Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

What does the year 2024 hold for us?
As the new year begins, we take a look at the trends and challenges ahead for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Most Popular This Week

Palestine
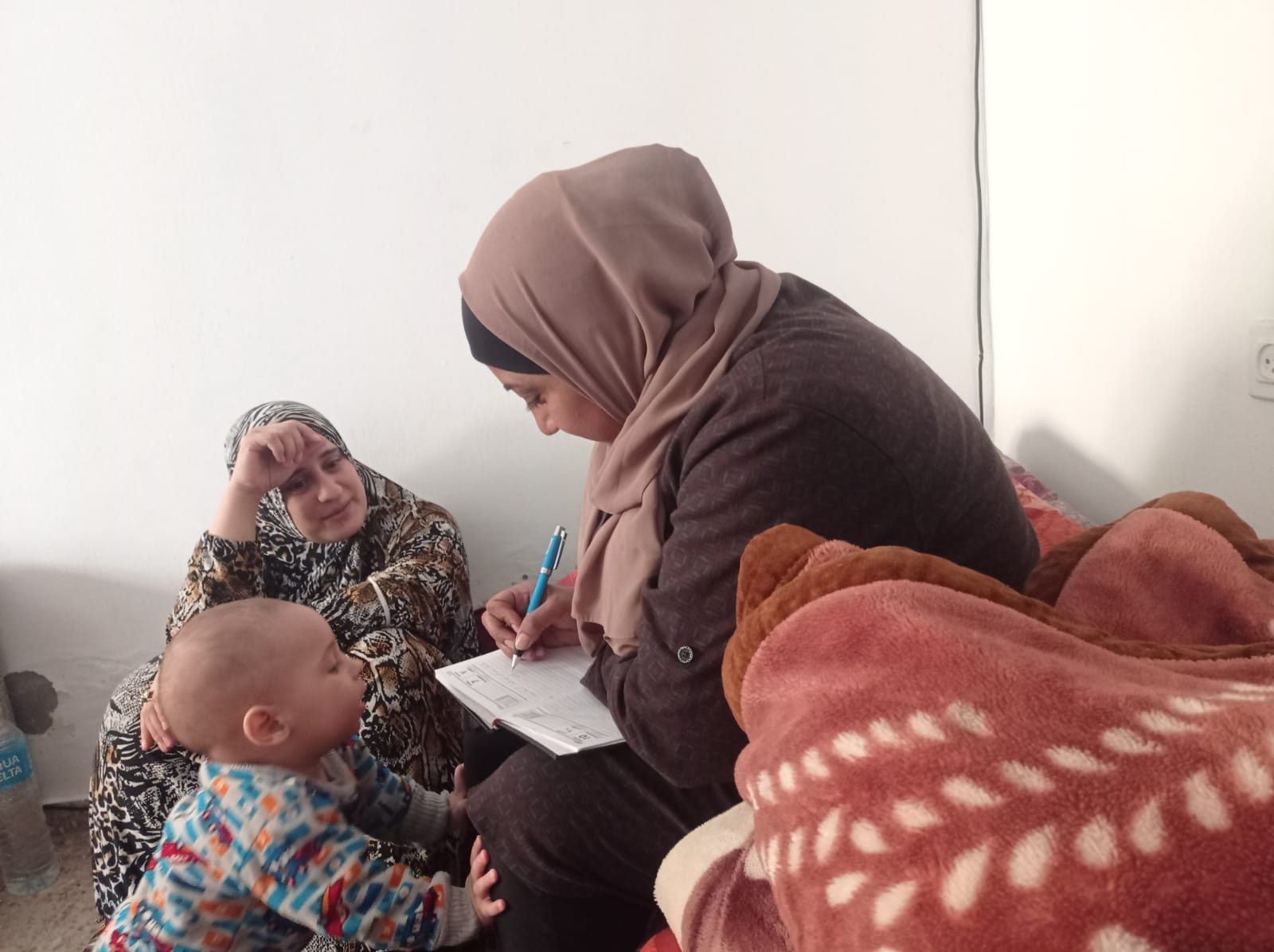

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
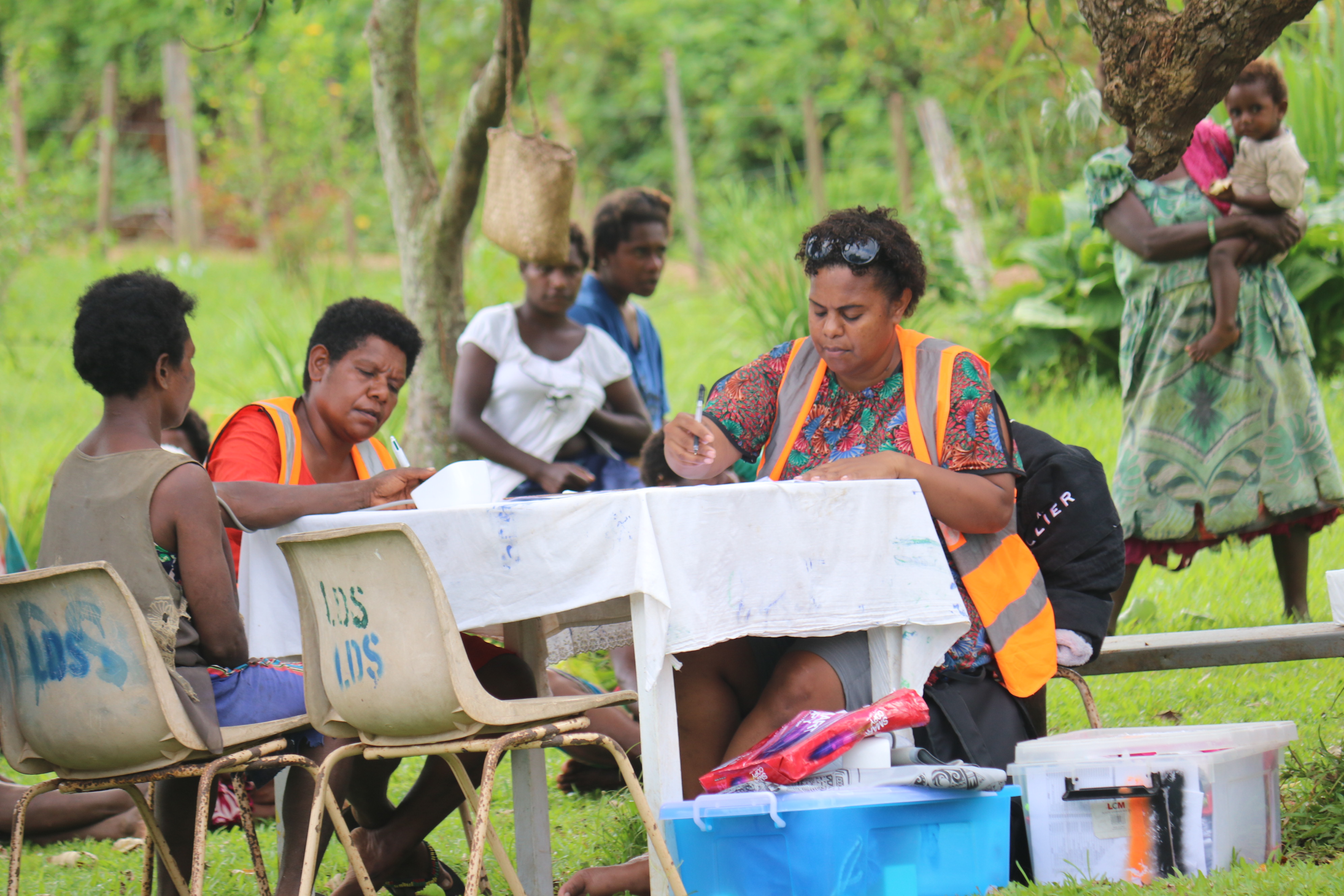

