Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.
Most Popular This Week
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
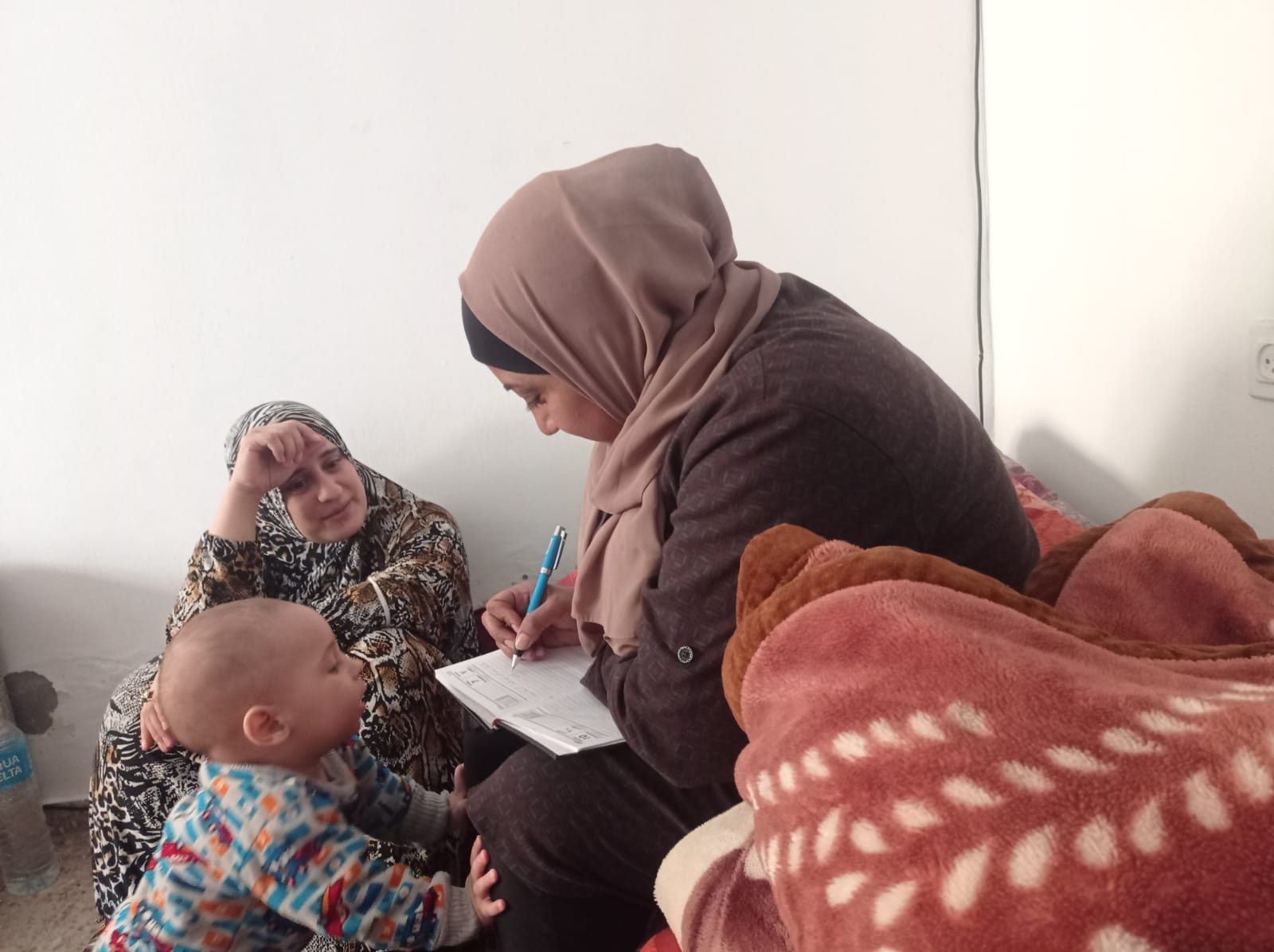

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
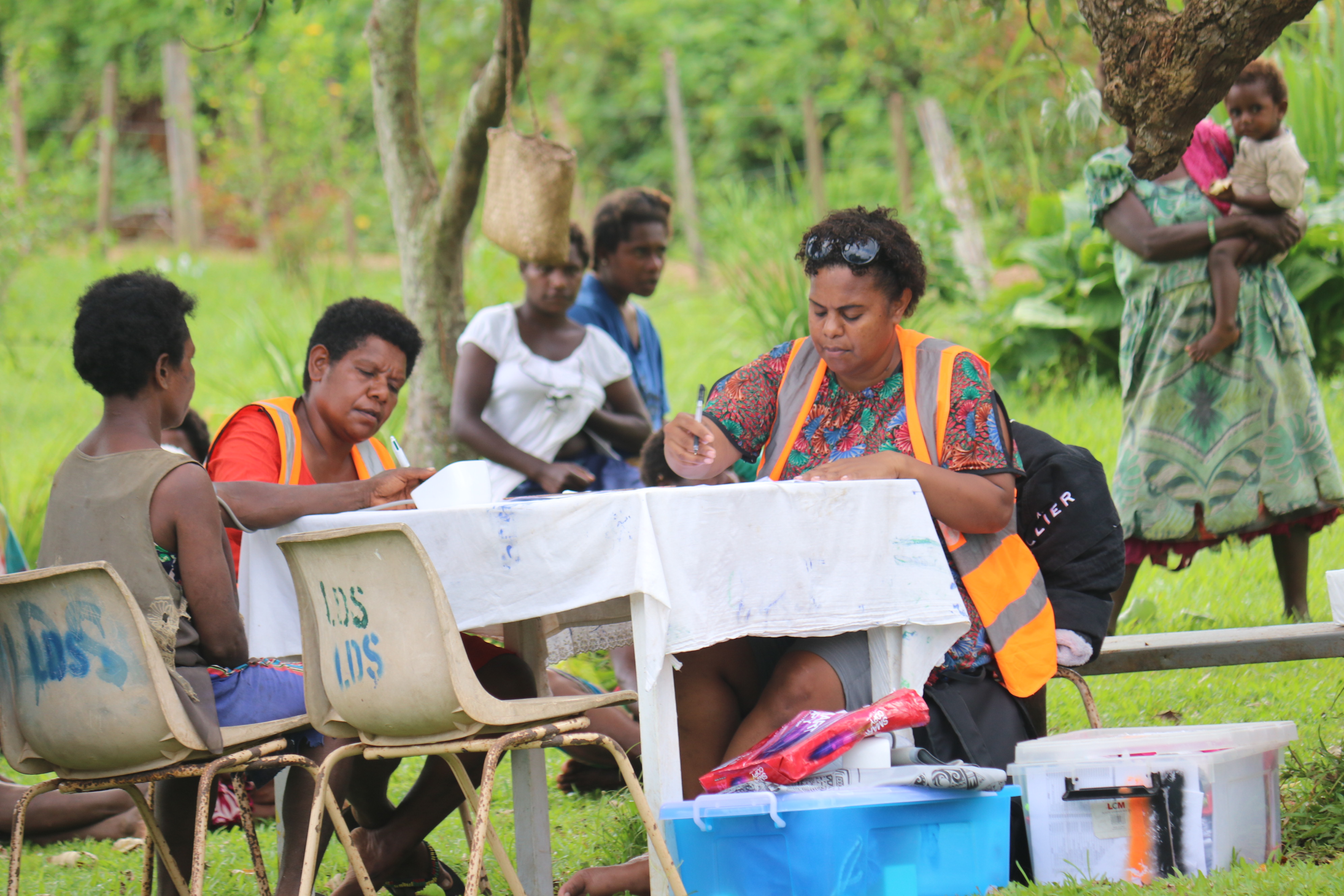

