Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

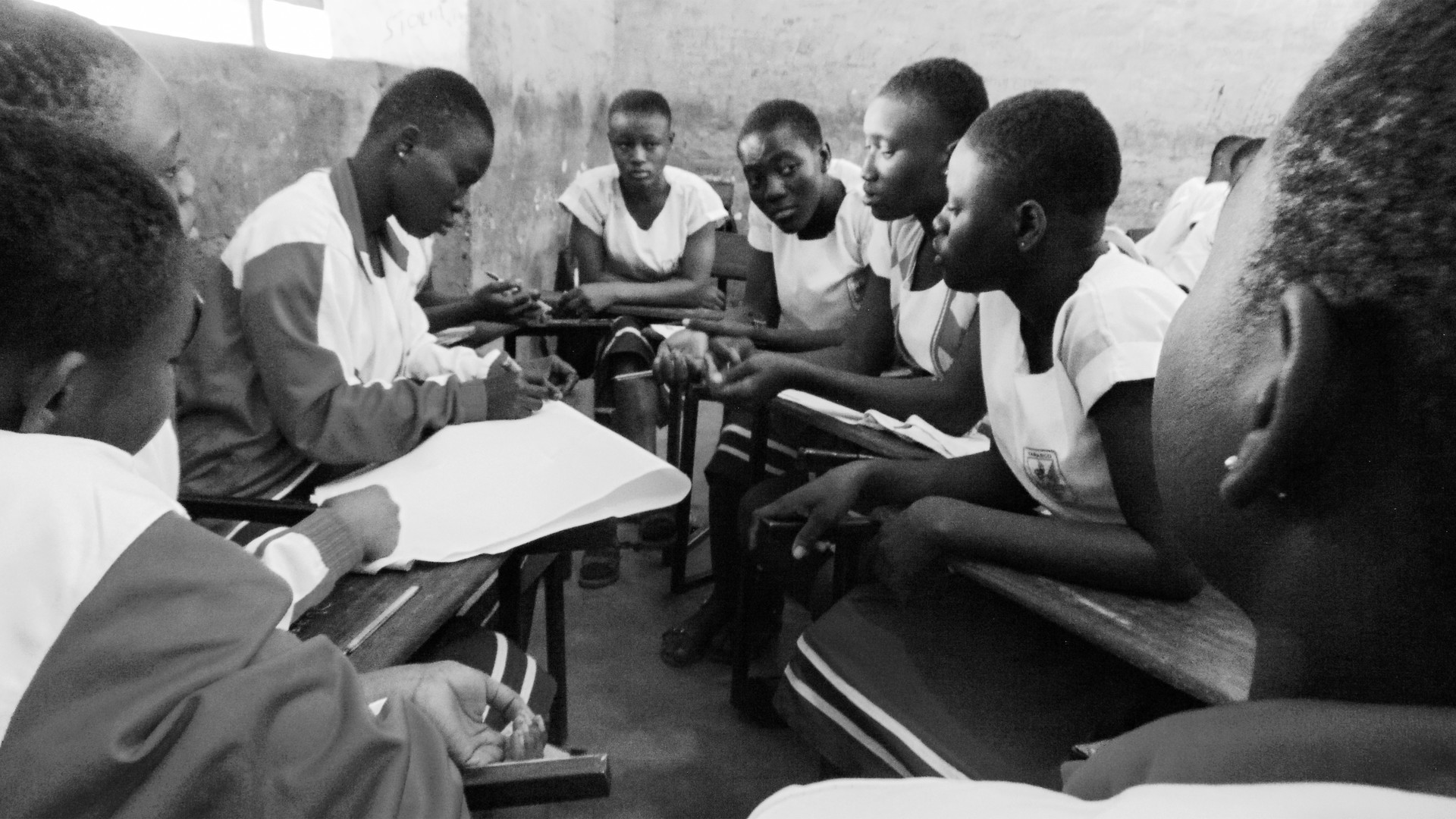
What does the year 2024 hold for us?
As the new year begins, we take a look at the trends and challenges ahead for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Most Popular This Week

