Katherine, went to the group for help: “There was violence in my marriage; my husband forced himself on me even if I was tired from working in the field. When I complained there was trouble. He did not provide even the bedding. “He is a fisherman and he makes a lot of cash which he used to buy beer but nothing for us.I overheard a watch group meeting once and I realised there was a solution. They talked to him and made him realise that what he was doing was violence and against the law. It was ignorance.Things are better now, he brings money home, sex is consensual and sometimes he helps with household chores.”

| 22 January 2018
"They are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.”
It is 9.00pm in Lilongwe, the capital of Malawi , the fish market is one of the “hotspots” where the Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) opens its trailer doors to sex workers, a “key population” in the fight against HIV. Thoko Mbendera is the Executive Director of FPAM: “Key populations are groups whose needs you have to address if you ever want to bring down HIV prevalence in the general population. Sex workers clearly need help here: the HIV prevalence rate among them is 77% while among the general population it is 10.2%.” The clinic offers STI screening, family planning, HIV testing, tuberculosis (TBC) testing and cervical cancer screening. Outside, peer educators distribute condoms and talk to waiting clients. Thoko Mbendera says: “This group does not (have) access the public health sector, it is simple not an option for women who do not disclose what they do to anyone, so in the Linkages program we reach out to the hot spots at night.” Florence Mushani, is the coordinator of Linkages: “In the project we trained 63 peer educators. They are HIV positive; they approach their colleagues with information and advice. Our goal is the 90-90-90 target meaning 90% of sex workers know their status, 90% of HIV positive women are on anti-retroviral treatment (ART), and 90% of the women on ARTs will be virally suppressed. We also trained 21 peer navigators; they support others to adhere to therapy. We pay them a small stipend of 25 dollars a month, we expect a lot of them.” Tusekele Mwakasungula is FPAM’s Programs Manager: “The goal of the peer educators training is to build up the person,” he says. And it shows: these women are no shy victims of an unjust society, they are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.” FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule.

| 25 April 2024
"They are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.”
It is 9.00pm in Lilongwe, the capital of Malawi , the fish market is one of the “hotspots” where the Family Planning Association of Malawi’s (FPAM) opens its trailer doors to sex workers, a “key population” in the fight against HIV. Thoko Mbendera is the Executive Director of FPAM: “Key populations are groups whose needs you have to address if you ever want to bring down HIV prevalence in the general population. Sex workers clearly need help here: the HIV prevalence rate among them is 77% while among the general population it is 10.2%.” The clinic offers STI screening, family planning, HIV testing, tuberculosis (TBC) testing and cervical cancer screening. Outside, peer educators distribute condoms and talk to waiting clients. Thoko Mbendera says: “This group does not (have) access the public health sector, it is simple not an option for women who do not disclose what they do to anyone, so in the Linkages program we reach out to the hot spots at night.” Florence Mushani, is the coordinator of Linkages: “In the project we trained 63 peer educators. They are HIV positive; they approach their colleagues with information and advice. Our goal is the 90-90-90 target meaning 90% of sex workers know their status, 90% of HIV positive women are on anti-retroviral treatment (ART), and 90% of the women on ARTs will be virally suppressed. We also trained 21 peer navigators; they support others to adhere to therapy. We pay them a small stipend of 25 dollars a month, we expect a lot of them.” Tusekele Mwakasungula is FPAM’s Programs Manager: “The goal of the peer educators training is to build up the person,” he says. And it shows: these women are no shy victims of an unjust society, they are self-confident and outspoken, determined to improve the situation of female sex workers.” FPAM’s Linkages project was phased out in 2016 due to the Global Gag Rule.