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
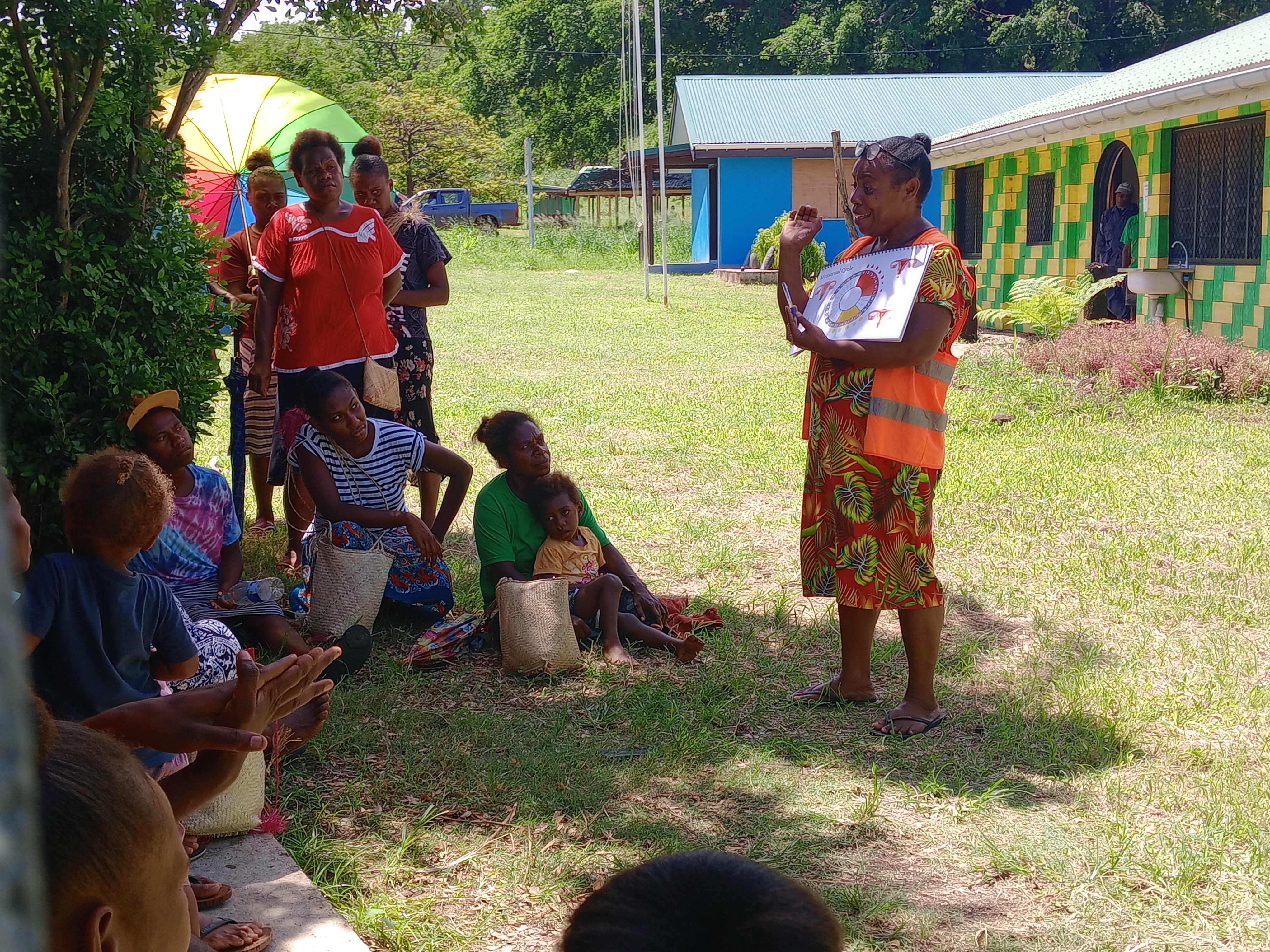

