Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

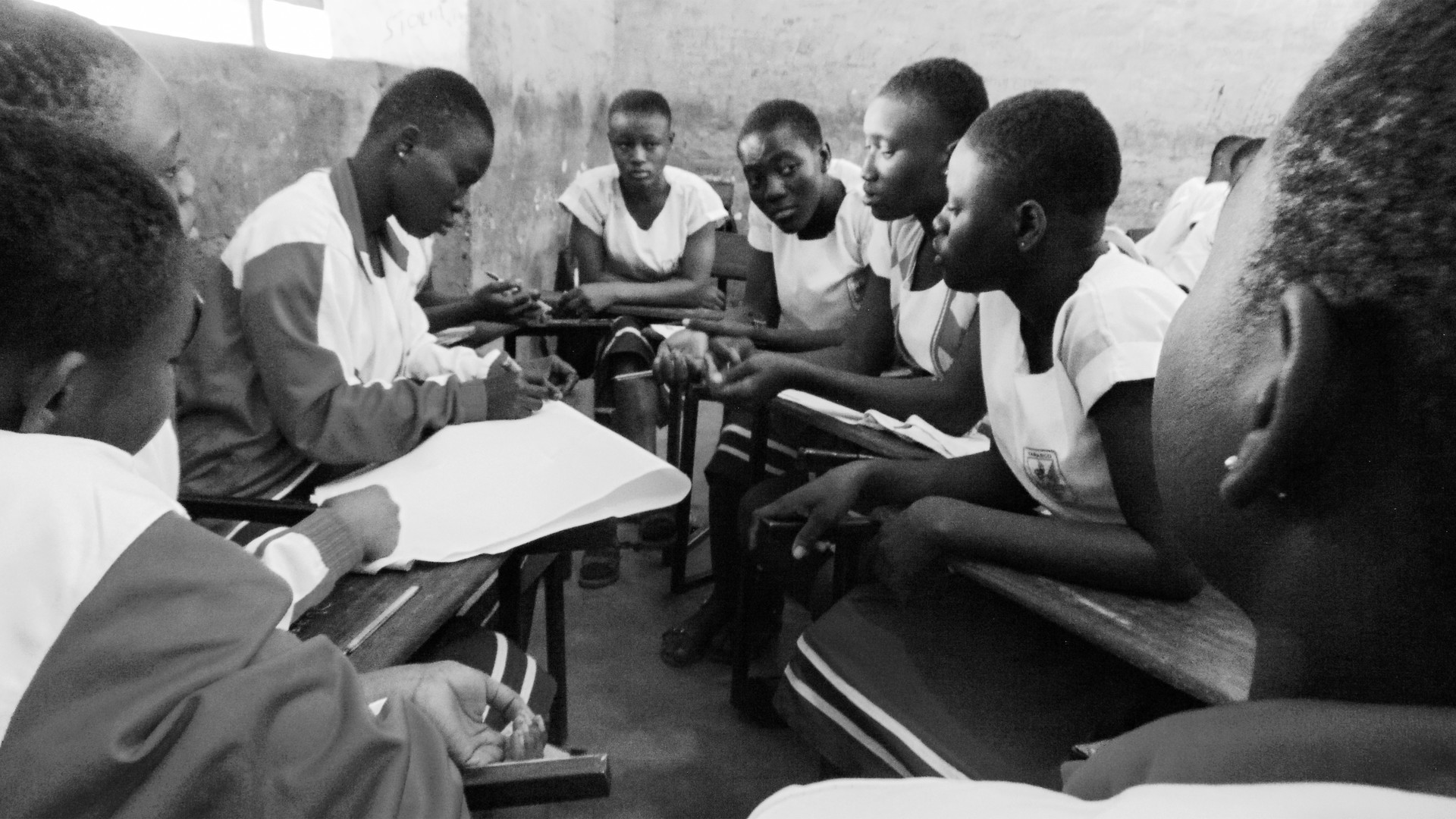
What does the year 2024 hold for us?
As the new year begins, we take a look at the trends and challenges ahead for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Most Popular This Week

