Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.
Most Popular This Week
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
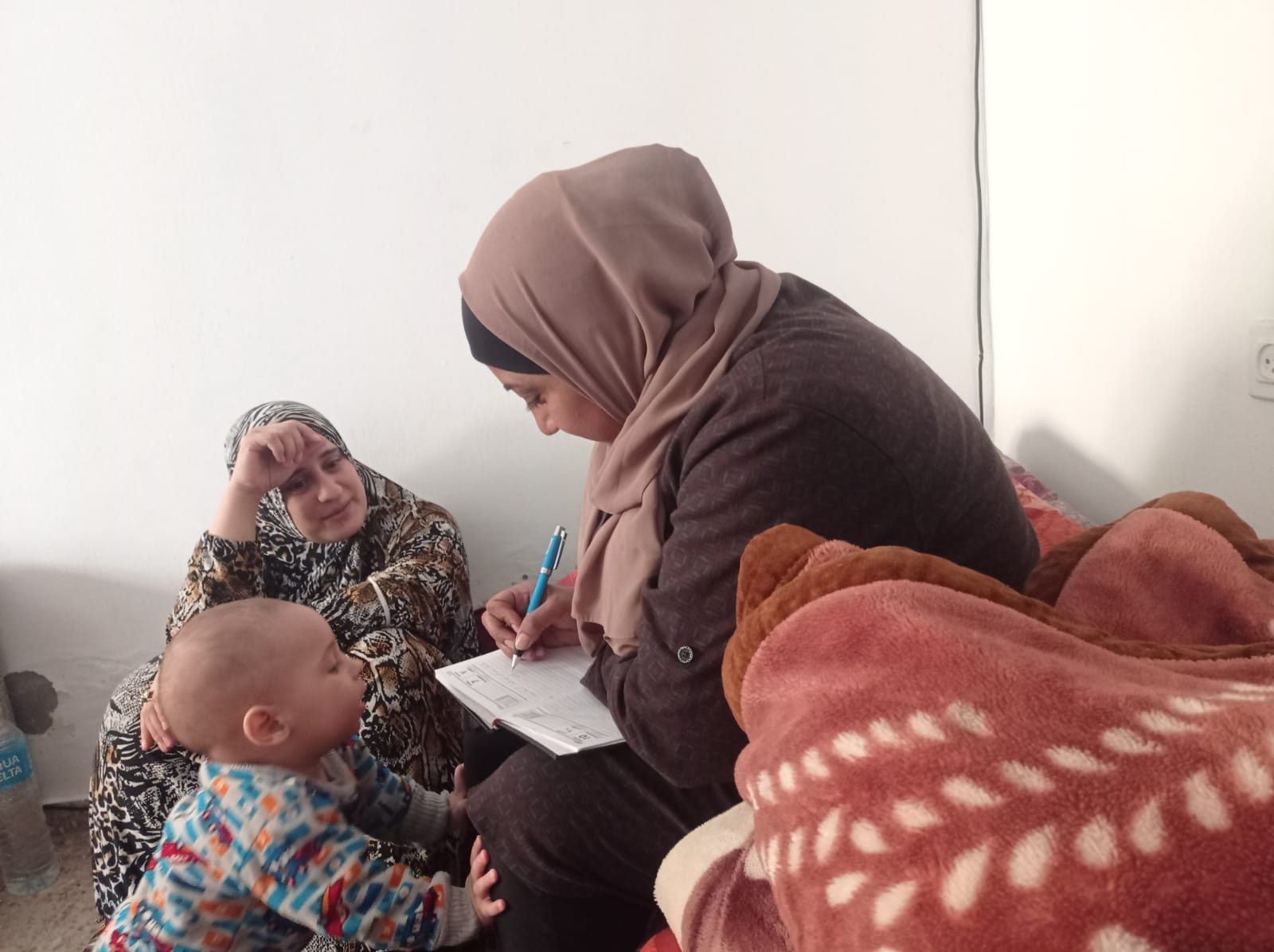

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
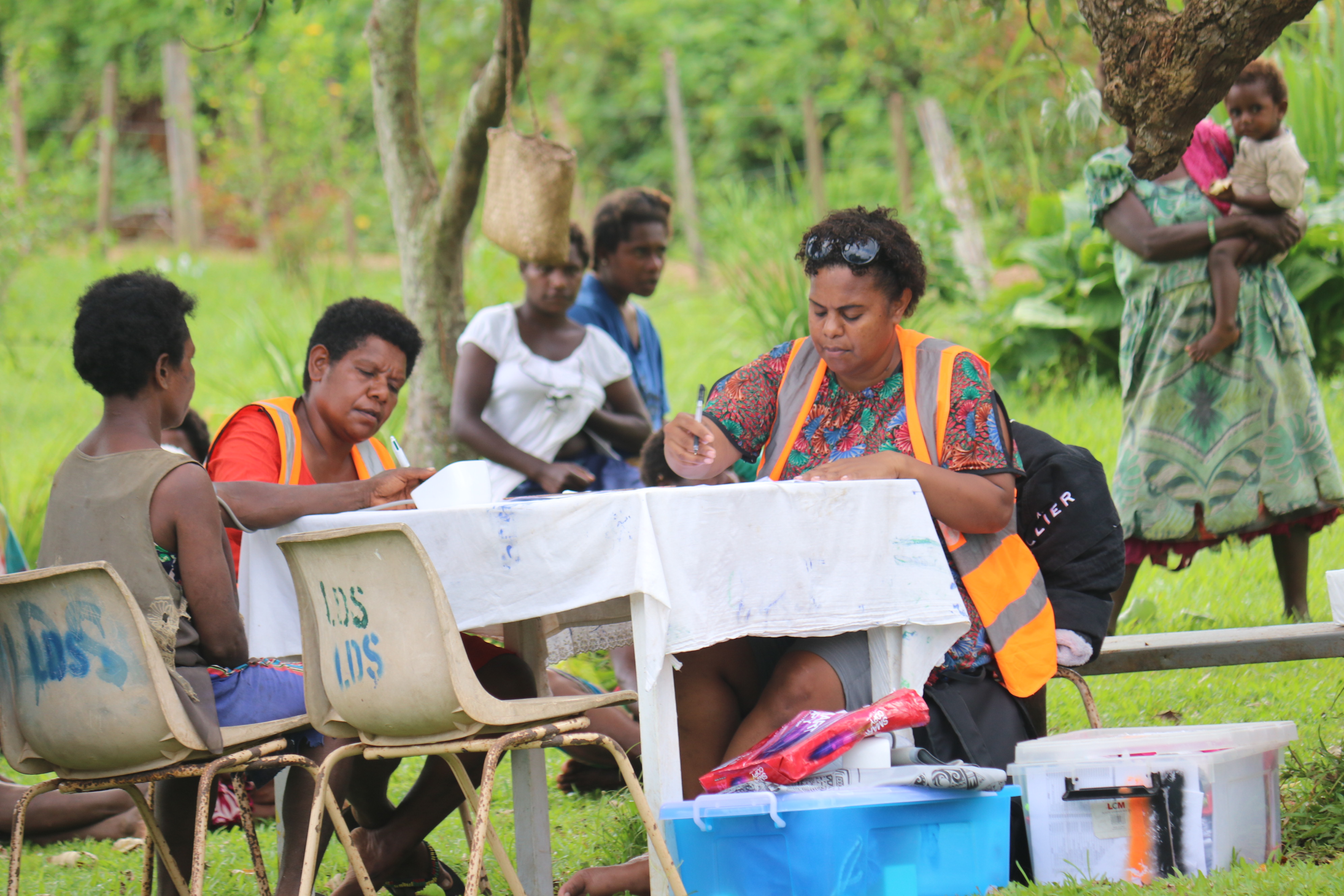