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Filter our stories by:
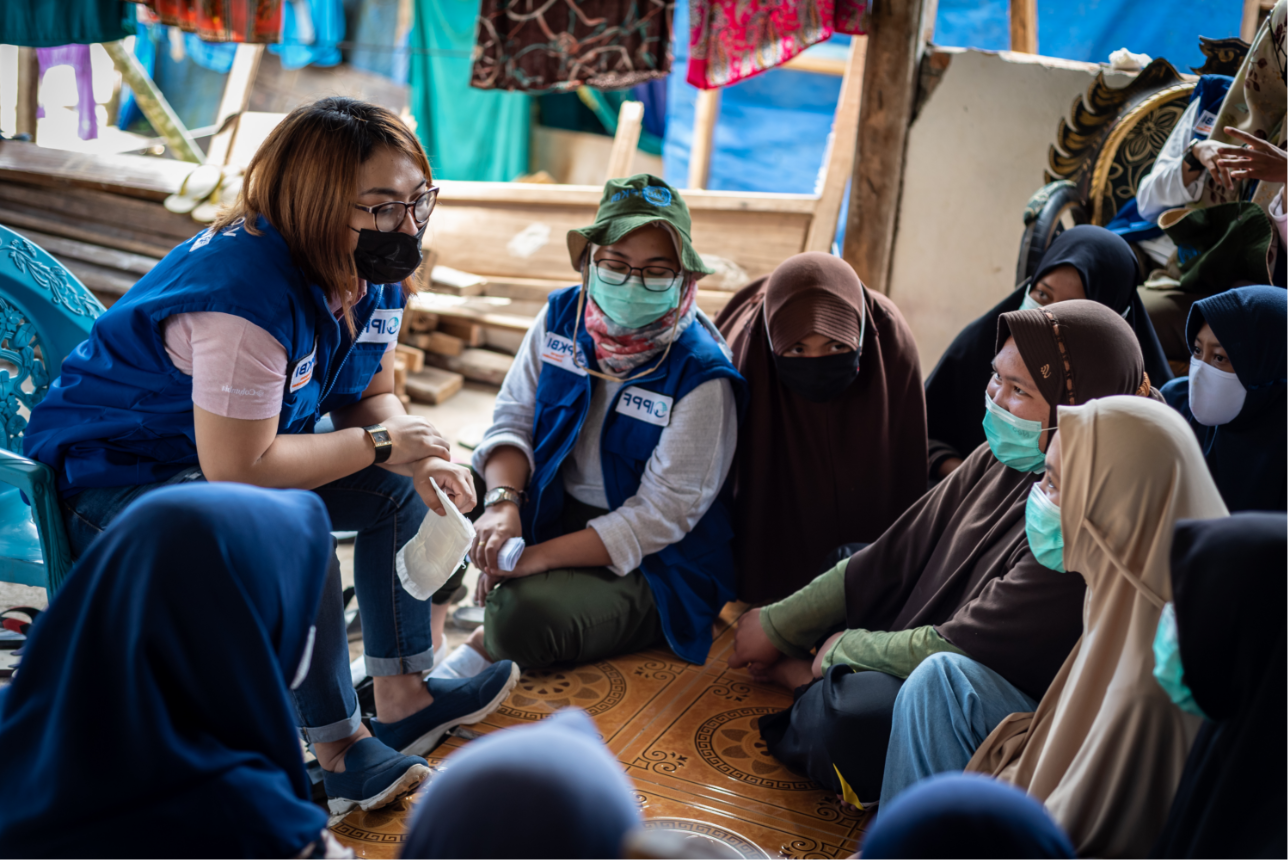


| 15 February 2019
"I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years”
In August 2017, weeks of continued and heavy rainfall across Nepal resulted in flash floods and landslides that affected 36 of the 75 districts. Many people lost their homes or were displaced. It was estimated that of those affected, 112,500 were women of reproductive age, including 8,694 pregnant women. IPPF Humanitarian, through their Member Association, The Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), activated its emergency response system early on. With funding support from the Australian Government, FPAN and IPPF Humanitarian initially mobilised their response in four of the worst affected districts (Sunsari, Saptari, Bardiya, and Dang). Mobile medical camps were established to meet the sexual and reproductive health needs of the affected population, including through the distribution of short and long acting methods of contraception, STI and HIV screening, and GBV referrals. In collaboration with the USAID-SIFPO project, services were then expanded into five more affected districts. IPPF Humanitarian spoke with 21-year old Muna in her home district of Sunsari in Nepal. “I got married at 16 years old and have two children, a four-year-old girl and two-year-old boy. In my caste, we get married early, so my parents took me to get an arranged marriage. I was in the 8th class at the time, and returned to school after I got married, but only lasted one year. My husband works in construction and had to stop working for two weeks when the floods came. When he doesn’t work, he doesn’t get paid, so it’s been very difficult. A FPAN social worker told me about the mobile medical camp today. I used to be on the three-month injectable but today I changed to the five-year implant in my arm. When my youngest child was eight months old I found out I was pregnant again. I decided to discontinue that pregnancy, so I took the five small tablets given to me by my neighbourhood doctor. I was two months pregnant at the time. From this, I had two days bleeding and cramp like pain, and then weakness. I decided to abort that pregnancy because my youngest will still only eight months old, and I didn’t want any more children. If I had more than two children, it would be very difficult to feed and educate them, and would badly affect my body too. I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years.” Want to know more about safe abortion access? Join IPPF'S I Decide movement