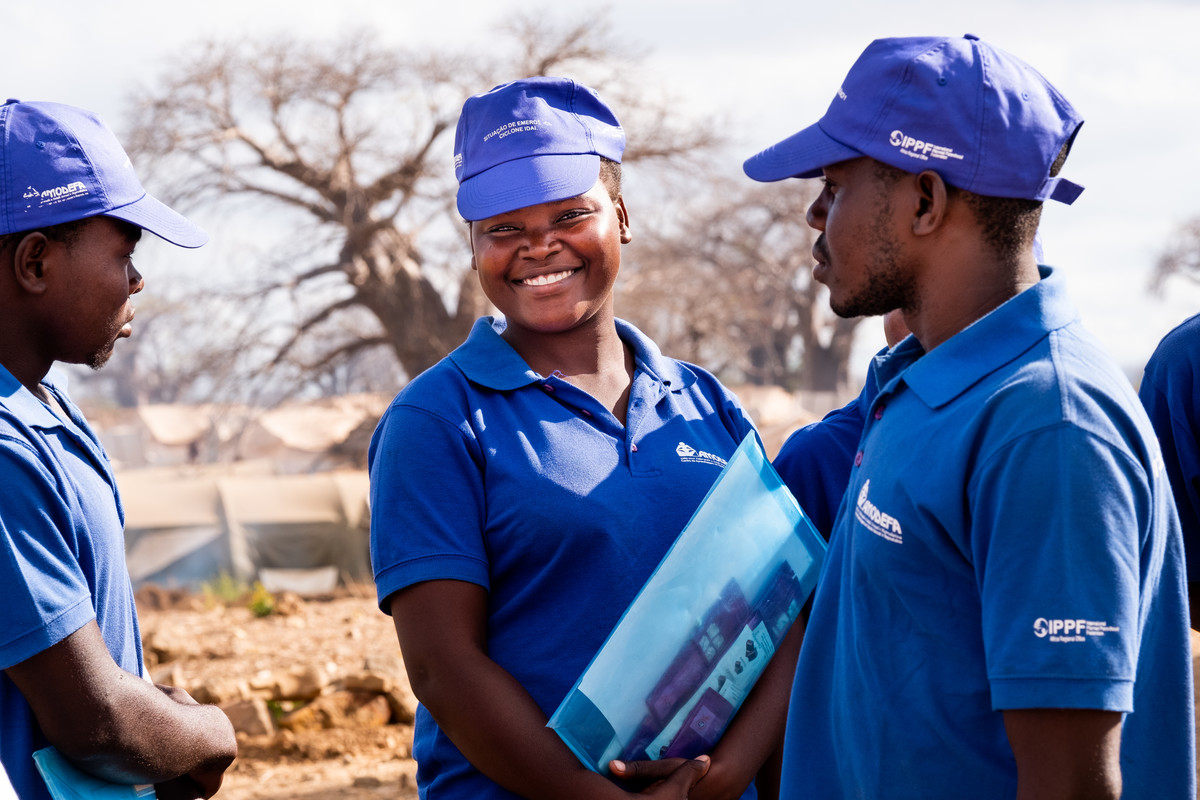
Palestine

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
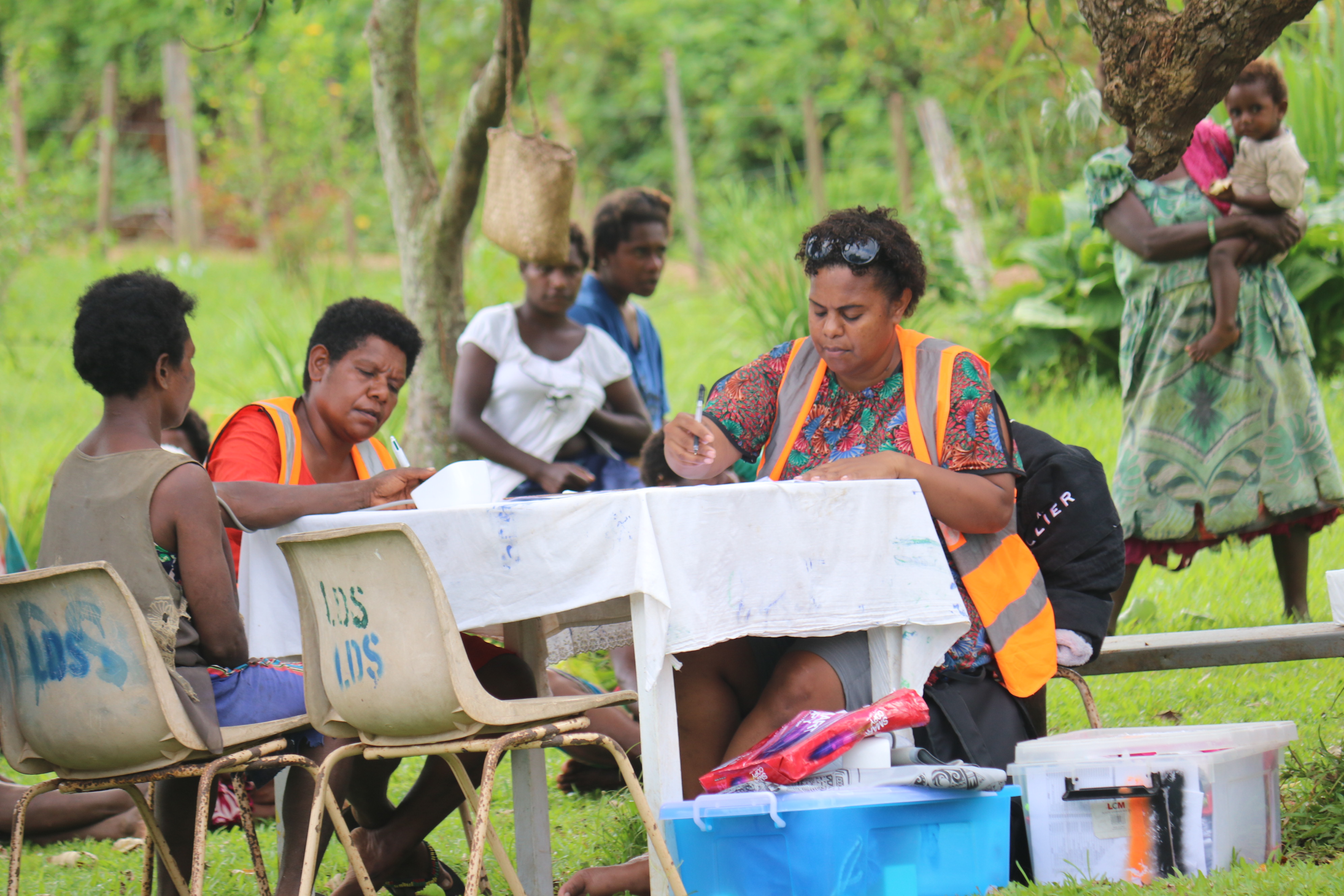

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
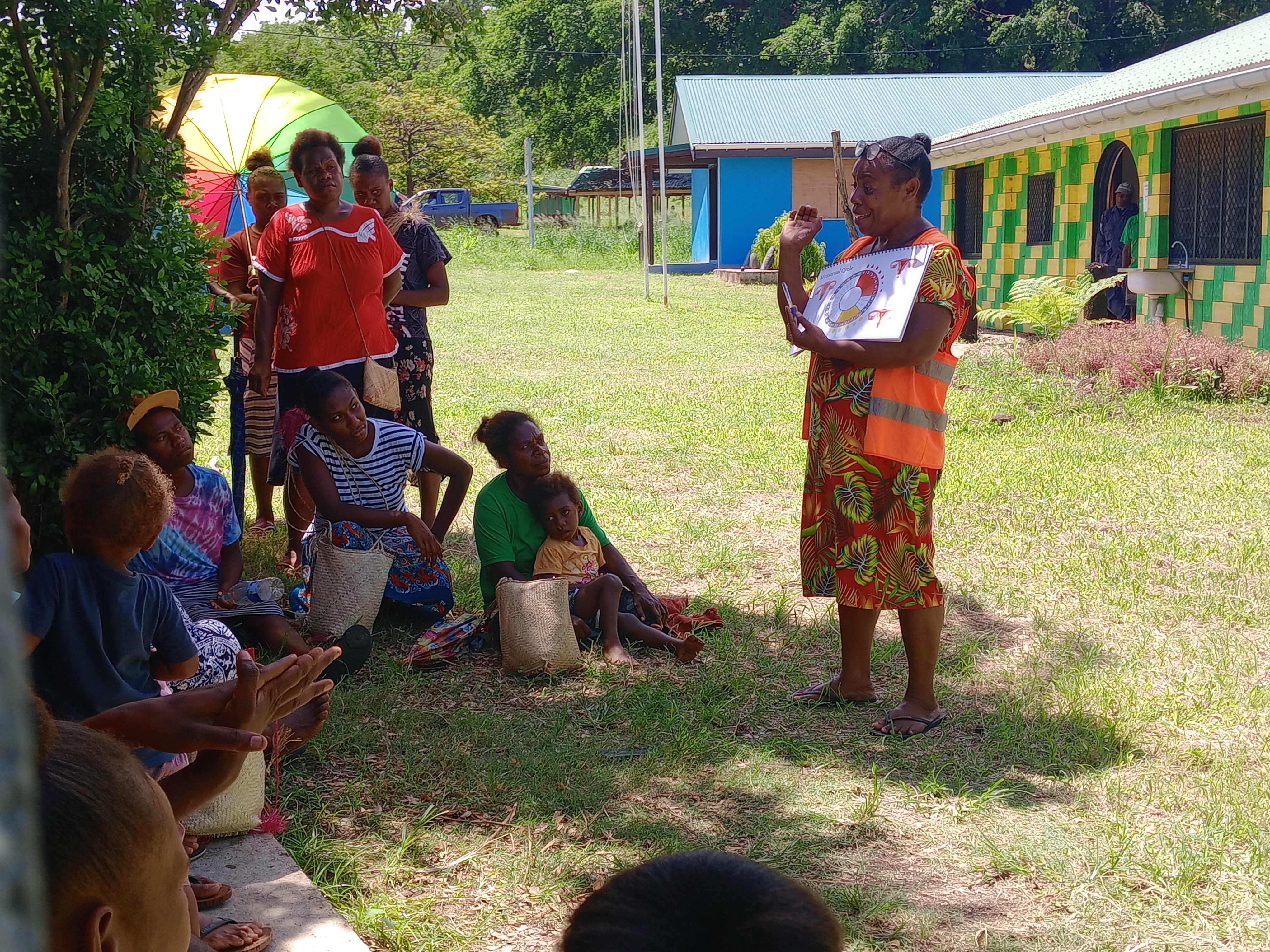