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

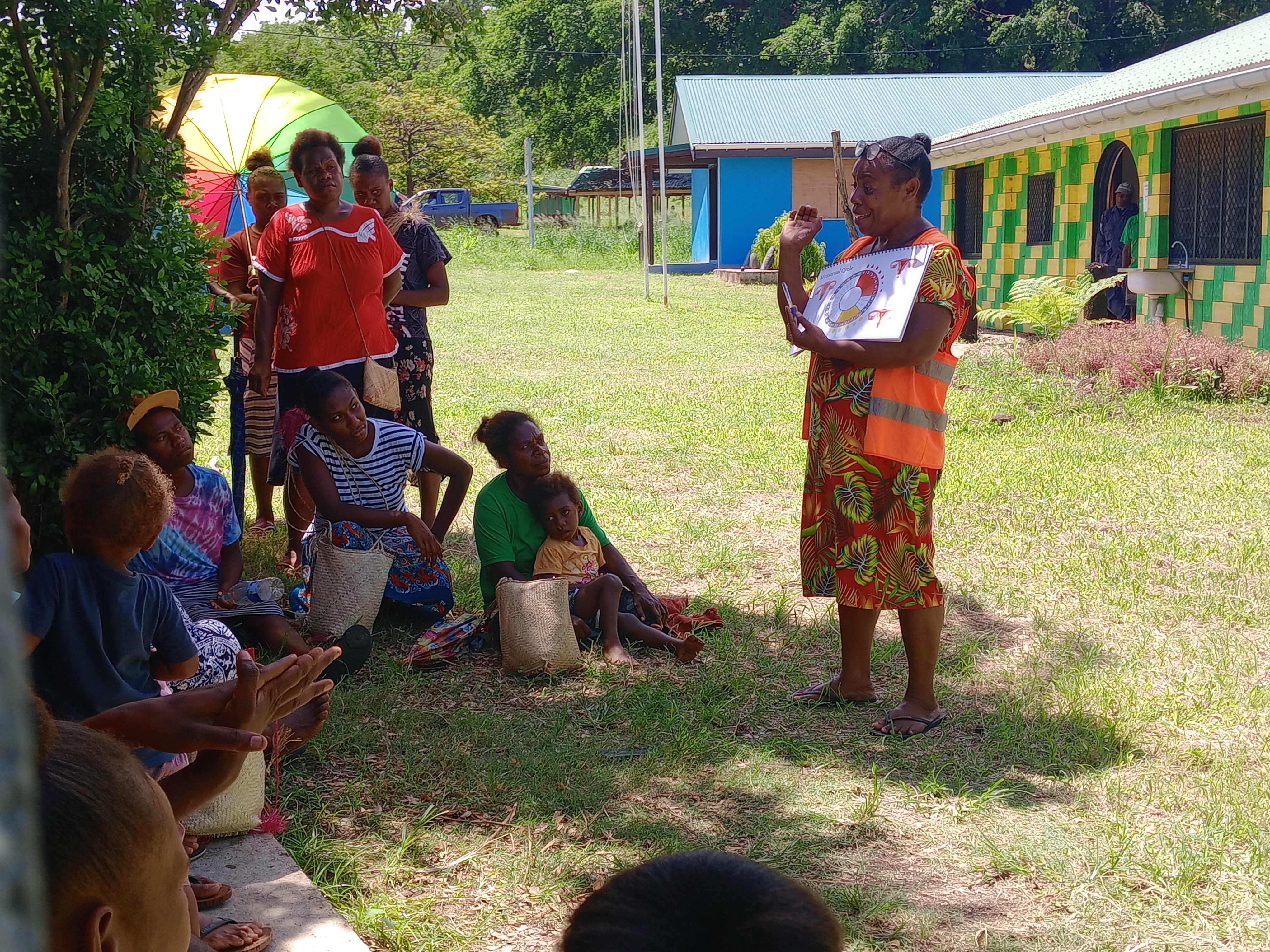
Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Filter our stories by:
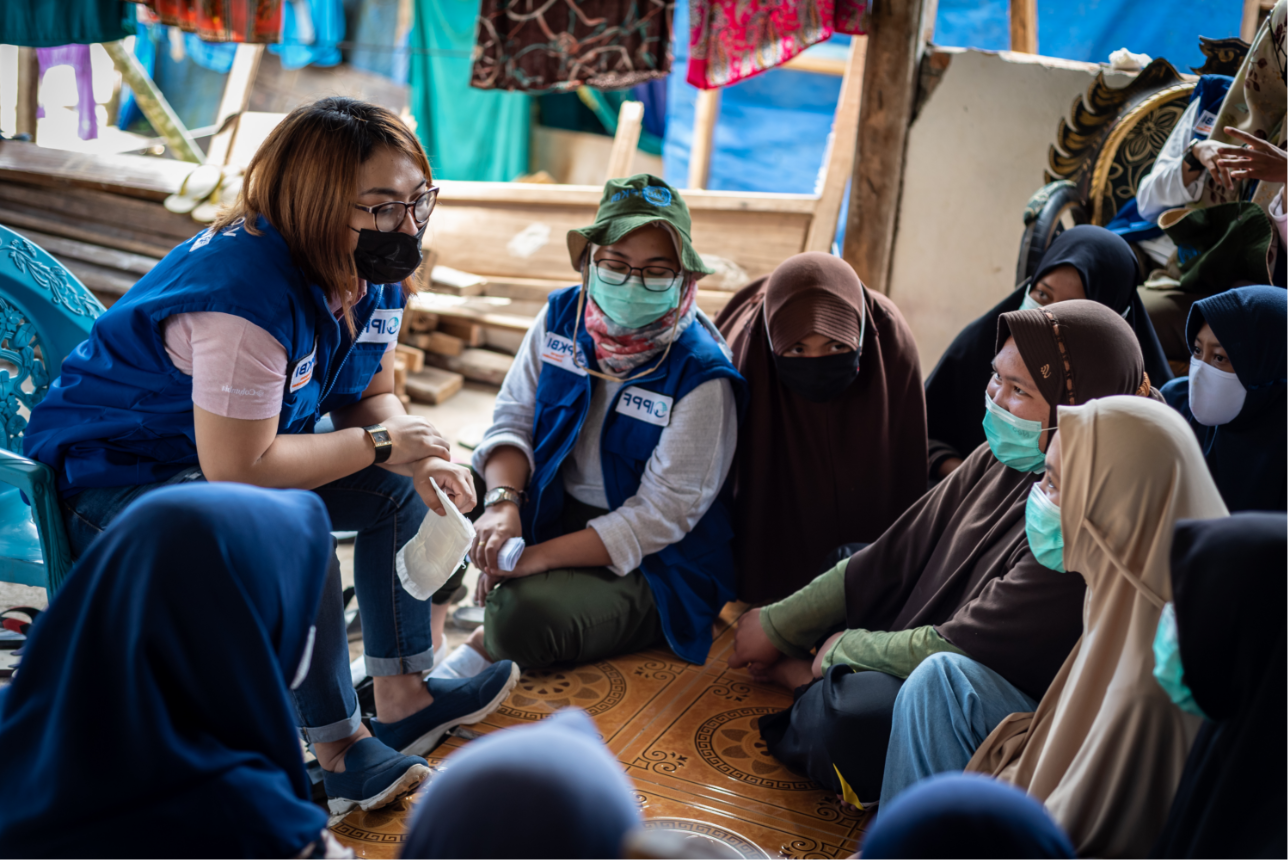


| 16 July 2020
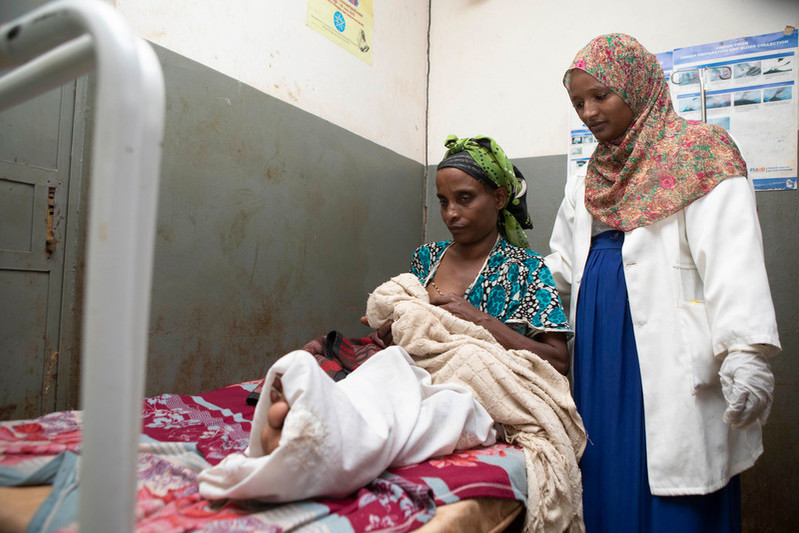
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 