| 20 April 2024
"I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years”
In August 2017, weeks of continued and heavy rainfall across Nepal resulted in flash floods and landslides that affected 36 of the 75 districts. Many people lost their homes or were displaced. It was estimated that of those affected, 112,500 were women of reproductive age, including 8,694 pregnant women. IPPF Humanitarian, through their Member Association, The Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), activated its emergency response system early on. With funding support from the Australian Government, FPAN and IPPF Humanitarian initially mobilised their response in four of the worst affected districts (Sunsari, Saptari, Bardiya, and Dang). Mobile medical camps were established to meet the sexual and reproductive health needs of the affected population, including through the distribution of short and long acting methods of contraception, STI and HIV screening, and GBV referrals. In collaboration with the USAID-SIFPO project, services were then expanded into five more affected districts. IPPF Humanitarian spoke with 21-year old Muna in her home district of Sunsari in Nepal. “I got married at 16 years old and have two children, a four-year-old girl and two-year-old boy. In my caste, we get married early, so my parents took me to get an arranged marriage. I was in the 8th class at the time, and returned to school after I got married, but only lasted one year. My husband works in construction and had to stop working for two weeks when the floods came. When he doesn’t work, he doesn’t get paid, so it’s been very difficult. A FPAN social worker told me about the mobile medical camp today. I used to be on the three-month injectable but today I changed to the five-year implant in my arm. When my youngest child was eight months old I found out I was pregnant again. I decided to discontinue that pregnancy, so I took the five small tablets given to me by my neighbourhood doctor. I was two months pregnant at the time. From this, I had two days bleeding and cramp like pain, and then weakness. I decided to abort that pregnancy because my youngest will still only eight months old, and I didn’t want any more children. If I had more than two children, it would be very difficult to feed and educate them, and would badly affect my body too. I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years.” Want to know more about safe abortion access? Join IPPF'S I Decide movement
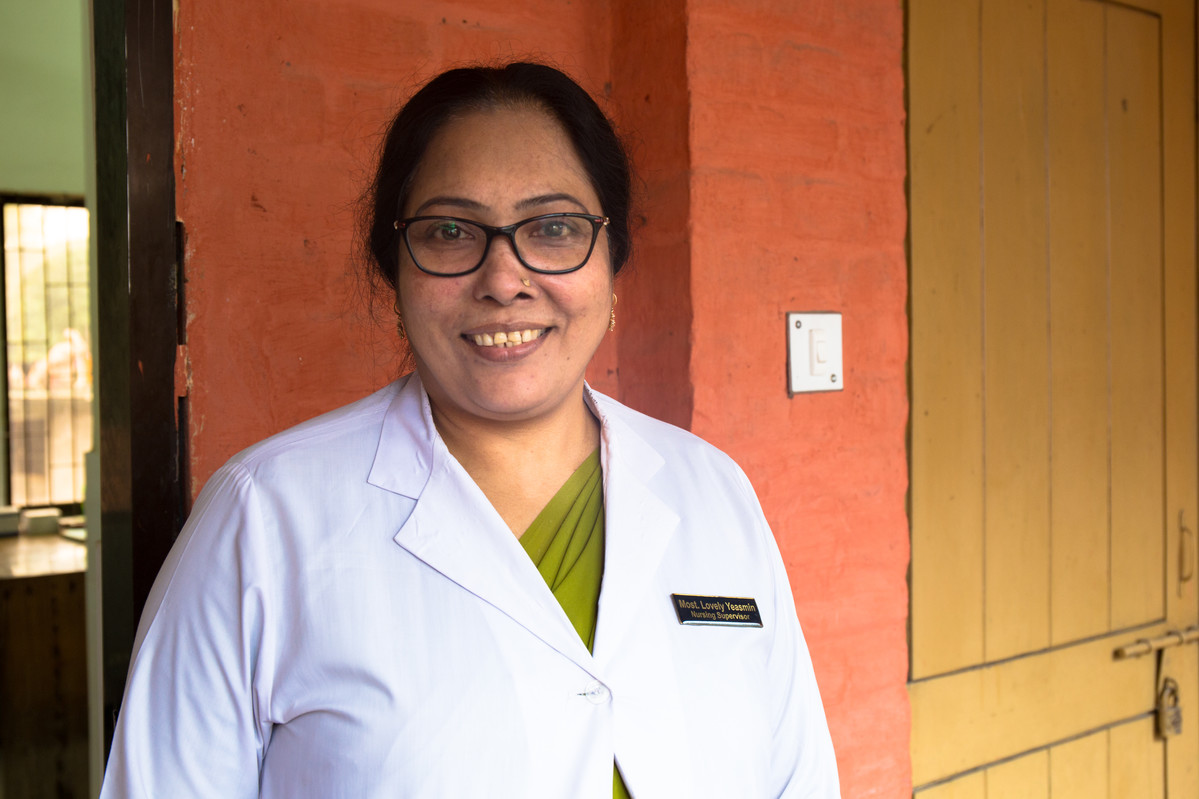