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Cook Islands

Dean and the Cook Islands Condom Car
On the island of Rarotonga, the main island of the Cook Islands in the South Pacific, a little white van makes its rounds on the palm-tree lined circular road.
Filter our stories by:
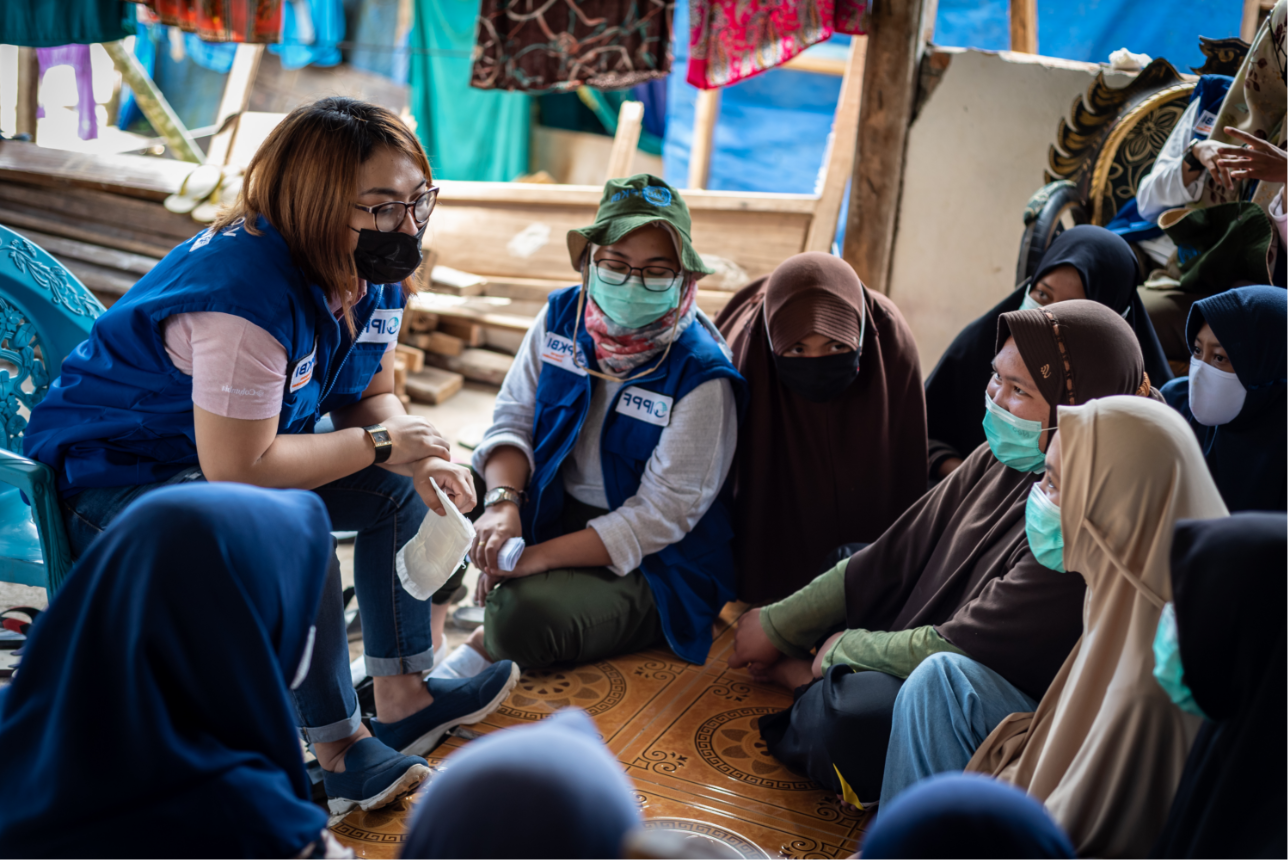


| 14 January 2021
“Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach”
Dressed in a sparkling white medical coat, Alinafe runs one of Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM) mobile clinics in the village of Chigude. Under the hot midday sun, she patiently answering the questions of staff, volunteers and clients - all while heavily pregnant herself. Delivering care to remote communities “Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach,” she says, as women queue up in neat lines in front of two khaki tents to receive anything from a cervical cancer screening to abortion counselling. Without the mobile clinic, local women risk life-threatening health issues as a result of unsafe abortion or illnesses linked to undiagnosed HIV status. According to the Guttmacher Institute, complications from abortion are the cause of 6–18% of maternal deaths in Malawi. District Manager Alinafe joined the Family Planning Association of Malawi in 2016, when she was just 20 years old, after going to nursing school and getting her degree in public health. She was one of the team involved in the Linkages project, which provided free family planning care to sex workers in Mzuzu until it was discontinued following the 2017 Global Gag Rule. Seeing the impact of lost funding on care “This change has reduced our reach,” Alinafe says, explaining that before the Gag Rule they were reaching sex workers in all four traditional authorities in Mzimba North - now they mostly work in just one. She says this means they are “denying people services which are very important” and without reaching people with sexual and reproductive healthcare, increasing the risk of STIs. The reduction in healthcare has also led to a breakdown in the trust FPAM had worked to build in communities, gaining support from those in respected positions such as chiefs. “Important people in the communities have been complaining to us, saying why did you do this? You were here, these things were happening and our people were benefiting a lot but now nothing is good at all,” explains Alinafe. Still, she is determined to serve her community against the odds - running the outreach clinic funded by Global Affairs Canada five times a week, in four traditional authorities, as well as the FPAM Youth Life Centre in Mzuzu. “On a serious note, unsafe abortions are happening in this area at a very high rate,” says Alinafe at the FPAM clinic in Chigude. “Talking about abortions is a very important thing. Whether we like it or not, on-the-ground these things are really happening, so we can’t ignore them.”