19 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
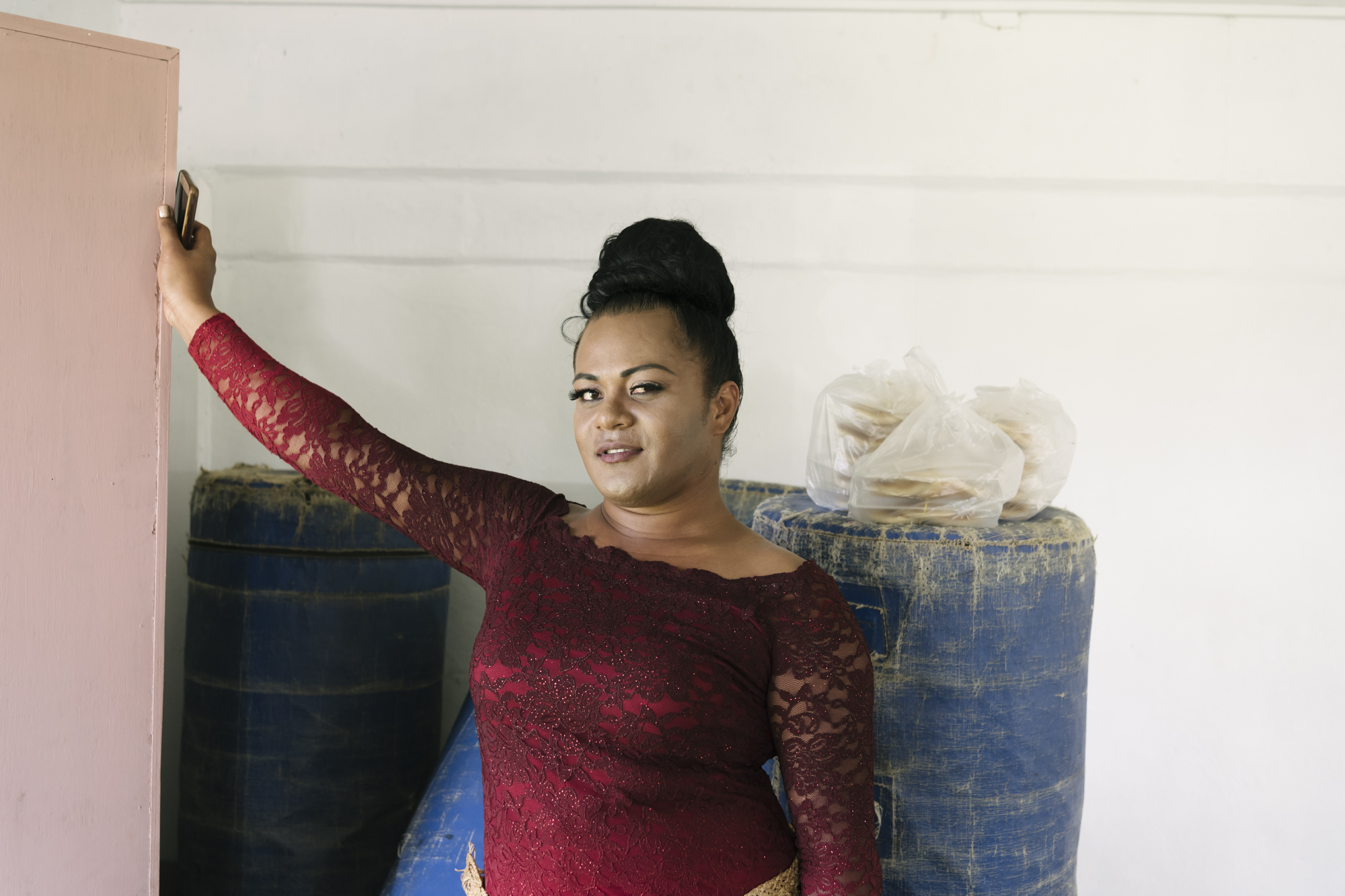
| 29 March 2018