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 20 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”
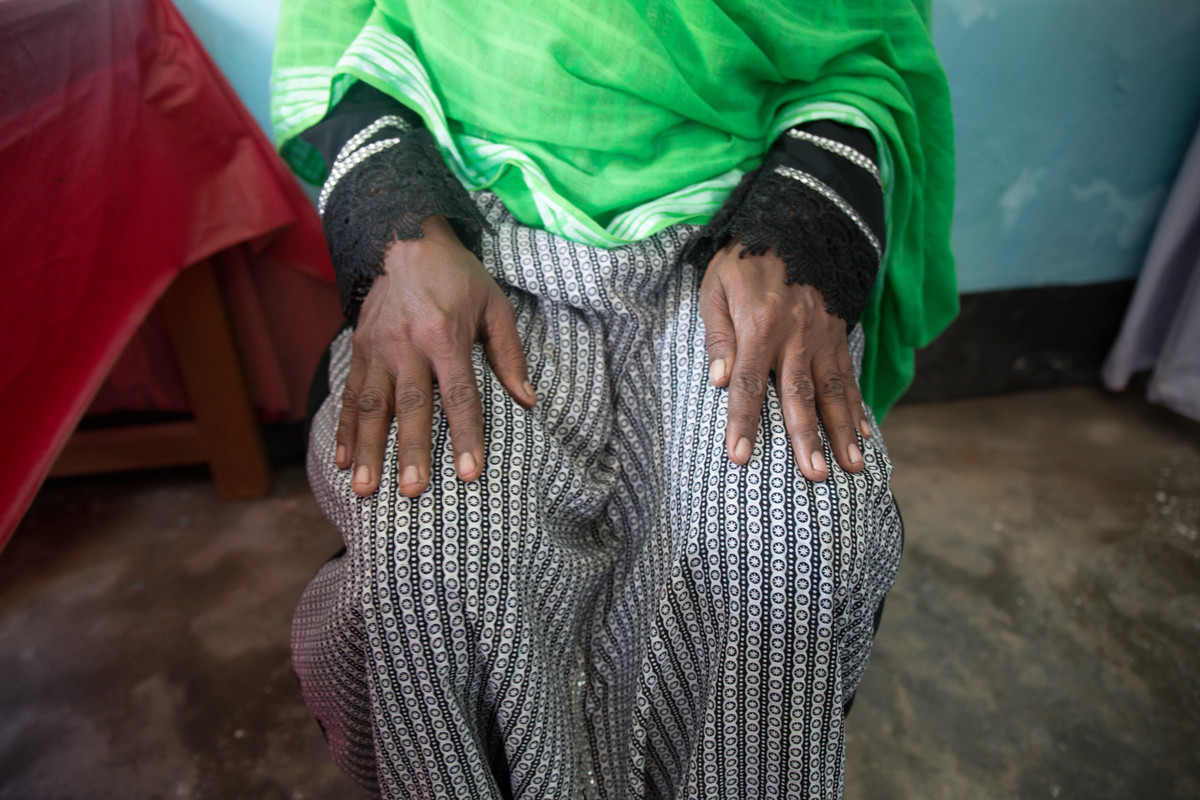
| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 20 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.
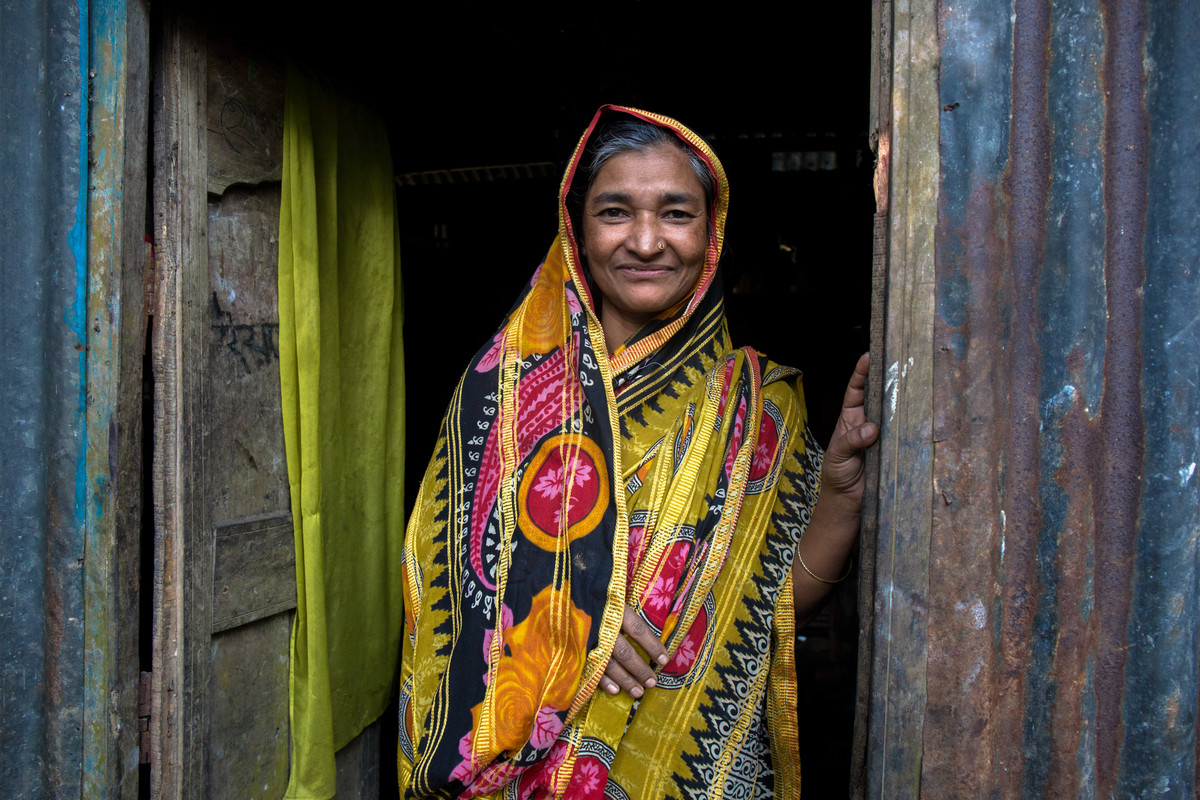

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 20 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”
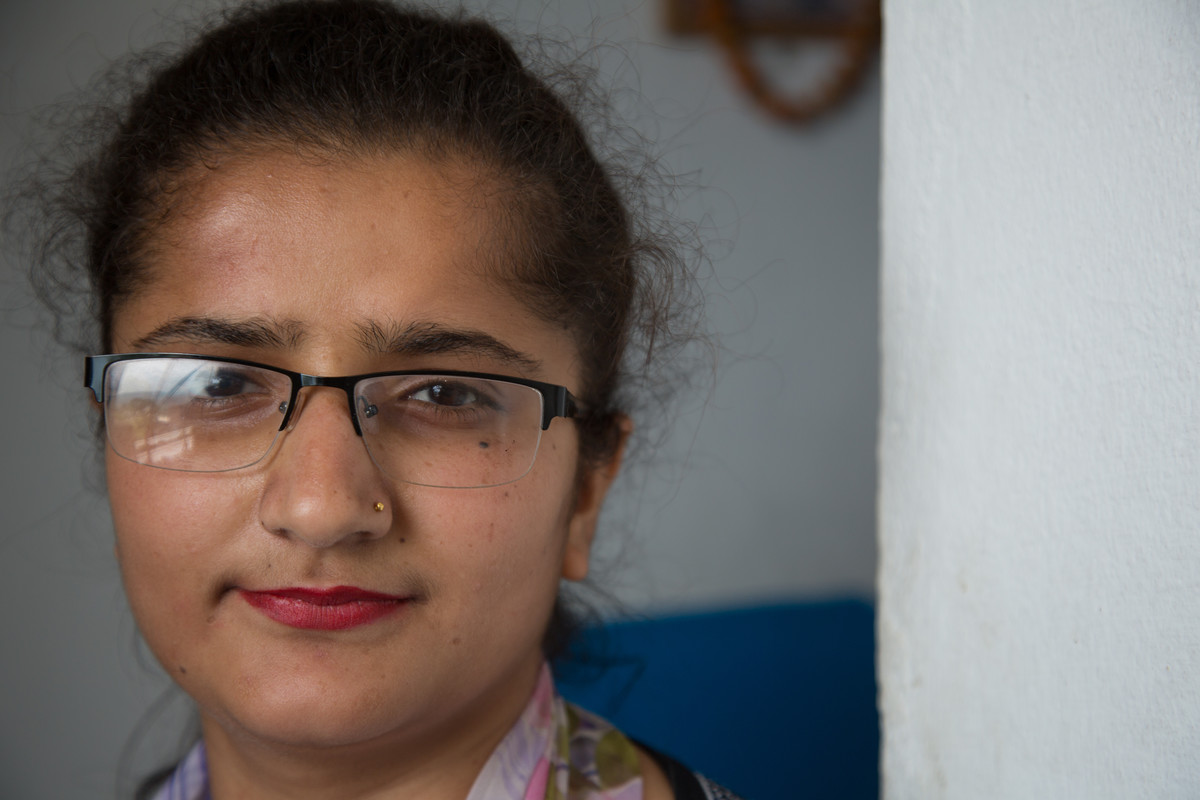

| 21 August 2017
How youth volunteers are leading the conversation on HIV with young people in Nepal
Mala Neupane is just 18 years old, but is already an experienced volunteer for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN). Mala lives in Tansen, the hillside capital of Palpa, a region of rolling hills, pine forests and lush terraced fields in western Nepal. She works as a community home-based care mobiliser focusing on HIV: her job involves travelling to villages around Tansen to provide people with information about HIV and contraception. “Before, the community had very little knowledge regarding HIV and there used to be so much stigma and discrimination,” she says. “But later, when the Community Health Based Carers (CHBCs) started working in those communities, they had more knowledge and less stigma.” The youth of the volunteers proved an effective tool during their conversations with villagers. “At first, when they talked to people about family planning, they were not receptive: they felt resistance to using those devices,” Mala explains. “The CHBCs said to them: ‘young people like us are doing this kind of work, so why are you feeling such hesitation?’ After talking with them, they became ready to use contraceptives.” Her age is also important for connecting with young people, in a society of rapid change, she says. “Because we are young, we may know more about what young people’s needs and wants are. We can talk to young people about what family planning methods might be suitable for them, and what the options are.” “Young people’s involvement [in FPAN programmes] is very important to helping out young people like us.” It’s a simple message, but one reaping rich rewards for the lives and wellbeing of people in Palpa.

| 20 April 2024
How youth volunteers are leading the conversation on HIV with young people in Nepal
Mala Neupane is just 18 years old, but is already an experienced volunteer for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN). Mala lives in Tansen, the hillside capital of Palpa, a region of rolling hills, pine forests and lush terraced fields in western Nepal. She works as a community home-based care mobiliser focusing on HIV: her job involves travelling to villages around Tansen to provide people with information about HIV and contraception. “Before, the community had very little knowledge regarding HIV and there used to be so much stigma and discrimination,” she says. “But later, when the Community Health Based Carers (CHBCs) started working in those communities, they had more knowledge and less stigma.” The youth of the volunteers proved an effective tool during their conversations with villagers. “At first, when they talked to people about family planning, they were not receptive: they felt resistance to using those devices,” Mala explains. “The CHBCs said to them: ‘young people like us are doing this kind of work, so why are you feeling such hesitation?’ After talking with them, they became ready to use contraceptives.” Her age is also important for connecting with young people, in a society of rapid change, she says. “Because we are young, we may know more about what young people’s needs and wants are. We can talk to young people about what family planning methods might be suitable for them, and what the options are.” “Young people’s involvement [in FPAN programmes] is very important to helping out young people like us.” It’s a simple message, but one reaping rich rewards for the lives and wellbeing of people in Palpa.
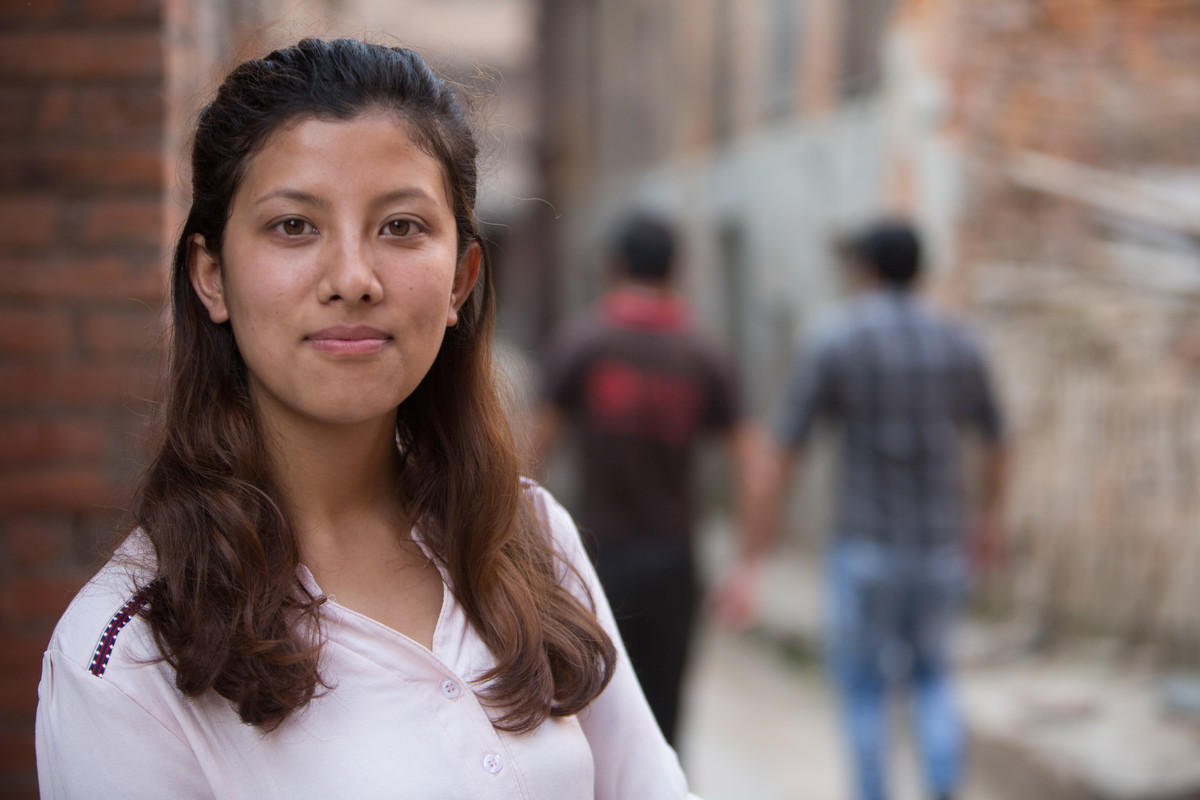