| 18 April 2024
“Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach”
Dressed in a sparkling white medical coat, Alinafe runs one of Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM) mobile clinics in the village of Chigude. Under the hot midday sun, she patiently answering the questions of staff, volunteers and clients - all while heavily pregnant herself. Delivering care to remote communities “Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach,” she says, as women queue up in neat lines in front of two khaki tents to receive anything from a cervical cancer screening to abortion counselling. Without the mobile clinic, local women risk life-threatening health issues as a result of unsafe abortion or illnesses linked to undiagnosed HIV status. According to the Guttmacher Institute, complications from abortion are the cause of 6–18% of maternal deaths in Malawi. District Manager Alinafe joined the Family Planning Association of Malawi in 2016, when she was just 20 years old, after going to nursing school and getting her degree in public health. She was one of the team involved in the Linkages project, which provided free family planning care to sex workers in Mzuzu until it was discontinued following the 2017 Global Gag Rule. Seeing the impact of lost funding on care “This change has reduced our reach,” Alinafe says, explaining that before the Gag Rule they were reaching sex workers in all four traditional authorities in Mzimba North - now they mostly work in just one. She says this means they are “denying people services which are very important” and without reaching people with sexual and reproductive healthcare, increasing the risk of STIs. The reduction in healthcare has also led to a breakdown in the trust FPAM had worked to build in communities, gaining support from those in respected positions such as chiefs. “Important people in the communities have been complaining to us, saying why did you do this? You were here, these things were happening and our people were benefiting a lot but now nothing is good at all,” explains Alinafe. Still, she is determined to serve her community against the odds - running the outreach clinic funded by Global Affairs Canada five times a week, in four traditional authorities, as well as the FPAM Youth Life Centre in Mzuzu. “On a serious note, unsafe abortions are happening in this area at a very high rate,” says Alinafe at the FPAM clinic in Chigude. “Talking about abortions is a very important thing. Whether we like it or not, on-the-ground these things are really happening, so we can’t ignore them.”

| 14 January 2021
“I learnt about condoms and even female condoms"
Mary, a 30-year-old sex worker, happily drinks a beer at one of the bars she works at in downtown Lilongwe. Her grin is reflected in the entirely mirrored walls, lit with red and blue neon lights. Above her, a DJ sat in an elevated booth is playing pumping dancehall while a handful of people around the bar nod and dance along to the music. It’s not even midday yet. Mary got introduced to the Family Planning Association of Malawi through friends, who invited her to a training session for sex worker ‘peer educators’ on issues related to sexual and reproductive health and rights as part of the Linkages project. “I learnt about condoms and even female condoms, which I hadn’t heard of before,” remembers Mary. Life-changing care and support But the most life-changing care she received was an HIV test, where she learnt that she was positive and began anti-retroviral treatment (ART). “It was hard for me at first, but then I realized I had to start a new life,” says Mary, saying this included being open with her son about her status, who was 15 at the time. According to UNAIDS 2018 data, 9.2% of adult Malawians are living with HIV. Women and sex workers are disproportionately affected - the same year, 55% of sex workers were estimated to be living with HIV. Mary says she now feels much healthier and is open with her friends in the sex worker community about her status, also encouraging them to get tested for HIV. “Linkages brought us all closer together as we became open about these issues with each other,” remembers Mary. Looking out for other sex workers As a peer educator, Mary became a go-to person for other sex workers to turn to in cases of sexual assault. “I’ll receive a message from someone who has been assaulted, then call everyone together to discuss the issue, and we’d escort that person to report to police,” says Mary. During the Linkages project - which was impacted by the Global Gag Rule and abruptly discontinued in 2017 - Mary was given an allowance to travel to different ‘hotspot’ areas. In these bars and lodges, she explains in detail how she would go from room-to-room handing out male and female condoms and showing her peers how to use them. FPAM healthcare teams would also go directly to the hotspots reaching women with healthcare such as STI testing and abortion counselling. FPAM’s teams know how crucial it is to provide healthcare to their clients ensuring it is non-judgmental and confidential. This is a vital service: Mary says she has had four sex worker friends die as a result of unsafe abortions, and lack of knowledge about post-abortion care. “Since the project ended, most of us find it difficult to access these services,” says Mary, adding that “New sex workers don’t have the information I have, and without Linkages we’re not able to reach all the hotspot bars in Lilongwe to educate them.”

| 18 April 2024
“I learnt about condoms and even female condoms"
Mary, a 30-year-old sex worker, happily drinks a beer at one of the bars she works at in downtown Lilongwe. Her grin is reflected in the entirely mirrored walls, lit with red and blue neon lights. Above her, a DJ sat in an elevated booth is playing pumping dancehall while a handful of people around the bar nod and dance along to the music. It’s not even midday yet. Mary got introduced to the Family Planning Association of Malawi through friends, who invited her to a training session for sex worker ‘peer educators’ on issues related to sexual and reproductive health and rights as part of the Linkages project. “I learnt about condoms and even female condoms, which I hadn’t heard of before,” remembers Mary. Life-changing care and support But the most life-changing care she received was an HIV test, where she learnt that she was positive and began anti-retroviral treatment (ART). “It was hard for me at first, but then I realized I had to start a new life,” says Mary, saying this included being open with her son about her status, who was 15 at the time. According to UNAIDS 2018 data, 9.2% of adult Malawians are living with HIV. Women and sex workers are disproportionately affected - the same year, 55% of sex workers were estimated to be living with HIV. Mary says she now feels much healthier and is open with her friends in the sex worker community about her status, also encouraging them to get tested for HIV. “Linkages brought us all closer together as we became open about these issues with each other,” remembers Mary. Looking out for other sex workers As a peer educator, Mary became a go-to person for other sex workers to turn to in cases of sexual assault. “I’ll receive a message from someone who has been assaulted, then call everyone together to discuss the issue, and we’d escort that person to report to police,” says Mary. During the Linkages project - which was impacted by the Global Gag Rule and abruptly discontinued in 2017 - Mary was given an allowance to travel to different ‘hotspot’ areas. In these bars and lodges, she explains in detail how she would go from room-to-room handing out male and female condoms and showing her peers how to use them. FPAM healthcare teams would also go directly to the hotspots reaching women with healthcare such as STI testing and abortion counselling. FPAM’s teams know how crucial it is to provide healthcare to their clients ensuring it is non-judgmental and confidential. This is a vital service: Mary says she has had four sex worker friends die as a result of unsafe abortions, and lack of knowledge about post-abortion care. “Since the project ended, most of us find it difficult to access these services,” says Mary, adding that “New sex workers don’t have the information I have, and without Linkages we’re not able to reach all the hotspot bars in Lilongwe to educate them.”