Palestine

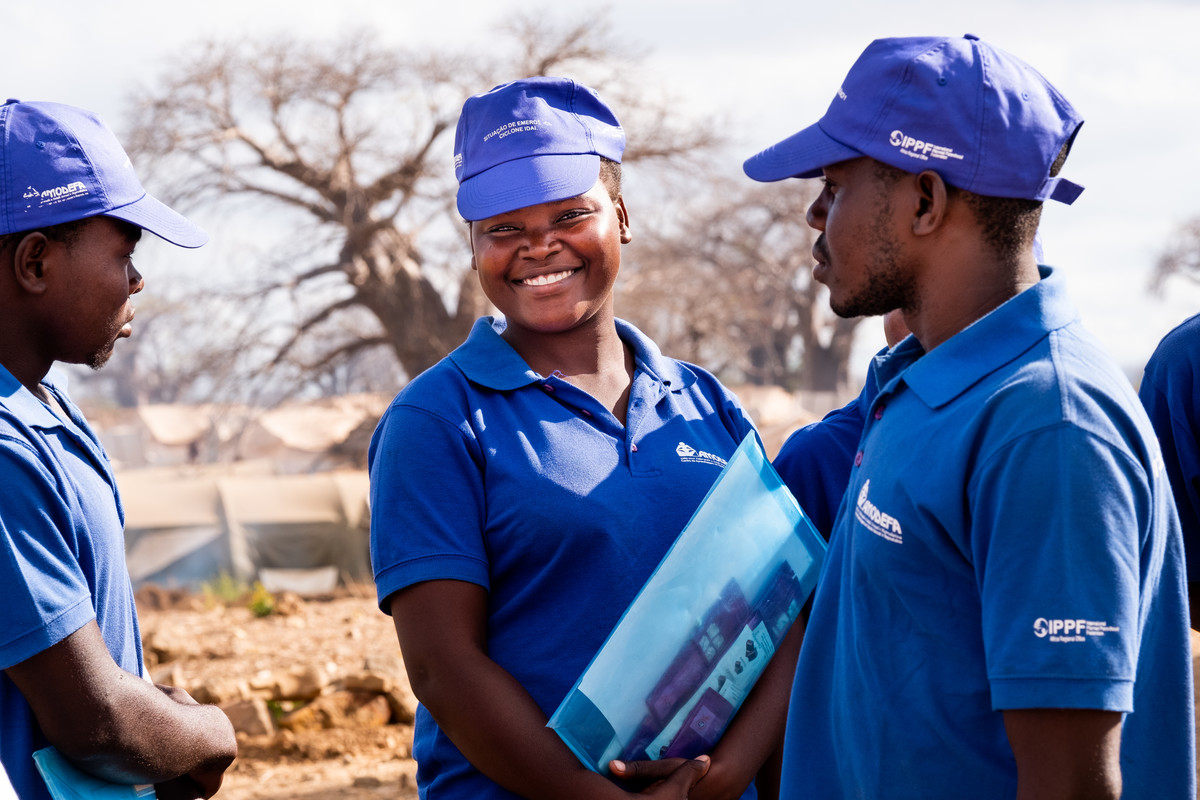
In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
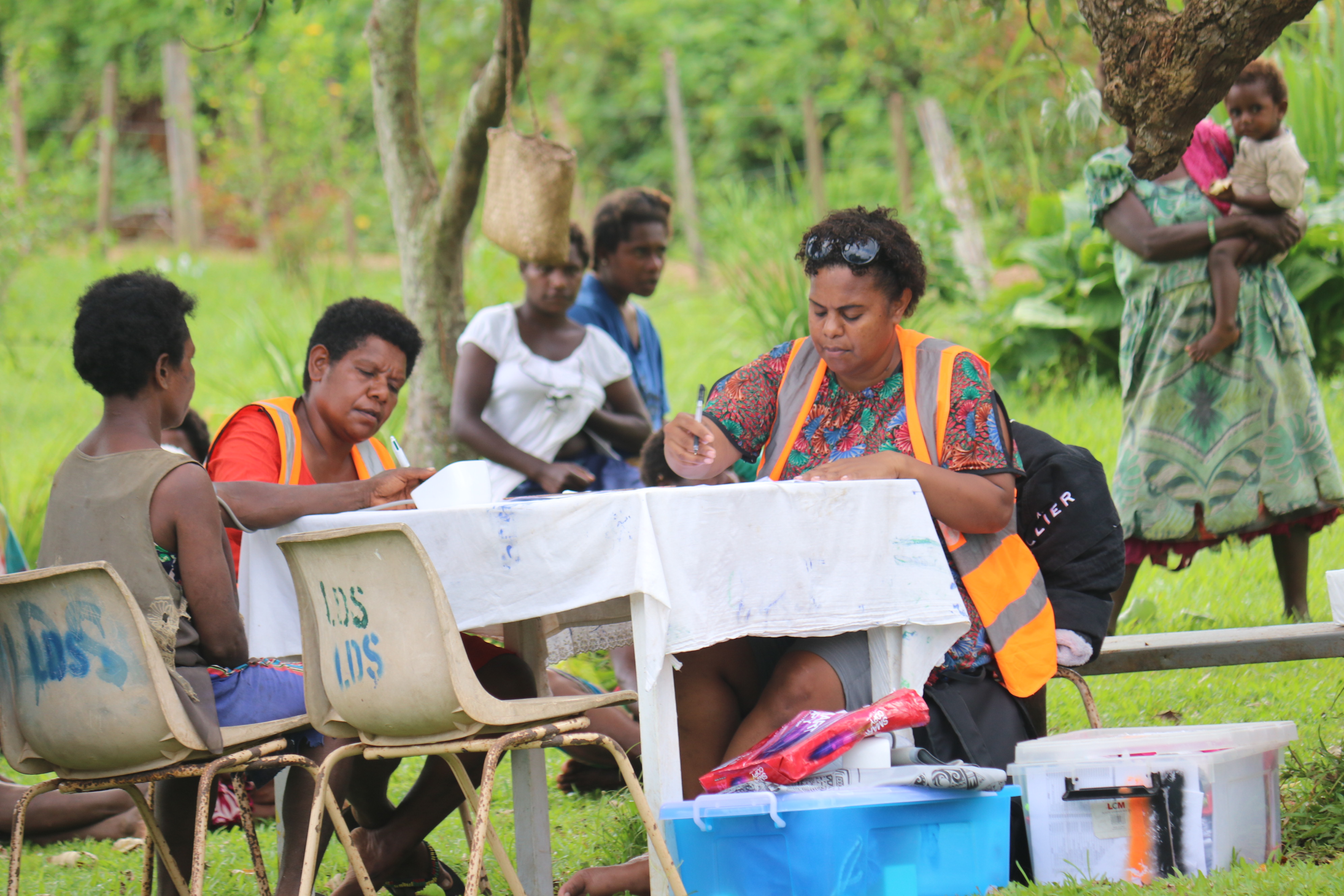

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
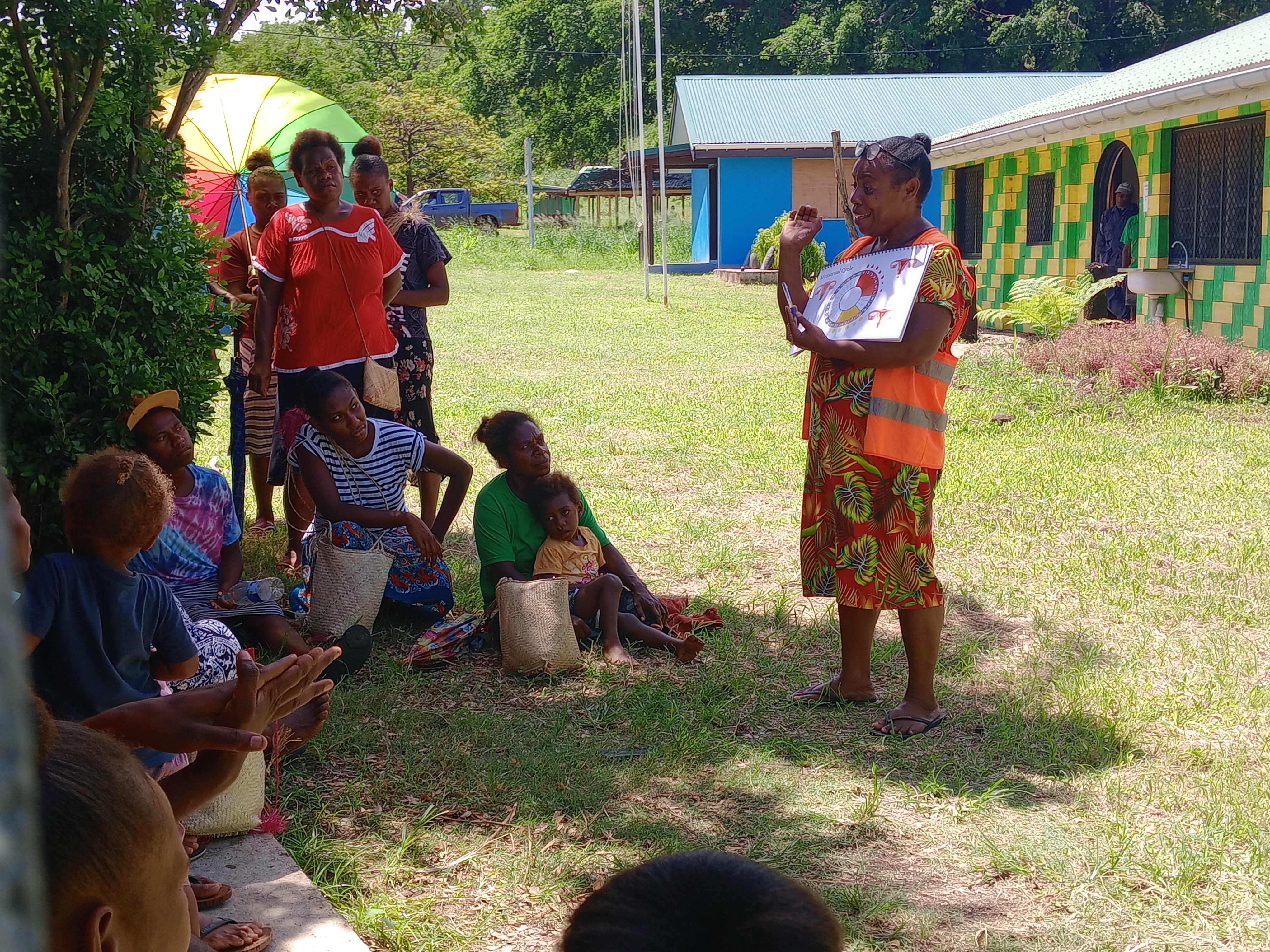