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita
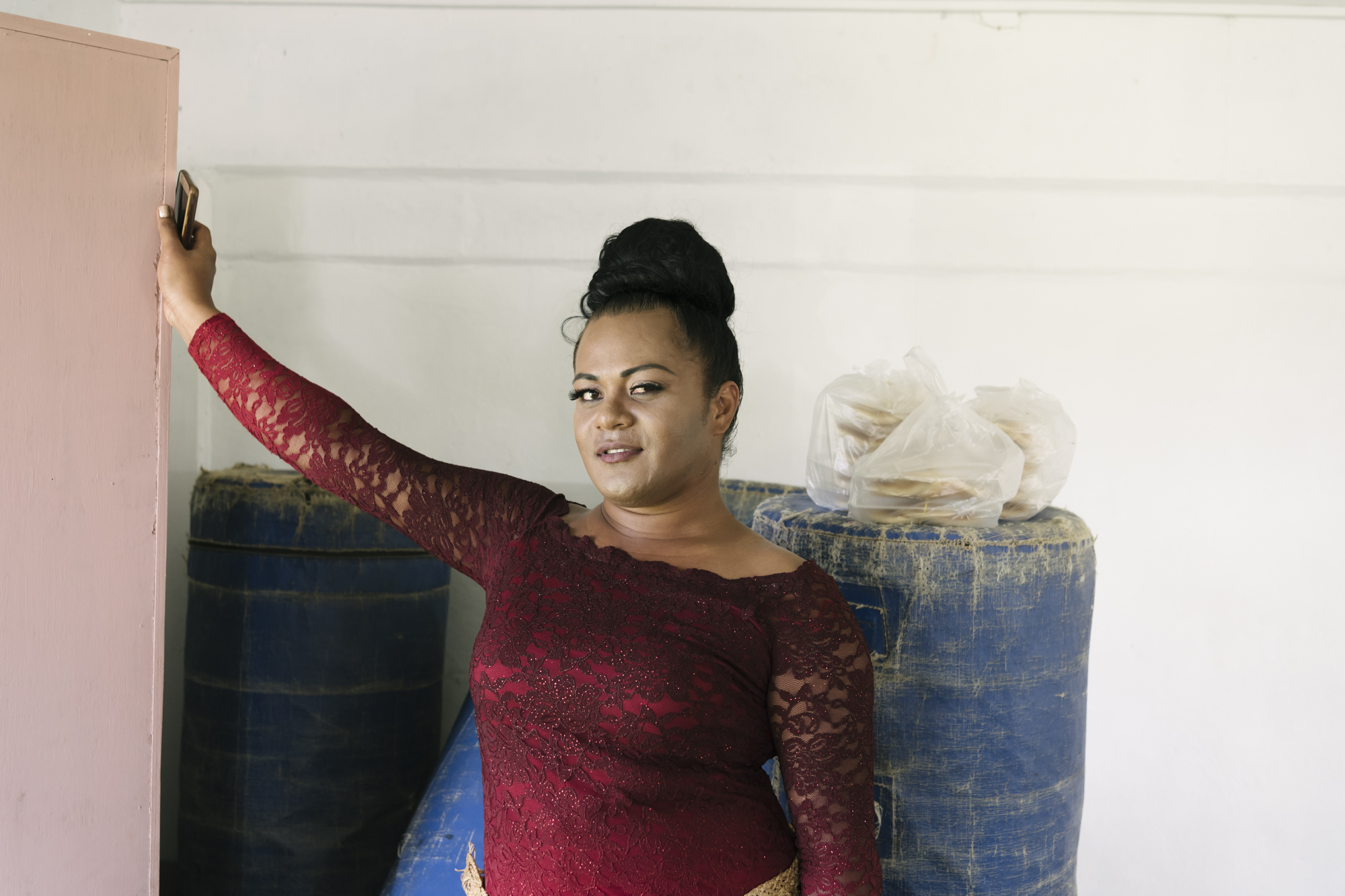
| 19 April 2024
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 