| 11 May 2017
Collaborating with public health providers in Nigeria
"I feel satisfied as a service provider and as a member of the outreach team." Shodunke Mary, 53, has been a midwife from the Local Government Area Council for seven years. Now she is working with PPFN providing family planning counselling and a range of integrated sexual and reproductive health services. In addition, Mary also conducts on the job training to other facilities which are providing services for the PPFN model. "The model used by PPFN is successful because the services we provide are free for those in need, the providers are motivated and the community leaders are also involved in the implementation. Also, the commodities and equipment are always available." As seen above, Mary administers an implant to Bukola Akami, who has one baby. The number of new contraceptive users has dramatically increased by 400,000 in less than a year as a result of PPFN's outreach and service delivery. Yetunde, 26, like Bukola, is a client with a young baby and was also seeking family planning. She says: "I don't want to have another baby in the next three years. I have a lot of things I want to do and I want to have time to take care of my children. My baby is really affecting my work and I always have to leave her with my mother-in-law. I will be recommending PPFN's family planning to my friends so they can also know what to do when they don't want to get pregnant again." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Collaborating with public health providers in Nigeria
"I feel satisfied as a service provider and as a member of the outreach team." Shodunke Mary, 53, has been a midwife from the Local Government Area Council for seven years. Now she is working with PPFN providing family planning counselling and a range of integrated sexual and reproductive health services. In addition, Mary also conducts on the job training to other facilities which are providing services for the PPFN model. "The model used by PPFN is successful because the services we provide are free for those in need, the providers are motivated and the community leaders are also involved in the implementation. Also, the commodities and equipment are always available." As seen above, Mary administers an implant to Bukola Akami, who has one baby. The number of new contraceptive users has dramatically increased by 400,000 in less than a year as a result of PPFN's outreach and service delivery. Yetunde, 26, like Bukola, is a client with a young baby and was also seeking family planning. She says: "I don't want to have another baby in the next three years. I have a lot of things I want to do and I want to have time to take care of my children. My baby is really affecting my work and I always have to leave her with my mother-in-law. I will be recommending PPFN's family planning to my friends so they can also know what to do when they don't want to get pregnant again." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 11 May 2017
Providing more than just one service to the community
"As a child I loved the medical profession so much. I always wanted to go with my aunt to the hospital for her antenatal check-ups. The neat and well-tailored uniform of the health workers always caught my eyes. And I knew one day, I would be wearing one of those uniforms serving my community.” Latifat Balogun explains how her childhood experiences led her to decide to train and work as a Community Health Extension Worker with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN), where she has worked for 20 years. She plays an integral part in delivering a wide range of services to women in her community. Here she is about to treat Zainab Akinsola, 52-years-old, who is waiting to have cervical cancer screening during a PPFN outreach programme at the Eni Ayo clinic in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. As a result of the strong integrated service delivery, non-contraceptive services increased from 42,700 in 2014 to 226,000 in 2015. Latifat's colleague, Adeyinka, is a faith-based health worker who encouraged a friend to undergo cervical cancer screening. "I counselled her and she went for screening, not knowing that she was going to test positive. If it wasn't for PPFN she might have died of cancer. I so nearly lost a friend. So I cannot forget that day. But now my friend is bouncing up and down, so excited about the project! During our last outreach she brought so many people." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Providing more than just one service to the community
"As a child I loved the medical profession so much. I always wanted to go with my aunt to the hospital for her antenatal check-ups. The neat and well-tailored uniform of the health workers always caught my eyes. And I knew one day, I would be wearing one of those uniforms serving my community.” Latifat Balogun explains how her childhood experiences led her to decide to train and work as a Community Health Extension Worker with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN), where she has worked for 20 years. She plays an integral part in delivering a wide range of services to women in her community. Here she is about to treat Zainab Akinsola, 52-years-old, who is waiting to have cervical cancer screening during a PPFN outreach programme at the Eni Ayo clinic in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. As a result of the strong integrated service delivery, non-contraceptive services increased from 42,700 in 2014 to 226,000 in 2015. Latifat's colleague, Adeyinka, is a faith-based health worker who encouraged a friend to undergo cervical cancer screening. "I counselled her and she went for screening, not knowing that she was going to test positive. If it wasn't for PPFN she might have died of cancer. I so nearly lost a friend. So I cannot forget that day. But now my friend is bouncing up and down, so excited about the project! During our last outreach she brought so many people." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success
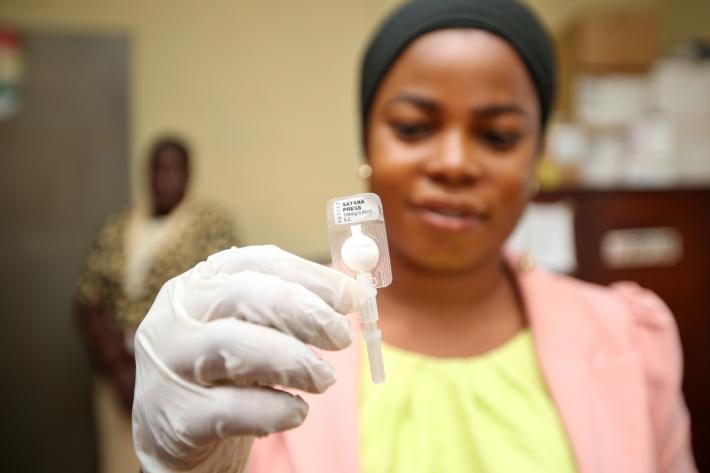
| 11 May 2017
Sayana Press: Finding the right contraception
"How do I feel about my role? I'm excited!" Emiade Kudirat, 24, is a Community Health Extension Worker doing outreach with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN) for the last 18 months. She specializes in the Sayana Press - a three-month, progestin-only injectable contraceptive favoured for its convenience in administration and portability. "I go from house-to-house to provide health education and introduce family planning services. I do counselling and provision of these services too. The PPFN model can really reduce the mortality rate of women in the community. We're taking the clinic to women at the market, to their homes and to their work." One patient, 24-year-old Bukola Polpoola, says she is happy that her treatment was free and easy. "In my village we don’t have any information about this. At first I was afraid it would stop me from getting pregnant again. I’d heard stories of side effects. I’m a nurse and even I began to wonder about it. But I called the clinic and they counselled me and reassured me.” She talked to her partner before she decided to get an implant. Now, she says, she’d recommend it to anyone. "I would be happy to spread the word in my village. Taking this will help you plan your life. For example, you know that for the next two years you can’t get pregnant and you’ll be able to plan your life properly because an unwanted pregnancy can stop you from getting an education or a job. This removes that fear for a time." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Sayana Press: Finding the right contraception
"How do I feel about my role? I'm excited!" Emiade Kudirat, 24, is a Community Health Extension Worker doing outreach with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN) for the last 18 months. She specializes in the Sayana Press - a three-month, progestin-only injectable contraceptive favoured for its convenience in administration and portability. "I go from house-to-house to provide health education and introduce family planning services. I do counselling and provision of these services too. The PPFN model can really reduce the mortality rate of women in the community. We're taking the clinic to women at the market, to their homes and to their work." One patient, 24-year-old Bukola Polpoola, says she is happy that her treatment was free and easy. "In my village we don’t have any information about this. At first I was afraid it would stop me from getting pregnant again. I’d heard stories of side effects. I’m a nurse and even I began to wonder about it. But I called the clinic and they counselled me and reassured me.” She talked to her partner before she decided to get an implant. Now, she says, she’d recommend it to anyone. "I would be happy to spread the word in my village. Taking this will help you plan your life. For example, you know that for the next two years you can’t get pregnant and you’ll be able to plan your life properly because an unwanted pregnancy can stop you from getting an education or a job. This removes that fear for a time." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success
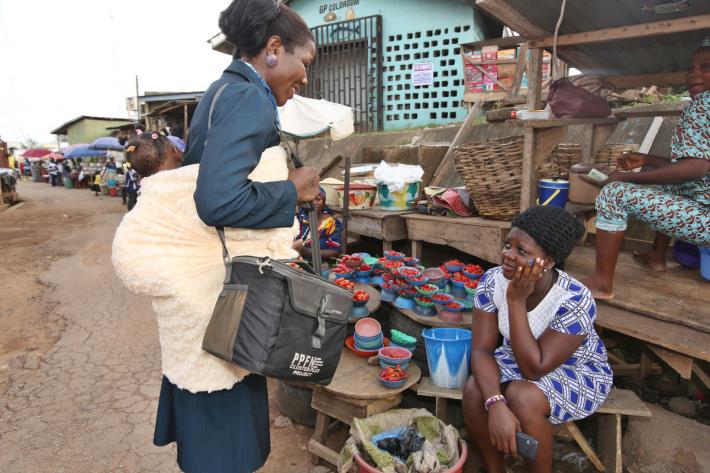