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Cook Islands

Dean and the Cook Islands Condom Car
On the island of Rarotonga, the main island of the Cook Islands in the South Pacific, a little white van makes its rounds on the palm-tree lined circular road.
Filter our stories by:
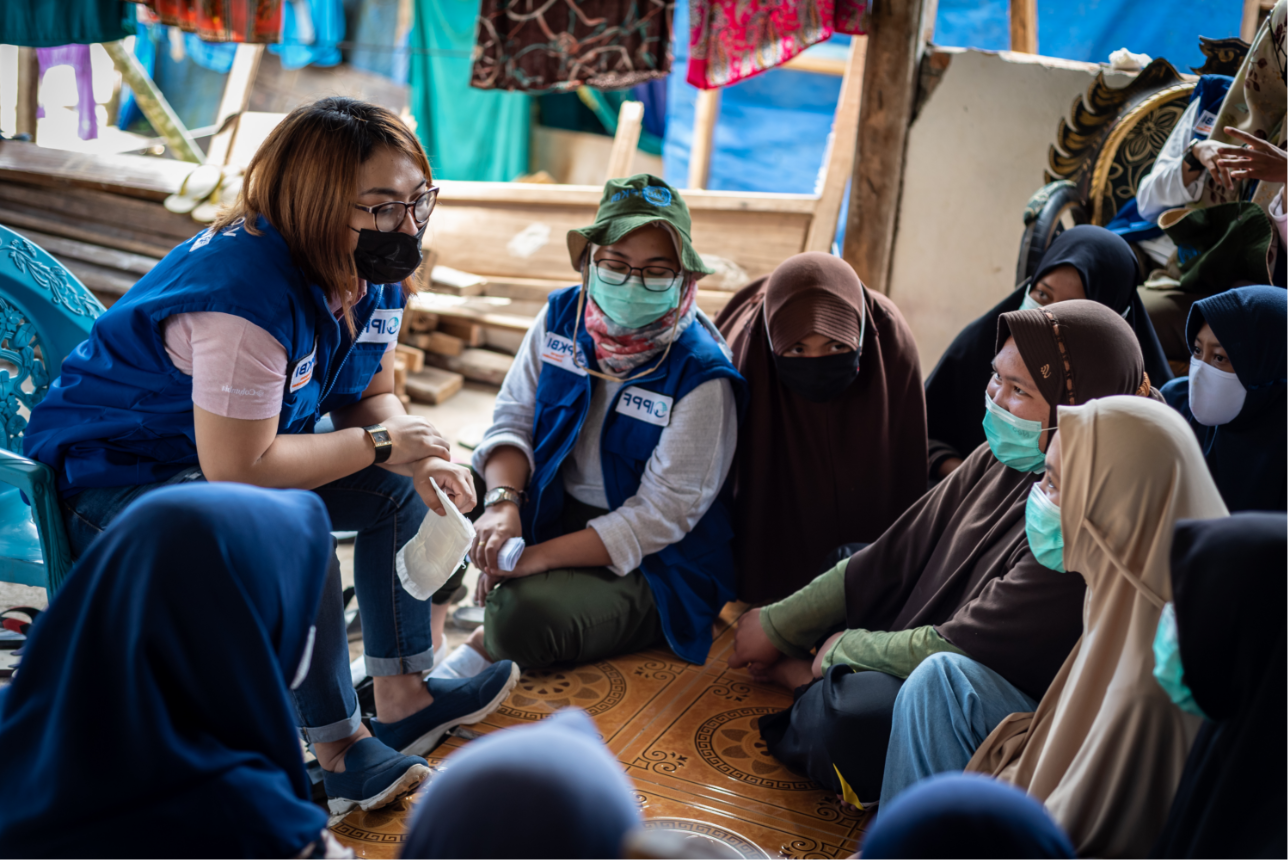