| 01 August 2017
"Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city"
“Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city,” says 23-year-old Sajana Kergi. “For example, when they’re menstruating they might have to stay at home and not touch any kitchen materials, or have to drop school. “It varies from family to family, but generally the more traditional and superstitious a family is, the more problems a girl will have.” For the past two years, Sajana has been volunteering as a peer educator and mentor for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), since hearing about the programme on Facebook. After an orientation and training programme, she visited different rural schools to give girls training on menstruation management. She now runs classes in schools in and around Bhaktapur. The classes aim to create a relaxed environment for young people to talk and learn about sexual health and rights. This fills a major gap in their learning and knowledge, Sajana says. “At school, these subjects are in the curriculum, but teachers skip these lessons and don’t talk about these issues openly,” she explains. “The teachers don’t create a comfortable environment, and this makes students hesitant to talk about these issues, so there’s no proper knowledge.” FPAN classes are an opportunity for young people to speak openly about sexual health and sexuality therefore are vital.

| 20 April 2024
"Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city"
“Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city,” says 23-year-old Sajana Kergi. “For example, when they’re menstruating they might have to stay at home and not touch any kitchen materials, or have to drop school. “It varies from family to family, but generally the more traditional and superstitious a family is, the more problems a girl will have.” For the past two years, Sajana has been volunteering as a peer educator and mentor for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), since hearing about the programme on Facebook. After an orientation and training programme, she visited different rural schools to give girls training on menstruation management. She now runs classes in schools in and around Bhaktapur. The classes aim to create a relaxed environment for young people to talk and learn about sexual health and rights. This fills a major gap in their learning and knowledge, Sajana says. “At school, these subjects are in the curriculum, but teachers skip these lessons and don’t talk about these issues openly,” she explains. “The teachers don’t create a comfortable environment, and this makes students hesitant to talk about these issues, so there’s no proper knowledge.” FPAN classes are an opportunity for young people to speak openly about sexual health and sexuality therefore are vital.

| 15 February 2019
"I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years”
In August 2017, weeks of continued and heavy rainfall across Nepal resulted in flash floods and landslides that affected 36 of the 75 districts. Many people lost their homes or were displaced. It was estimated that of those affected, 112,500 were women of reproductive age, including 8,694 pregnant women. IPPF Humanitarian, through their Member Association, The Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), activated its emergency response system early on. With funding support from the Australian Government, FPAN and IPPF Humanitarian initially mobilised their response in four of the worst affected districts (Sunsari, Saptari, Bardiya, and Dang). Mobile medical camps were established to meet the sexual and reproductive health needs of the affected population, including through the distribution of short and long acting methods of contraception, STI and HIV screening, and GBV referrals. In collaboration with the USAID-SIFPO project, services were then expanded into five more affected districts. IPPF Humanitarian spoke with 21-year old Muna in her home district of Sunsari in Nepal. “I got married at 16 years old and have two children, a four-year-old girl and two-year-old boy. In my caste, we get married early, so my parents took me to get an arranged marriage. I was in the 8th class at the time, and returned to school after I got married, but only lasted one year. My husband works in construction and had to stop working for two weeks when the floods came. When he doesn’t work, he doesn’t get paid, so it’s been very difficult. A FPAN social worker told me about the mobile medical camp today. I used to be on the three-month injectable but today I changed to the five-year implant in my arm. When my youngest child was eight months old I found out I was pregnant again. I decided to discontinue that pregnancy, so I took the five small tablets given to me by my neighbourhood doctor. I was two months pregnant at the time. From this, I had two days bleeding and cramp like pain, and then weakness. I decided to abort that pregnancy because my youngest will still only eight months old, and I didn’t want any more children. If I had more than two children, it would be very difficult to feed and educate them, and would badly affect my body too. I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years.” Want to know more about safe abortion access? Join IPPF'S I Decide movement

| 20 April 2024
"I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years”
In August 2017, weeks of continued and heavy rainfall across Nepal resulted in flash floods and landslides that affected 36 of the 75 districts. Many people lost their homes or were displaced. It was estimated that of those affected, 112,500 were women of reproductive age, including 8,694 pregnant women. IPPF Humanitarian, through their Member Association, The Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), activated its emergency response system early on. With funding support from the Australian Government, FPAN and IPPF Humanitarian initially mobilised their response in four of the worst affected districts (Sunsari, Saptari, Bardiya, and Dang). Mobile medical camps were established to meet the sexual and reproductive health needs of the affected population, including through the distribution of short and long acting methods of contraception, STI and HIV screening, and GBV referrals. In collaboration with the USAID-SIFPO project, services were then expanded into five more affected districts. IPPF Humanitarian spoke with 21-year old Muna in her home district of Sunsari in Nepal. “I got married at 16 years old and have two children, a four-year-old girl and two-year-old boy. In my caste, we get married early, so my parents took me to get an arranged marriage. I was in the 8th class at the time, and returned to school after I got married, but only lasted one year. My husband works in construction and had to stop working for two weeks when the floods came. When he doesn’t work, he doesn’t get paid, so it’s been very difficult. A FPAN social worker told me about the mobile medical camp today. I used to be on the three-month injectable but today I changed to the five-year implant in my arm. When my youngest child was eight months old I found out I was pregnant again. I decided to discontinue that pregnancy, so I took the five small tablets given to me by my neighbourhood doctor. I was two months pregnant at the time. From this, I had two days bleeding and cramp like pain, and then weakness. I decided to abort that pregnancy because my youngest will still only eight months old, and I didn’t want any more children. If I had more than two children, it would be very difficult to feed and educate them, and would badly affect my body too. I’m so happy I now don’t have to worry about contraception for another five years.” Want to know more about safe abortion access? Join IPPF'S I Decide movement

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 20 April 2024
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 20 April 2024
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 20 April 2024
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 21 August 2017
How youth volunteers are leading the conversation on HIV with young people in Nepal
Mala Neupane is just 18 years old, but is already an experienced volunteer for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN). Mala lives in Tansen, the hillside capital of Palpa, a region of rolling hills, pine forests and lush terraced fields in western Nepal. She works as a community home-based care mobiliser focusing on HIV: her job involves travelling to villages around Tansen to provide people with information about HIV and contraception. “Before, the community had very little knowledge regarding HIV and there used to be so much stigma and discrimination,” she says. “But later, when the Community Health Based Carers (CHBCs) started working in those communities, they had more knowledge and less stigma.” The youth of the volunteers proved an effective tool during their conversations with villagers. “At first, when they talked to people about family planning, they were not receptive: they felt resistance to using those devices,” Mala explains. “The CHBCs said to them: ‘young people like us are doing this kind of work, so why are you feeling such hesitation?’ After talking with them, they became ready to use contraceptives.” Her age is also important for connecting with young people, in a society of rapid change, she says. “Because we are young, we may know more about what young people’s needs and wants are. We can talk to young people about what family planning methods might be suitable for them, and what the options are.” “Young people’s involvement [in FPAN programmes] is very important to helping out young people like us.” It’s a simple message, but one reaping rich rewards for the lives and wellbeing of people in Palpa.

| 20 April 2024
How youth volunteers are leading the conversation on HIV with young people in Nepal
Mala Neupane is just 18 years old, but is already an experienced volunteer for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN). Mala lives in Tansen, the hillside capital of Palpa, a region of rolling hills, pine forests and lush terraced fields in western Nepal. She works as a community home-based care mobiliser focusing on HIV: her job involves travelling to villages around Tansen to provide people with information about HIV and contraception. “Before, the community had very little knowledge regarding HIV and there used to be so much stigma and discrimination,” she says. “But later, when the Community Health Based Carers (CHBCs) started working in those communities, they had more knowledge and less stigma.” The youth of the volunteers proved an effective tool during their conversations with villagers. “At first, when they talked to people about family planning, they were not receptive: they felt resistance to using those devices,” Mala explains. “The CHBCs said to them: ‘young people like us are doing this kind of work, so why are you feeling such hesitation?’ After talking with them, they became ready to use contraceptives.” Her age is also important for connecting with young people, in a society of rapid change, she says. “Because we are young, we may know more about what young people’s needs and wants are. We can talk to young people about what family planning methods might be suitable for them, and what the options are.” “Young people’s involvement [in FPAN programmes] is very important to helping out young people like us.” It’s a simple message, but one reaping rich rewards for the lives and wellbeing of people in Palpa.

| 01 August 2017
"Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city"
“Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city,” says 23-year-old Sajana Kergi. “For example, when they’re menstruating they might have to stay at home and not touch any kitchen materials, or have to drop school. “It varies from family to family, but generally the more traditional and superstitious a family is, the more problems a girl will have.” For the past two years, Sajana has been volunteering as a peer educator and mentor for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), since hearing about the programme on Facebook. After an orientation and training programme, she visited different rural schools to give girls training on menstruation management. She now runs classes in schools in and around Bhaktapur. The classes aim to create a relaxed environment for young people to talk and learn about sexual health and rights. This fills a major gap in their learning and knowledge, Sajana says. “At school, these subjects are in the curriculum, but teachers skip these lessons and don’t talk about these issues openly,” she explains. “The teachers don’t create a comfortable environment, and this makes students hesitant to talk about these issues, so there’s no proper knowledge.” FPAN classes are an opportunity for young people to speak openly about sexual health and sexuality therefore are vital.

| 20 April 2024
"Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city"
“Girls in rural areas often face more problems than girls in the city,” says 23-year-old Sajana Kergi. “For example, when they’re menstruating they might have to stay at home and not touch any kitchen materials, or have to drop school. “It varies from family to family, but generally the more traditional and superstitious a family is, the more problems a girl will have.” For the past two years, Sajana has been volunteering as a peer educator and mentor for the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), since hearing about the programme on Facebook. After an orientation and training programme, she visited different rural schools to give girls training on menstruation management. She now runs classes in schools in and around Bhaktapur. The classes aim to create a relaxed environment for young people to talk and learn about sexual health and rights. This fills a major gap in their learning and knowledge, Sajana says. “At school, these subjects are in the curriculum, but teachers skip these lessons and don’t talk about these issues openly,” she explains. “The teachers don’t create a comfortable environment, and this makes students hesitant to talk about these issues, so there’s no proper knowledge.” FPAN classes are an opportunity for young people to speak openly about sexual health and sexuality therefore are vital.