| 11 May 2017
Nigeria's Cluster Plus model: Working in the community
"I find this work very interesting. I love to interact with the women in the markets. And I get to work all day with my 10-month-old baby, Bejide, with me!" Olusula, 40, is a Community Health Extension Worker, conducting outreach for the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN). In 2014, PPFN received a one year grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation through IPPF. The purpose of the grant was to expand family planning and reproductive health services. PPFN used this grant to improve on its current model of service delivery known as the Cluster model. PPFN piloted a successful project over 9 months around family planning. This project exceeded targets significantly and has the potential to be rolled out in Nigeria and other countries. "I refer clients through vouchers to the facility of their choice for long acting and reversible contraceptive methods too", explains Olusula. She works closely with her local community providing information and choice about contraceptive methods. Women and men are able to make informed decisions that ensure suitability to them and their circumstances. Choice promotes convenience and acceptability. "This PPFN outreach and service model will reduce a lot of abortions in our community. It also encourages women to space their children and lets them do the other things they want." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Nigeria's Cluster Plus model: Working in the community
"I find this work very interesting. I love to interact with the women in the markets. And I get to work all day with my 10-month-old baby, Bejide, with me!" Olusula, 40, is a Community Health Extension Worker, conducting outreach for the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN). In 2014, PPFN received a one year grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation through IPPF. The purpose of the grant was to expand family planning and reproductive health services. PPFN used this grant to improve on its current model of service delivery known as the Cluster model. PPFN piloted a successful project over 9 months around family planning. This project exceeded targets significantly and has the potential to be rolled out in Nigeria and other countries. "I refer clients through vouchers to the facility of their choice for long acting and reversible contraceptive methods too", explains Olusula. She works closely with her local community providing information and choice about contraceptive methods. Women and men are able to make informed decisions that ensure suitability to them and their circumstances. Choice promotes convenience and acceptability. "This PPFN outreach and service model will reduce a lot of abortions in our community. It also encourages women to space their children and lets them do the other things they want." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 14 January 2021
“Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach”
Dressed in a sparkling white medical coat, Alinafe runs one of Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM) mobile clinics in the village of Chigude. Under the hot midday sun, she patiently answering the questions of staff, volunteers and clients - all while heavily pregnant herself. Delivering care to remote communities “Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach,” she says, as women queue up in neat lines in front of two khaki tents to receive anything from a cervical cancer screening to abortion counselling. Without the mobile clinic, local women risk life-threatening health issues as a result of unsafe abortion or illnesses linked to undiagnosed HIV status. According to the Guttmacher Institute, complications from abortion are the cause of 6–18% of maternal deaths in Malawi. District Manager Alinafe joined the Family Planning Association of Malawi in 2016, when she was just 20 years old, after going to nursing school and getting her degree in public health. She was one of the team involved in the Linkages project, which provided free family planning care to sex workers in Mzuzu until it was discontinued following the 2017 Global Gag Rule. Seeing the impact of lost funding on care “This change has reduced our reach,” Alinafe says, explaining that before the Gag Rule they were reaching sex workers in all four traditional authorities in Mzimba North - now they mostly work in just one. She says this means they are “denying people services which are very important” and without reaching people with sexual and reproductive healthcare, increasing the risk of STIs. The reduction in healthcare has also led to a breakdown in the trust FPAM had worked to build in communities, gaining support from those in respected positions such as chiefs. “Important people in the communities have been complaining to us, saying why did you do this? You were here, these things were happening and our people were benefiting a lot but now nothing is good at all,” explains Alinafe. Still, she is determined to serve her community against the odds - running the outreach clinic funded by Global Affairs Canada five times a week, in four traditional authorities, as well as the FPAM Youth Life Centre in Mzuzu. “On a serious note, unsafe abortions are happening in this area at a very high rate,” says Alinafe at the FPAM clinic in Chigude. “Talking about abortions is a very important thing. Whether we like it or not, on-the-ground these things are really happening, so we can’t ignore them.”

| 18 April 2024
“Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach”
Dressed in a sparkling white medical coat, Alinafe runs one of Family Planning Association of Malawi (FPAM) mobile clinics in the village of Chigude. Under the hot midday sun, she patiently answering the questions of staff, volunteers and clients - all while heavily pregnant herself. Delivering care to remote communities “Most NGOs don’t come here because it’s so hard to reach,” she says, as women queue up in neat lines in front of two khaki tents to receive anything from a cervical cancer screening to abortion counselling. Without the mobile clinic, local women risk life-threatening health issues as a result of unsafe abortion or illnesses linked to undiagnosed HIV status. According to the Guttmacher Institute, complications from abortion are the cause of 6–18% of maternal deaths in Malawi. District Manager Alinafe joined the Family Planning Association of Malawi in 2016, when she was just 20 years old, after going to nursing school and getting her degree in public health. She was one of the team involved in the Linkages project, which provided free family planning care to sex workers in Mzuzu until it was discontinued following the 2017 Global Gag Rule. Seeing the impact of lost funding on care “This change has reduced our reach,” Alinafe says, explaining that before the Gag Rule they were reaching sex workers in all four traditional authorities in Mzimba North - now they mostly work in just one. She says this means they are “denying people services which are very important” and without reaching people with sexual and reproductive healthcare, increasing the risk of STIs. The reduction in healthcare has also led to a breakdown in the trust FPAM had worked to build in communities, gaining support from those in respected positions such as chiefs. “Important people in the communities have been complaining to us, saying why did you do this? You were here, these things were happening and our people were benefiting a lot but now nothing is good at all,” explains Alinafe. Still, she is determined to serve her community against the odds - running the outreach clinic funded by Global Affairs Canada five times a week, in four traditional authorities, as well as the FPAM Youth Life Centre in Mzuzu. “On a serious note, unsafe abortions are happening in this area at a very high rate,” says Alinafe at the FPAM clinic in Chigude. “Talking about abortions is a very important thing. Whether we like it or not, on-the-ground these things are really happening, so we can’t ignore them.”

| 14 January 2021
“I learnt about condoms and even female condoms"
Mary, a 30-year-old sex worker, happily drinks a beer at one of the bars she works at in downtown Lilongwe. Her grin is reflected in the entirely mirrored walls, lit with red and blue neon lights. Above her, a DJ sat in an elevated booth is playing pumping dancehall while a handful of people around the bar nod and dance along to the music. It’s not even midday yet. Mary got introduced to the Family Planning Association of Malawi through friends, who invited her to a training session for sex worker ‘peer educators’ on issues related to sexual and reproductive health and rights as part of the Linkages project. “I learnt about condoms and even female condoms, which I hadn’t heard of before,” remembers Mary. Life-changing care and support But the most life-changing care she received was an HIV test, where she learnt that she was positive and began anti-retroviral treatment (ART). “It was hard for me at first, but then I realized I had to start a new life,” says Mary, saying this included being open with her son about her status, who was 15 at the time. According to UNAIDS 2018 data, 9.2% of adult Malawians are living with HIV. Women and sex workers are disproportionately affected - the same year, 55% of sex workers were estimated to be living with HIV. Mary says she now feels much healthier and is open with her friends in the sex worker community about her status, also encouraging them to get tested for HIV. “Linkages brought us all closer together as we became open about these issues with each other,” remembers Mary. Looking out for other sex workers As a peer educator, Mary became a go-to person for other sex workers to turn to in cases of sexual assault. “I’ll receive a message from someone who has been assaulted, then call everyone together to discuss the issue, and we’d escort that person to report to police,” says Mary. During the Linkages project - which was impacted by the Global Gag Rule and abruptly discontinued in 2017 - Mary was given an allowance to travel to different ‘hotspot’ areas. In these bars and lodges, she explains in detail how she would go from room-to-room handing out male and female condoms and showing her peers how to use them. FPAM healthcare teams would also go directly to the hotspots reaching women with healthcare such as STI testing and abortion counselling. FPAM’s teams know how crucial it is to provide healthcare to their clients ensuring it is non-judgmental and confidential. This is a vital service: Mary says she has had four sex worker friends die as a result of unsafe abortions, and lack of knowledge about post-abortion care. “Since the project ended, most of us find it difficult to access these services,” says Mary, adding that “New sex workers don’t have the information I have, and without Linkages we’re not able to reach all the hotspot bars in Lilongwe to educate them.”

| 18 April 2024
“I learnt about condoms and even female condoms"
Mary, a 30-year-old sex worker, happily drinks a beer at one of the bars she works at in downtown Lilongwe. Her grin is reflected in the entirely mirrored walls, lit with red and blue neon lights. Above her, a DJ sat in an elevated booth is playing pumping dancehall while a handful of people around the bar nod and dance along to the music. It’s not even midday yet. Mary got introduced to the Family Planning Association of Malawi through friends, who invited her to a training session for sex worker ‘peer educators’ on issues related to sexual and reproductive health and rights as part of the Linkages project. “I learnt about condoms and even female condoms, which I hadn’t heard of before,” remembers Mary. Life-changing care and support But the most life-changing care she received was an HIV test, where she learnt that she was positive and began anti-retroviral treatment (ART). “It was hard for me at first, but then I realized I had to start a new life,” says Mary, saying this included being open with her son about her status, who was 15 at the time. According to UNAIDS 2018 data, 9.2% of adult Malawians are living with HIV. Women and sex workers are disproportionately affected - the same year, 55% of sex workers were estimated to be living with HIV. Mary says she now feels much healthier and is open with her friends in the sex worker community about her status, also encouraging them to get tested for HIV. “Linkages brought us all closer together as we became open about these issues with each other,” remembers Mary. Looking out for other sex workers As a peer educator, Mary became a go-to person for other sex workers to turn to in cases of sexual assault. “I’ll receive a message from someone who has been assaulted, then call everyone together to discuss the issue, and we’d escort that person to report to police,” says Mary. During the Linkages project - which was impacted by the Global Gag Rule and abruptly discontinued in 2017 - Mary was given an allowance to travel to different ‘hotspot’ areas. In these bars and lodges, she explains in detail how she would go from room-to-room handing out male and female condoms and showing her peers how to use them. FPAM healthcare teams would also go directly to the hotspots reaching women with healthcare such as STI testing and abortion counselling. FPAM’s teams know how crucial it is to provide healthcare to their clients ensuring it is non-judgmental and confidential. This is a vital service: Mary says she has had four sex worker friends die as a result of unsafe abortions, and lack of knowledge about post-abortion care. “Since the project ended, most of us find it difficult to access these services,” says Mary, adding that “New sex workers don’t have the information I have, and without Linkages we’re not able to reach all the hotspot bars in Lilongwe to educate them.”

| 11 May 2017
Collaborating with public health providers in Nigeria
"I feel satisfied as a service provider and as a member of the outreach team." Shodunke Mary, 53, has been a midwife from the Local Government Area Council for seven years. Now she is working with PPFN providing family planning counselling and a range of integrated sexual and reproductive health services. In addition, Mary also conducts on the job training to other facilities which are providing services for the PPFN model. "The model used by PPFN is successful because the services we provide are free for those in need, the providers are motivated and the community leaders are also involved in the implementation. Also, the commodities and equipment are always available." As seen above, Mary administers an implant to Bukola Akami, who has one baby. The number of new contraceptive users has dramatically increased by 400,000 in less than a year as a result of PPFN's outreach and service delivery. Yetunde, 26, like Bukola, is a client with a young baby and was also seeking family planning. She says: "I don't want to have another baby in the next three years. I have a lot of things I want to do and I want to have time to take care of my children. My baby is really affecting my work and I always have to leave her with my mother-in-law. I will be recommending PPFN's family planning to my friends so they can also know what to do when they don't want to get pregnant again." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Collaborating with public health providers in Nigeria
"I feel satisfied as a service provider and as a member of the outreach team." Shodunke Mary, 53, has been a midwife from the Local Government Area Council for seven years. Now she is working with PPFN providing family planning counselling and a range of integrated sexual and reproductive health services. In addition, Mary also conducts on the job training to other facilities which are providing services for the PPFN model. "The model used by PPFN is successful because the services we provide are free for those in need, the providers are motivated and the community leaders are also involved in the implementation. Also, the commodities and equipment are always available." As seen above, Mary administers an implant to Bukola Akami, who has one baby. The number of new contraceptive users has dramatically increased by 400,000 in less than a year as a result of PPFN's outreach and service delivery. Yetunde, 26, like Bukola, is a client with a young baby and was also seeking family planning. She says: "I don't want to have another baby in the next three years. I have a lot of things I want to do and I want to have time to take care of my children. My baby is really affecting my work and I always have to leave her with my mother-in-law. I will be recommending PPFN's family planning to my friends so they can also know what to do when they don't want to get pregnant again." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 11 May 2017
Providing more than just one service to the community
"As a child I loved the medical profession so much. I always wanted to go with my aunt to the hospital for her antenatal check-ups. The neat and well-tailored uniform of the health workers always caught my eyes. And I knew one day, I would be wearing one of those uniforms serving my community.” Latifat Balogun explains how her childhood experiences led her to decide to train and work as a Community Health Extension Worker with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN), where she has worked for 20 years. She plays an integral part in delivering a wide range of services to women in her community. Here she is about to treat Zainab Akinsola, 52-years-old, who is waiting to have cervical cancer screening during a PPFN outreach programme at the Eni Ayo clinic in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. As a result of the strong integrated service delivery, non-contraceptive services increased from 42,700 in 2014 to 226,000 in 2015. Latifat's colleague, Adeyinka, is a faith-based health worker who encouraged a friend to undergo cervical cancer screening. "I counselled her and she went for screening, not knowing that she was going to test positive. If it wasn't for PPFN she might have died of cancer. I so nearly lost a friend. So I cannot forget that day. But now my friend is bouncing up and down, so excited about the project! During our last outreach she brought so many people." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Providing more than just one service to the community
"As a child I loved the medical profession so much. I always wanted to go with my aunt to the hospital for her antenatal check-ups. The neat and well-tailored uniform of the health workers always caught my eyes. And I knew one day, I would be wearing one of those uniforms serving my community.” Latifat Balogun explains how her childhood experiences led her to decide to train and work as a Community Health Extension Worker with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN), where she has worked for 20 years. She plays an integral part in delivering a wide range of services to women in her community. Here she is about to treat Zainab Akinsola, 52-years-old, who is waiting to have cervical cancer screening during a PPFN outreach programme at the Eni Ayo clinic in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. As a result of the strong integrated service delivery, non-contraceptive services increased from 42,700 in 2014 to 226,000 in 2015. Latifat's colleague, Adeyinka, is a faith-based health worker who encouraged a friend to undergo cervical cancer screening. "I counselled her and she went for screening, not knowing that she was going to test positive. If it wasn't for PPFN she might have died of cancer. I so nearly lost a friend. So I cannot forget that day. But now my friend is bouncing up and down, so excited about the project! During our last outreach she brought so many people." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 11 May 2017
Sayana Press: Finding the right contraception
"How do I feel about my role? I'm excited!" Emiade Kudirat, 24, is a Community Health Extension Worker doing outreach with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN) for the last 18 months. She specializes in the Sayana Press - a three-month, progestin-only injectable contraceptive favoured for its convenience in administration and portability. "I go from house-to-house to provide health education and introduce family planning services. I do counselling and provision of these services too. The PPFN model can really reduce the mortality rate of women in the community. We're taking the clinic to women at the market, to their homes and to their work." One patient, 24-year-old Bukola Polpoola, says she is happy that her treatment was free and easy. "In my village we don’t have any information about this. At first I was afraid it would stop me from getting pregnant again. I’d heard stories of side effects. I’m a nurse and even I began to wonder about it. But I called the clinic and they counselled me and reassured me.” She talked to her partner before she decided to get an implant. Now, she says, she’d recommend it to anyone. "I would be happy to spread the word in my village. Taking this will help you plan your life. For example, you know that for the next two years you can’t get pregnant and you’ll be able to plan your life properly because an unwanted pregnancy can stop you from getting an education or a job. This removes that fear for a time." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Sayana Press: Finding the right contraception
"How do I feel about my role? I'm excited!" Emiade Kudirat, 24, is a Community Health Extension Worker doing outreach with the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN) for the last 18 months. She specializes in the Sayana Press - a three-month, progestin-only injectable contraceptive favoured for its convenience in administration and portability. "I go from house-to-house to provide health education and introduce family planning services. I do counselling and provision of these services too. The PPFN model can really reduce the mortality rate of women in the community. We're taking the clinic to women at the market, to their homes and to their work." One patient, 24-year-old Bukola Polpoola, says she is happy that her treatment was free and easy. "In my village we don’t have any information about this. At first I was afraid it would stop me from getting pregnant again. I’d heard stories of side effects. I’m a nurse and even I began to wonder about it. But I called the clinic and they counselled me and reassured me.” She talked to her partner before she decided to get an implant. Now, she says, she’d recommend it to anyone. "I would be happy to spread the word in my village. Taking this will help you plan your life. For example, you know that for the next two years you can’t get pregnant and you’ll be able to plan your life properly because an unwanted pregnancy can stop you from getting an education or a job. This removes that fear for a time." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 11 May 2017
Nigeria's Cluster Plus model: Working in the community
"I find this work very interesting. I love to interact with the women in the markets. And I get to work all day with my 10-month-old baby, Bejide, with me!" Olusula, 40, is a Community Health Extension Worker, conducting outreach for the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN). In 2014, PPFN received a one year grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation through IPPF. The purpose of the grant was to expand family planning and reproductive health services. PPFN used this grant to improve on its current model of service delivery known as the Cluster model. PPFN piloted a successful project over 9 months around family planning. This project exceeded targets significantly and has the potential to be rolled out in Nigeria and other countries. "I refer clients through vouchers to the facility of their choice for long acting and reversible contraceptive methods too", explains Olusula. She works closely with her local community providing information and choice about contraceptive methods. Women and men are able to make informed decisions that ensure suitability to them and their circumstances. Choice promotes convenience and acceptability. "This PPFN outreach and service model will reduce a lot of abortions in our community. It also encourages women to space their children and lets them do the other things they want." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success

| 18 April 2024
Nigeria's Cluster Plus model: Working in the community
"I find this work very interesting. I love to interact with the women in the markets. And I get to work all day with my 10-month-old baby, Bejide, with me!" Olusula, 40, is a Community Health Extension Worker, conducting outreach for the Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria (PPFN). In 2014, PPFN received a one year grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation through IPPF. The purpose of the grant was to expand family planning and reproductive health services. PPFN used this grant to improve on its current model of service delivery known as the Cluster model. PPFN piloted a successful project over 9 months around family planning. This project exceeded targets significantly and has the potential to be rolled out in Nigeria and other countries. "I refer clients through vouchers to the facility of their choice for long acting and reversible contraceptive methods too", explains Olusula. She works closely with her local community providing information and choice about contraceptive methods. Women and men are able to make informed decisions that ensure suitability to them and their circumstances. Choice promotes convenience and acceptability. "This PPFN outreach and service model will reduce a lot of abortions in our community. It also encourages women to space their children and lets them do the other things they want." The team Read more about the team behind Nigeria's amazing success