| 08 February 2018
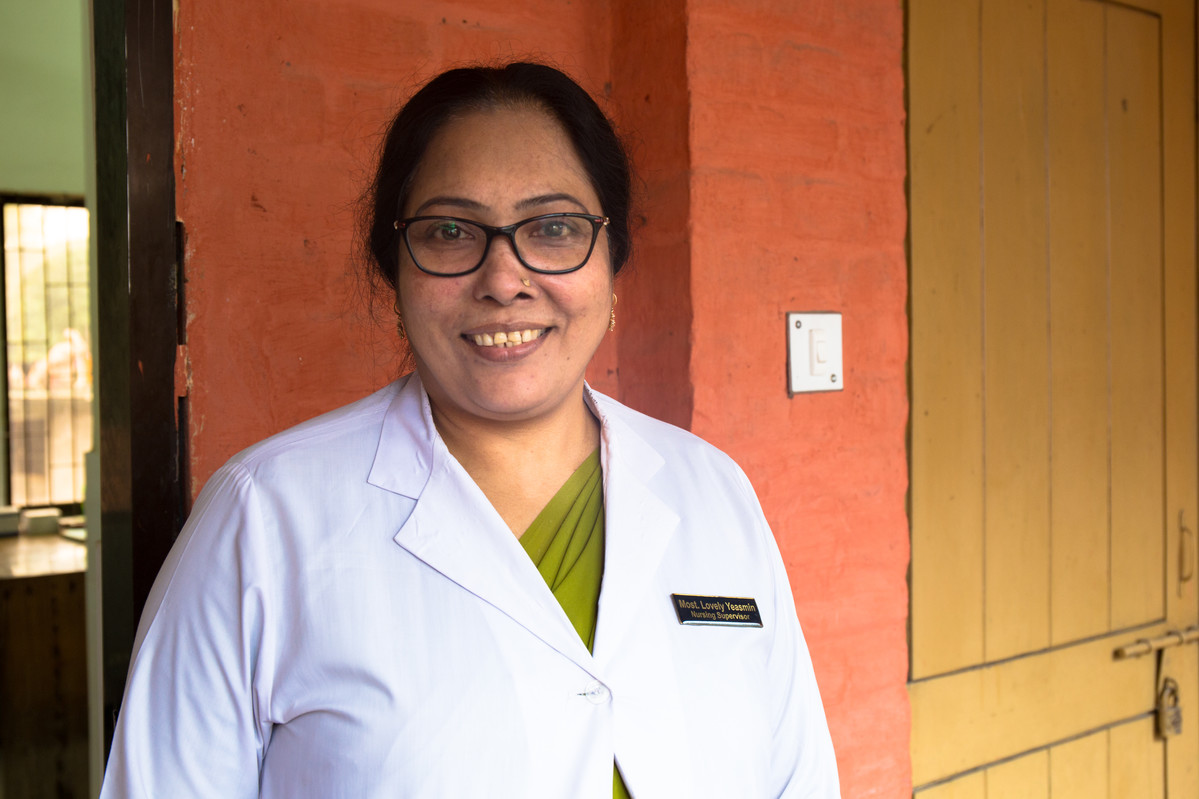
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 16 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”
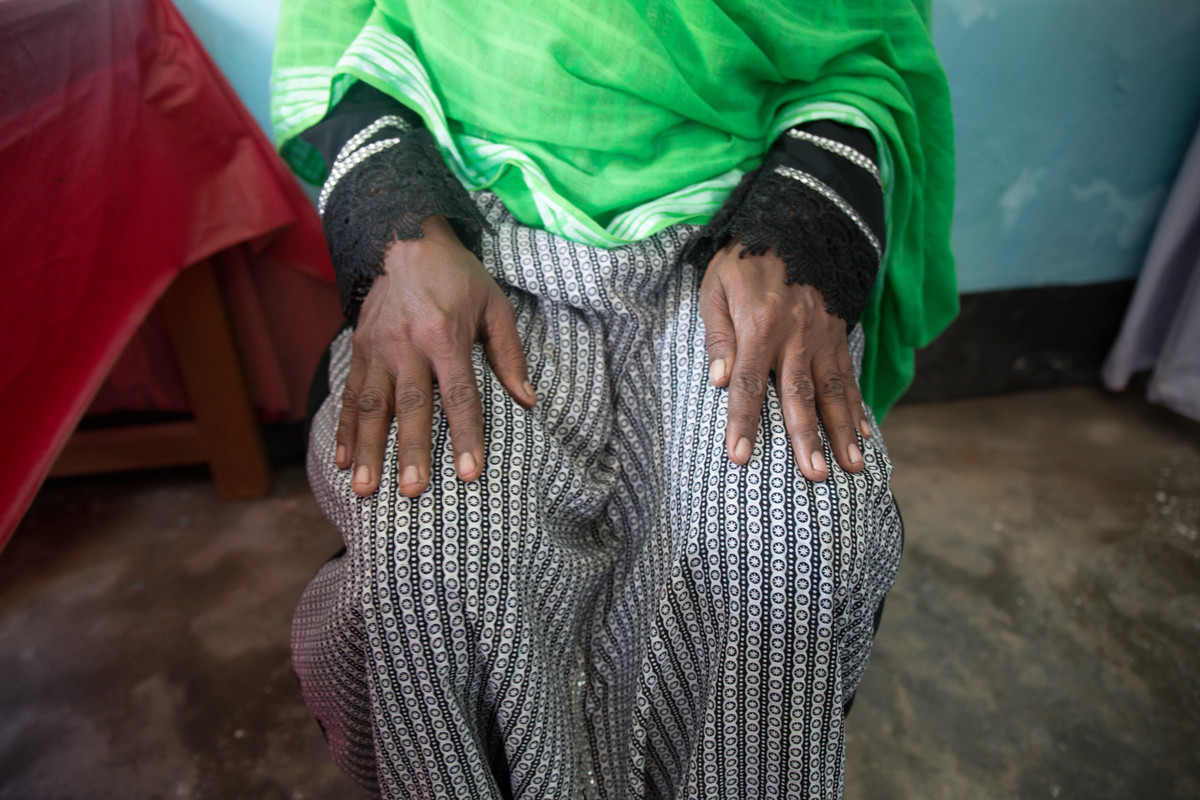
| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 16 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.
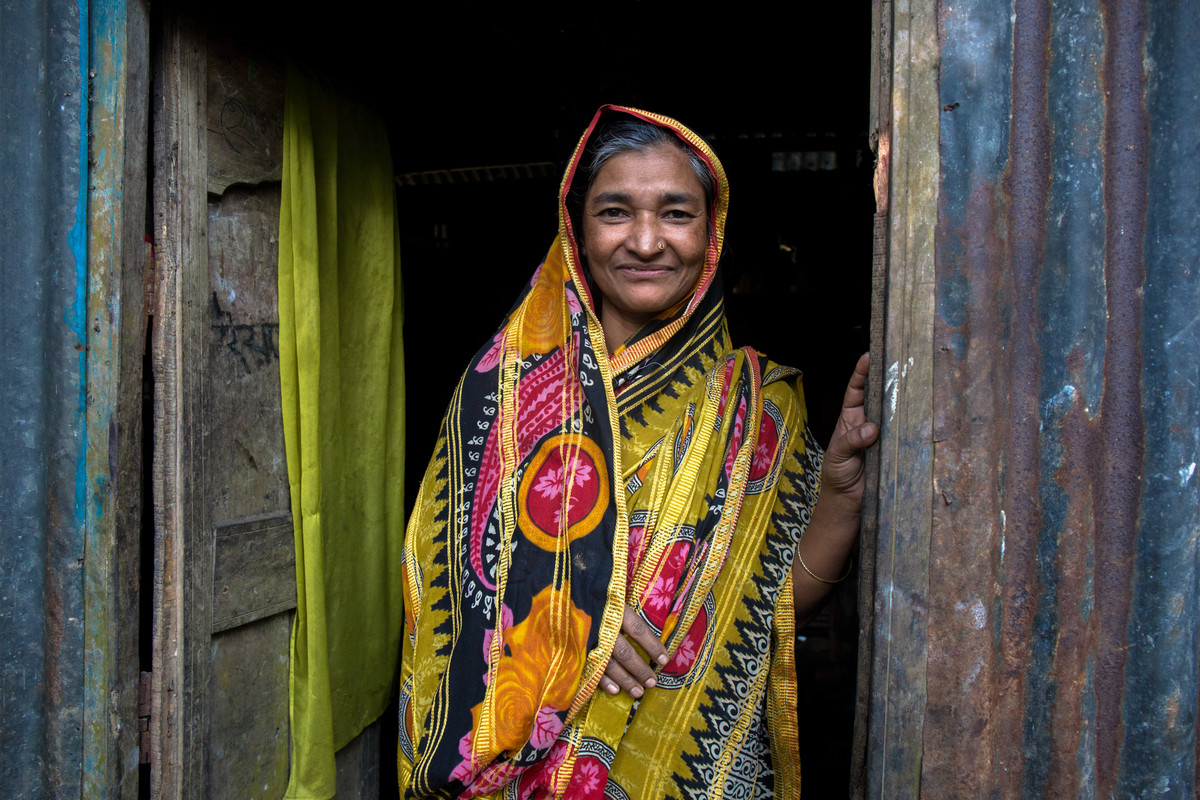