19 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
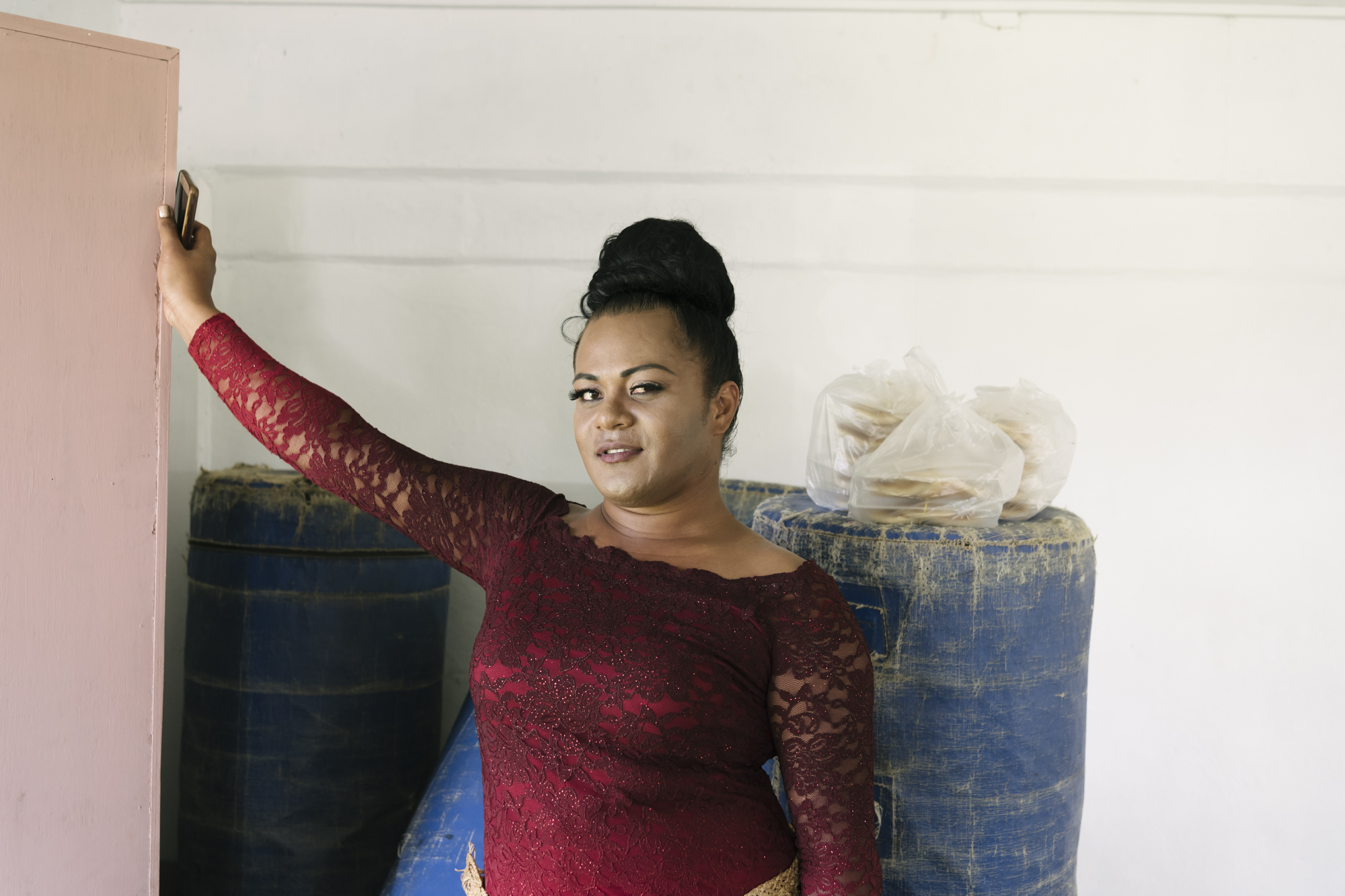
| 29 March 2018
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita
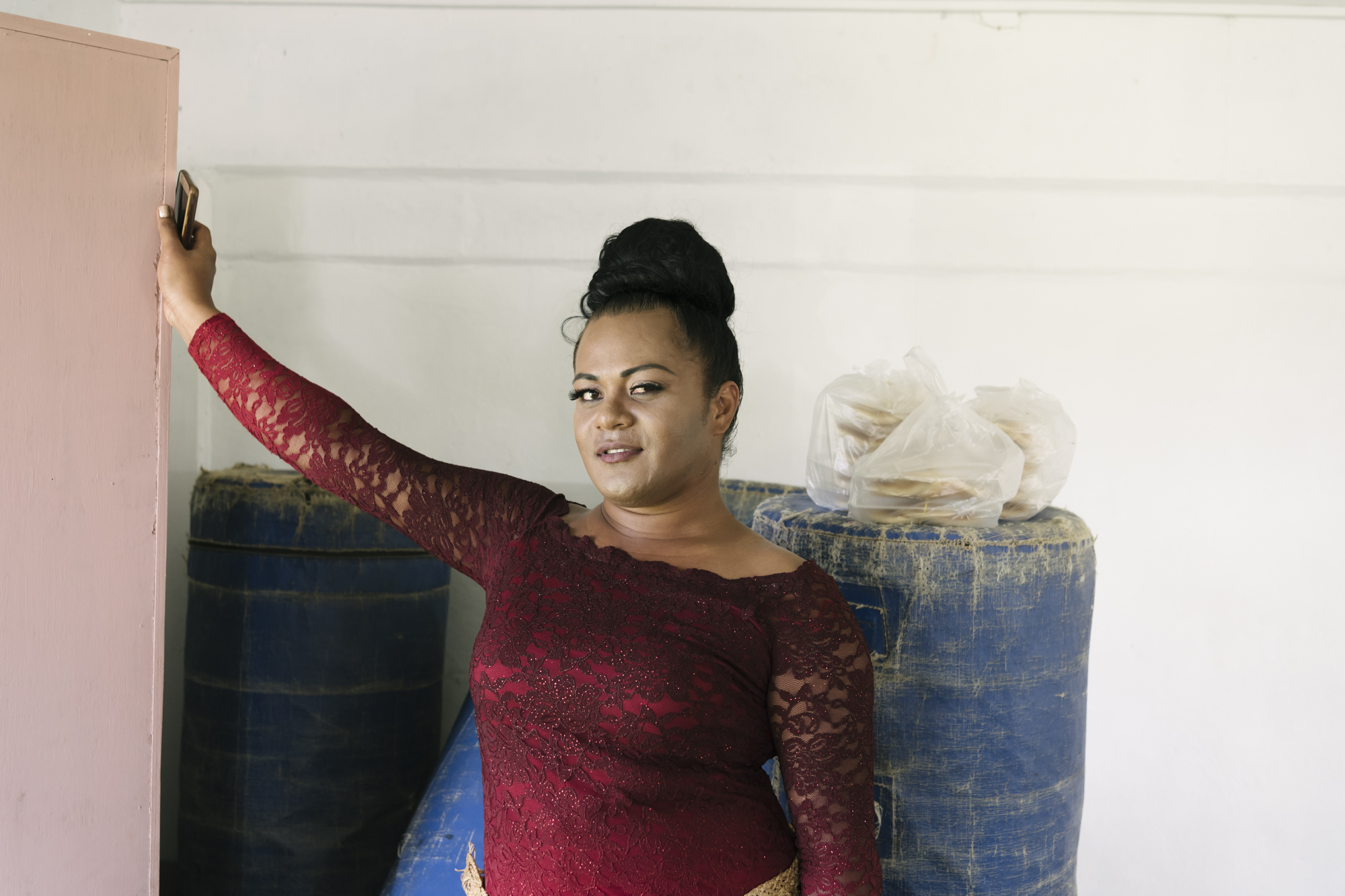
| 19 April 2024
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita