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 16 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”
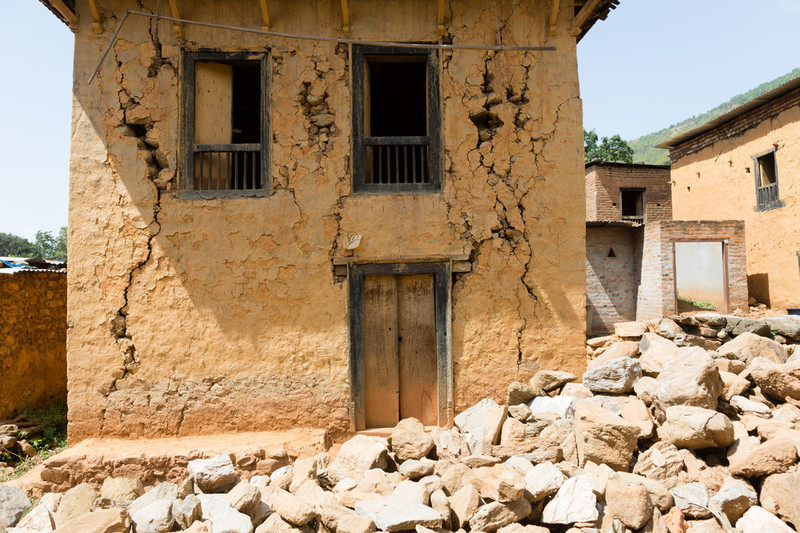

| 25 July 2017
Mobile camps provide emergency services for those unable to return home
Muna Shrestha lives with her husband and two children in Bakultar, a rambling village of mud houses, tea shacks and vegetable, miles off a main road, at the end of a long dirt track in Kavre district, a few hours west of Kathmandu. On the morning of Saturday 25 April 2015, when the earthquake struck, she and her family were cleaning the cowshed. “It was so scary,” she says. “The children were not at home: we were so worried about the children and went looking for them. They were also looking for us.” The days after the earthquake were chaotic. “The schools were closed for a month,” Muna says. “And because all our clothes and possessions were in the ruins, it was difficult to get our things.” Their children were deeply traumatised. “They became scared, and, because of this fear, they wouldn’t eat and they suffered from nausea,” Muna says. As she speaks, she gestures around the family’s old home, at the deep fissures in the mud walls. “This home is cracked by the earthquake. Our family also have another house but that was completely destroyed.” Like many families across Nepal, the Shresthas have been unable to afford to rebuild and make their old home structurally safe. It is a story now ubiquitous across Nepal: a family losing their house and possessions, scarred by trauma, and unable to return home.

| 16 April 2024
Mobile camps provide emergency services for those unable to return home
Muna Shrestha lives with her husband and two children in Bakultar, a rambling village of mud houses, tea shacks and vegetable, miles off a main road, at the end of a long dirt track in Kavre district, a few hours west of Kathmandu. On the morning of Saturday 25 April 2015, when the earthquake struck, she and her family were cleaning the cowshed. “It was so scary,” she says. “The children were not at home: we were so worried about the children and went looking for them. They were also looking for us.” The days after the earthquake were chaotic. “The schools were closed for a month,” Muna says. “And because all our clothes and possessions were in the ruins, it was difficult to get our things.” Their children were deeply traumatised. “They became scared, and, because of this fear, they wouldn’t eat and they suffered from nausea,” Muna says. As she speaks, she gestures around the family’s old home, at the deep fissures in the mud walls. “This home is cracked by the earthquake. Our family also have another house but that was completely destroyed.” Like many families across Nepal, the Shresthas have been unable to afford to rebuild and make their old home structurally safe. It is a story now ubiquitous across Nepal: a family losing their house and possessions, scarred by trauma, and unable to return home.
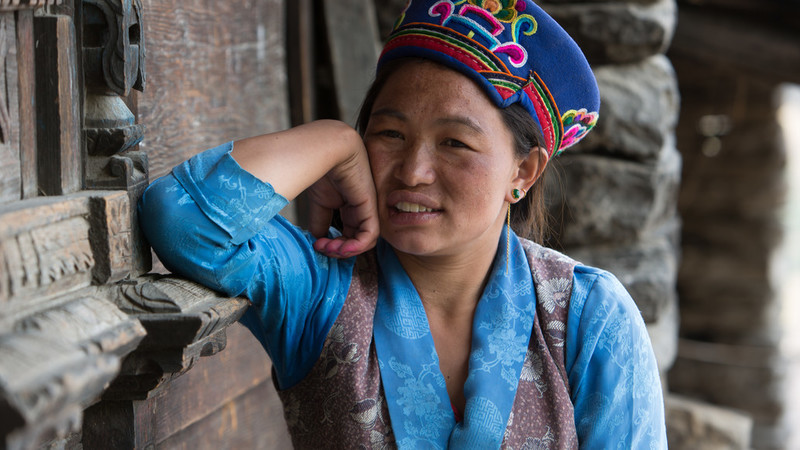

| 25 July 2017
Female volunteers take the lead to deliver life critical health advice after the earthquake
“After the earthquake, there were so many problems. So many homes were destroyed. People are still living in temporary homes because they’re unable to rebuild their homes.” Pasang Tamang lives in Gatlang, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, 15 kilometres from the Tibetan border. It is a sublimely beautiful village of traditional three-storied houses and Buddhist shrines resting on the slopes of a mountain and thronged by lush potato fields. The 2000 or so people living here are ethnic Tamang, a people of strong cultural traditions, who live across across Nepal but particularly in the lands bordering Tibet. The earthquake of 25 April had a devastating impact on Gatlang. Most of the traditional houses in the heart of the village were damaged or destroyed, and people were forced to move into small shacks of corrugated iron and plastic, where many still live. “Seven people died and three were injured and then later died,” says Pasang. These numbers might seems small compared to some casualty numbers in Nepal, but in a tightknit village like Gatlang, the impact was felt keenly. Hundreds of people were forced into tents. “People suffered badly from the cold,” Pasang says. “Some people caught pneumonia.” At 2240 metres above sea level, nighttime temperatures in Gatlang can plunge. Pregnant women fared particularly badly: “They were unable to access nutritious food or find a warm place. They really suffered.” Pasang herself was badly injured. “During the earthquake, I was asleep in the house because I was ill,” she says. “When I felt the earthquake, I ran out of the house and while I was running I got injured, and my mouth was damaged.” Help was at hand . “After the earthquake, there were so many organisations that came to help, including FPAN,” Pasang says. As well as setting up health camps and providing a range of health care, “they provided family planning devices to people who were in need.” Hundreds of families still live in the corrugated iron and plastic sheds that were erected as a replacement for tents. The government has been slow to distribute funds, and the villagers say that any money they have received falls far short of the cost of rebuilding their old stone homes. Pasang’s house stands empty. “We will not be able to return home because the house is cracked and if there was another earthquake, it would be completely destroyed,” she says. Since the earthquake, she has begun working as a volunteer for FPAN. Her role involves travelling around villages in the area, raising awareness about different contraceptive methods and family planning. Volunteers like Pasang perform a crucial function in a region where literacy levels and a strongly patriarchal culture mean that women marry young and have to get consent from their husbands before using contraception. In this remote community, direct contact with a volunteer who can offer advice and guidance orally, and talk to women about their broader health needs, is absolutely vital.

| 16 April 2024
Female volunteers take the lead to deliver life critical health advice after the earthquake
“After the earthquake, there were so many problems. So many homes were destroyed. People are still living in temporary homes because they’re unable to rebuild their homes.” Pasang Tamang lives in Gatlang, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, 15 kilometres from the Tibetan border. It is a sublimely beautiful village of traditional three-storied houses and Buddhist shrines resting on the slopes of a mountain and thronged by lush potato fields. The 2000 or so people living here are ethnic Tamang, a people of strong cultural traditions, who live across across Nepal but particularly in the lands bordering Tibet. The earthquake of 25 April had a devastating impact on Gatlang. Most of the traditional houses in the heart of the village were damaged or destroyed, and people were forced to move into small shacks of corrugated iron and plastic, where many still live. “Seven people died and three were injured and then later died,” says Pasang. These numbers might seems small compared to some casualty numbers in Nepal, but in a tightknit village like Gatlang, the impact was felt keenly. Hundreds of people were forced into tents. “People suffered badly from the cold,” Pasang says. “Some people caught pneumonia.” At 2240 metres above sea level, nighttime temperatures in Gatlang can plunge. Pregnant women fared particularly badly: “They were unable to access nutritious food or find a warm place. They really suffered.” Pasang herself was badly injured. “During the earthquake, I was asleep in the house because I was ill,” she says. “When I felt the earthquake, I ran out of the house and while I was running I got injured, and my mouth was damaged.” Help was at hand . “After the earthquake, there were so many organisations that came to help, including FPAN,” Pasang says. As well as setting up health camps and providing a range of health care, “they provided family planning devices to people who were in need.” Hundreds of families still live in the corrugated iron and plastic sheds that were erected as a replacement for tents. The government has been slow to distribute funds, and the villagers say that any money they have received falls far short of the cost of rebuilding their old stone homes. Pasang’s house stands empty. “We will not be able to return home because the house is cracked and if there was another earthquake, it would be completely destroyed,” she says. Since the earthquake, she has begun working as a volunteer for FPAN. Her role involves travelling around villages in the area, raising awareness about different contraceptive methods and family planning. Volunteers like Pasang perform a crucial function in a region where literacy levels and a strongly patriarchal culture mean that women marry young and have to get consent from their husbands before using contraception. In this remote community, direct contact with a volunteer who can offer advice and guidance orally, and talk to women about their broader health needs, is absolutely vital.
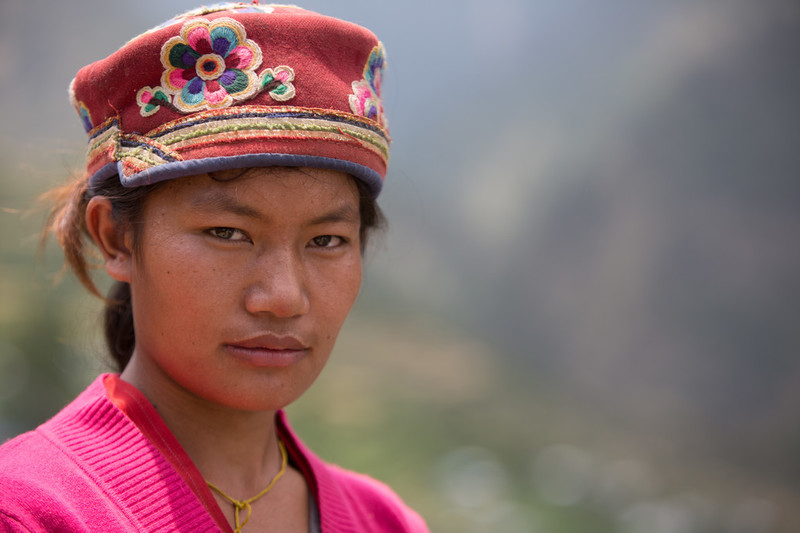

| 25 July 2017
Reproductive health for Nepalese female farmers after the earthquake
Two years after the earthquake that struck Nepal in April 2015, the village of Gatlang in the country’s mountainous north still lies in partial ruin. The houses here are built from enormous slabs of local stone, carved windows and doors, and roofs of stacked wooden planks. They face east towards the rising sun, their facades bedecked in intricate wooden carvings patterns linked to the ancient Buddhist culture of the Tamang people. Today, most of these houses lie in ruin, emptying the heart of the village of people, with most moving to temporary shacks on Gatlang’s fringes. Kopila Tamang is a 24-year-old farmer and mother to two young boys. Her husband, Nakul, works as a lorry driver and is often away. “When the earthquake struck, I was working in the fields,” she says. “If I had been at home, I would have died.” Kopila’s house – or what remains of it – lies at the centre of old Gatlang, on a street of traditional houses that have either entirely collapsed or are uninhabitable due to cracks and structural damage. Piles of stone and wooden cross beams are strewn in what was once a thriving village street. Like many families here, Kopila and her husband and boys have moved into a small shack built from corrugated iron and plastic. This was meant to be a temporary solution, but two years later, they are still living in it, unable to afford the enormous cost of rebuilding their old home. “It needs lots of money,” she says. “I don’t know when we will have the money to build this home again.” FPAN provided emergency health support to families like Kopila’s in the weeks and months after the earthquake. Mobile health camps offered medicines, health check ups, dignity kits, family planning, antenatal checks and other vital services. These days, Kopila gets regular advice from Pasang Tamang, the FPAN reproductive health female volunteer in the village. Kopila had suffered after the birth of her last child. “I didn’t menstruate for eight months, and then after that I started using the [contraceptive] injection,” she says. “But there were some side effects: I started menstruating twice a month.” She then went to a mobile health camp run by FPAN and started using the intrauterine coil. “After that, my menstruation went back to normal,” she says. In a village scarred by the earthquake, access to family planning has brought some much needed stability and relief to Kopila and her small family. “FPAN provide different services and knowledge: I have come to know that having more children can bring suffering, because it’s not enough to just feed children, they must be educated too” she says. “A small family is a happy family.”

| 16 April 2024
Reproductive health for Nepalese female farmers after the earthquake
Two years after the earthquake that struck Nepal in April 2015, the village of Gatlang in the country’s mountainous north still lies in partial ruin. The houses here are built from enormous slabs of local stone, carved windows and doors, and roofs of stacked wooden planks. They face east towards the rising sun, their facades bedecked in intricate wooden carvings patterns linked to the ancient Buddhist culture of the Tamang people. Today, most of these houses lie in ruin, emptying the heart of the village of people, with most moving to temporary shacks on Gatlang’s fringes. Kopila Tamang is a 24-year-old farmer and mother to two young boys. Her husband, Nakul, works as a lorry driver and is often away. “When the earthquake struck, I was working in the fields,” she says. “If I had been at home, I would have died.” Kopila’s house – or what remains of it – lies at the centre of old Gatlang, on a street of traditional houses that have either entirely collapsed or are uninhabitable due to cracks and structural damage. Piles of stone and wooden cross beams are strewn in what was once a thriving village street. Like many families here, Kopila and her husband and boys have moved into a small shack built from corrugated iron and plastic. This was meant to be a temporary solution, but two years later, they are still living in it, unable to afford the enormous cost of rebuilding their old home. “It needs lots of money,” she says. “I don’t know when we will have the money to build this home again.” FPAN provided emergency health support to families like Kopila’s in the weeks and months after the earthquake. Mobile health camps offered medicines, health check ups, dignity kits, family planning, antenatal checks and other vital services. These days, Kopila gets regular advice from Pasang Tamang, the FPAN reproductive health female volunteer in the village. Kopila had suffered after the birth of her last child. “I didn’t menstruate for eight months, and then after that I started using the [contraceptive] injection,” she says. “But there were some side effects: I started menstruating twice a month.” She then went to a mobile health camp run by FPAN and started using the intrauterine coil. “After that, my menstruation went back to normal,” she says. In a village scarred by the earthquake, access to family planning has brought some much needed stability and relief to Kopila and her small family. “FPAN provide different services and knowledge: I have come to know that having more children can bring suffering, because it’s not enough to just feed children, they must be educated too” she says. “A small family is a happy family.”

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 16 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 16 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 16 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 25 July 2017
Mobile camps provide emergency services for those unable to return home
Muna Shrestha lives with her husband and two children in Bakultar, a rambling village of mud houses, tea shacks and vegetable, miles off a main road, at the end of a long dirt track in Kavre district, a few hours west of Kathmandu. On the morning of Saturday 25 April 2015, when the earthquake struck, she and her family were cleaning the cowshed. “It was so scary,” she says. “The children were not at home: we were so worried about the children and went looking for them. They were also looking for us.” The days after the earthquake were chaotic. “The schools were closed for a month,” Muna says. “And because all our clothes and possessions were in the ruins, it was difficult to get our things.” Their children were deeply traumatised. “They became scared, and, because of this fear, they wouldn’t eat and they suffered from nausea,” Muna says. As she speaks, she gestures around the family’s old home, at the deep fissures in the mud walls. “This home is cracked by the earthquake. Our family also have another house but that was completely destroyed.” Like many families across Nepal, the Shresthas have been unable to afford to rebuild and make their old home structurally safe. It is a story now ubiquitous across Nepal: a family losing their house and possessions, scarred by trauma, and unable to return home.

| 16 April 2024
Mobile camps provide emergency services for those unable to return home
Muna Shrestha lives with her husband and two children in Bakultar, a rambling village of mud houses, tea shacks and vegetable, miles off a main road, at the end of a long dirt track in Kavre district, a few hours west of Kathmandu. On the morning of Saturday 25 April 2015, when the earthquake struck, she and her family were cleaning the cowshed. “It was so scary,” she says. “The children were not at home: we were so worried about the children and went looking for them. They were also looking for us.” The days after the earthquake were chaotic. “The schools were closed for a month,” Muna says. “And because all our clothes and possessions were in the ruins, it was difficult to get our things.” Their children were deeply traumatised. “They became scared, and, because of this fear, they wouldn’t eat and they suffered from nausea,” Muna says. As she speaks, she gestures around the family’s old home, at the deep fissures in the mud walls. “This home is cracked by the earthquake. Our family also have another house but that was completely destroyed.” Like many families across Nepal, the Shresthas have been unable to afford to rebuild and make their old home structurally safe. It is a story now ubiquitous across Nepal: a family losing their house and possessions, scarred by trauma, and unable to return home.

| 25 July 2017
Female volunteers take the lead to deliver life critical health advice after the earthquake
“After the earthquake, there were so many problems. So many homes were destroyed. People are still living in temporary homes because they’re unable to rebuild their homes.” Pasang Tamang lives in Gatlang, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, 15 kilometres from the Tibetan border. It is a sublimely beautiful village of traditional three-storied houses and Buddhist shrines resting on the slopes of a mountain and thronged by lush potato fields. The 2000 or so people living here are ethnic Tamang, a people of strong cultural traditions, who live across across Nepal but particularly in the lands bordering Tibet. The earthquake of 25 April had a devastating impact on Gatlang. Most of the traditional houses in the heart of the village were damaged or destroyed, and people were forced to move into small shacks of corrugated iron and plastic, where many still live. “Seven people died and three were injured and then later died,” says Pasang. These numbers might seems small compared to some casualty numbers in Nepal, but in a tightknit village like Gatlang, the impact was felt keenly. Hundreds of people were forced into tents. “People suffered badly from the cold,” Pasang says. “Some people caught pneumonia.” At 2240 metres above sea level, nighttime temperatures in Gatlang can plunge. Pregnant women fared particularly badly: “They were unable to access nutritious food or find a warm place. They really suffered.” Pasang herself was badly injured. “During the earthquake, I was asleep in the house because I was ill,” she says. “When I felt the earthquake, I ran out of the house and while I was running I got injured, and my mouth was damaged.” Help was at hand . “After the earthquake, there were so many organisations that came to help, including FPAN,” Pasang says. As well as setting up health camps and providing a range of health care, “they provided family planning devices to people who were in need.” Hundreds of families still live in the corrugated iron and plastic sheds that were erected as a replacement for tents. The government has been slow to distribute funds, and the villagers say that any money they have received falls far short of the cost of rebuilding their old stone homes. Pasang’s house stands empty. “We will not be able to return home because the house is cracked and if there was another earthquake, it would be completely destroyed,” she says. Since the earthquake, she has begun working as a volunteer for FPAN. Her role involves travelling around villages in the area, raising awareness about different contraceptive methods and family planning. Volunteers like Pasang perform a crucial function in a region where literacy levels and a strongly patriarchal culture mean that women marry young and have to get consent from their husbands before using contraception. In this remote community, direct contact with a volunteer who can offer advice and guidance orally, and talk to women about their broader health needs, is absolutely vital.

| 16 April 2024
Female volunteers take the lead to deliver life critical health advice after the earthquake
“After the earthquake, there were so many problems. So many homes were destroyed. People are still living in temporary homes because they’re unable to rebuild their homes.” Pasang Tamang lives in Gatlang, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, 15 kilometres from the Tibetan border. It is a sublimely beautiful village of traditional three-storied houses and Buddhist shrines resting on the slopes of a mountain and thronged by lush potato fields. The 2000 or so people living here are ethnic Tamang, a people of strong cultural traditions, who live across across Nepal but particularly in the lands bordering Tibet. The earthquake of 25 April had a devastating impact on Gatlang. Most of the traditional houses in the heart of the village were damaged or destroyed, and people were forced to move into small shacks of corrugated iron and plastic, where many still live. “Seven people died and three were injured and then later died,” says Pasang. These numbers might seems small compared to some casualty numbers in Nepal, but in a tightknit village like Gatlang, the impact was felt keenly. Hundreds of people were forced into tents. “People suffered badly from the cold,” Pasang says. “Some people caught pneumonia.” At 2240 metres above sea level, nighttime temperatures in Gatlang can plunge. Pregnant women fared particularly badly: “They were unable to access nutritious food or find a warm place. They really suffered.” Pasang herself was badly injured. “During the earthquake, I was asleep in the house because I was ill,” she says. “When I felt the earthquake, I ran out of the house and while I was running I got injured, and my mouth was damaged.” Help was at hand . “After the earthquake, there were so many organisations that came to help, including FPAN,” Pasang says. As well as setting up health camps and providing a range of health care, “they provided family planning devices to people who were in need.” Hundreds of families still live in the corrugated iron and plastic sheds that were erected as a replacement for tents. The government has been slow to distribute funds, and the villagers say that any money they have received falls far short of the cost of rebuilding their old stone homes. Pasang’s house stands empty. “We will not be able to return home because the house is cracked and if there was another earthquake, it would be completely destroyed,” she says. Since the earthquake, she has begun working as a volunteer for FPAN. Her role involves travelling around villages in the area, raising awareness about different contraceptive methods and family planning. Volunteers like Pasang perform a crucial function in a region where literacy levels and a strongly patriarchal culture mean that women marry young and have to get consent from their husbands before using contraception. In this remote community, direct contact with a volunteer who can offer advice and guidance orally, and talk to women about their broader health needs, is absolutely vital.

| 25 July 2017
Reproductive health for Nepalese female farmers after the earthquake
Two years after the earthquake that struck Nepal in April 2015, the village of Gatlang in the country’s mountainous north still lies in partial ruin. The houses here are built from enormous slabs of local stone, carved windows and doors, and roofs of stacked wooden planks. They face east towards the rising sun, their facades bedecked in intricate wooden carvings patterns linked to the ancient Buddhist culture of the Tamang people. Today, most of these houses lie in ruin, emptying the heart of the village of people, with most moving to temporary shacks on Gatlang’s fringes. Kopila Tamang is a 24-year-old farmer and mother to two young boys. Her husband, Nakul, works as a lorry driver and is often away. “When the earthquake struck, I was working in the fields,” she says. “If I had been at home, I would have died.” Kopila’s house – or what remains of it – lies at the centre of old Gatlang, on a street of traditional houses that have either entirely collapsed or are uninhabitable due to cracks and structural damage. Piles of stone and wooden cross beams are strewn in what was once a thriving village street. Like many families here, Kopila and her husband and boys have moved into a small shack built from corrugated iron and plastic. This was meant to be a temporary solution, but two years later, they are still living in it, unable to afford the enormous cost of rebuilding their old home. “It needs lots of money,” she says. “I don’t know when we will have the money to build this home again.” FPAN provided emergency health support to families like Kopila’s in the weeks and months after the earthquake. Mobile health camps offered medicines, health check ups, dignity kits, family planning, antenatal checks and other vital services. These days, Kopila gets regular advice from Pasang Tamang, the FPAN reproductive health female volunteer in the village. Kopila had suffered after the birth of her last child. “I didn’t menstruate for eight months, and then after that I started using the [contraceptive] injection,” she says. “But there were some side effects: I started menstruating twice a month.” She then went to a mobile health camp run by FPAN and started using the intrauterine coil. “After that, my menstruation went back to normal,” she says. In a village scarred by the earthquake, access to family planning has brought some much needed stability and relief to Kopila and her small family. “FPAN provide different services and knowledge: I have come to know that having more children can bring suffering, because it’s not enough to just feed children, they must be educated too” she says. “A small family is a happy family.”

| 16 April 2024
Reproductive health for Nepalese female farmers after the earthquake
Two years after the earthquake that struck Nepal in April 2015, the village of Gatlang in the country’s mountainous north still lies in partial ruin. The houses here are built from enormous slabs of local stone, carved windows and doors, and roofs of stacked wooden planks. They face east towards the rising sun, their facades bedecked in intricate wooden carvings patterns linked to the ancient Buddhist culture of the Tamang people. Today, most of these houses lie in ruin, emptying the heart of the village of people, with most moving to temporary shacks on Gatlang’s fringes. Kopila Tamang is a 24-year-old farmer and mother to two young boys. Her husband, Nakul, works as a lorry driver and is often away. “When the earthquake struck, I was working in the fields,” she says. “If I had been at home, I would have died.” Kopila’s house – or what remains of it – lies at the centre of old Gatlang, on a street of traditional houses that have either entirely collapsed or are uninhabitable due to cracks and structural damage. Piles of stone and wooden cross beams are strewn in what was once a thriving village street. Like many families here, Kopila and her husband and boys have moved into a small shack built from corrugated iron and plastic. This was meant to be a temporary solution, but two years later, they are still living in it, unable to afford the enormous cost of rebuilding their old home. “It needs lots of money,” she says. “I don’t know when we will have the money to build this home again.” FPAN provided emergency health support to families like Kopila’s in the weeks and months after the earthquake. Mobile health camps offered medicines, health check ups, dignity kits, family planning, antenatal checks and other vital services. These days, Kopila gets regular advice from Pasang Tamang, the FPAN reproductive health female volunteer in the village. Kopila had suffered after the birth of her last child. “I didn’t menstruate for eight months, and then after that I started using the [contraceptive] injection,” she says. “But there were some side effects: I started menstruating twice a month.” She then went to a mobile health camp run by FPAN and started using the intrauterine coil. “After that, my menstruation went back to normal,” she says. In a village scarred by the earthquake, access to family planning has brought some much needed stability and relief to Kopila and her small family. “FPAN provide different services and knowledge: I have come to know that having more children can bring suffering, because it’s not enough to just feed children, they must be educated too” she says. “A small family is a happy family.”