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
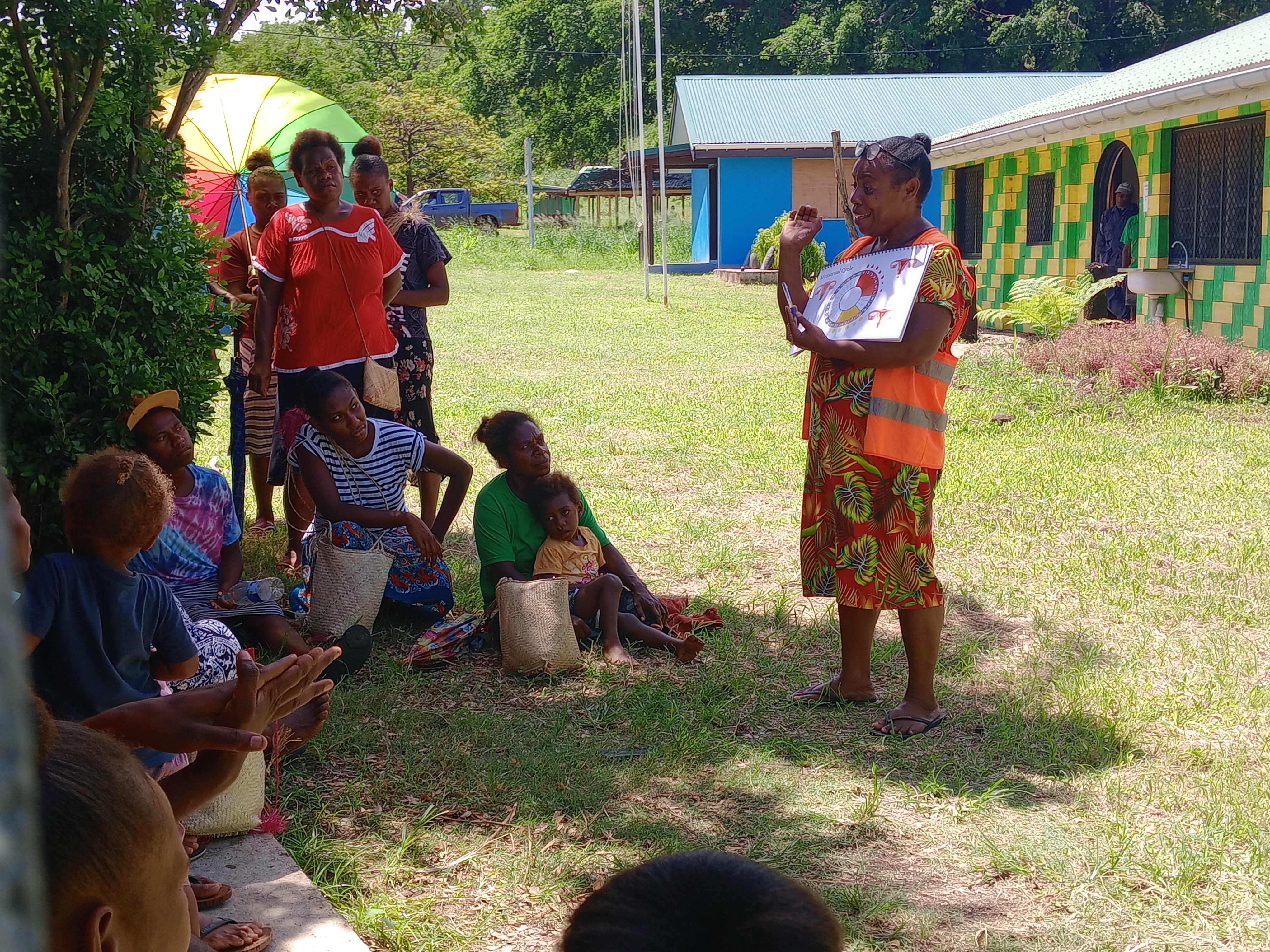

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Cook Islands

Dean and the Cook Islands Condom Car
On the island of Rarotonga, the main island of the Cook Islands in the South Pacific, a little white van makes its rounds on the palm-tree lined circular road.
Filter our stories by:


| 20 May 2017
From garbage collector to sexual health counsellor
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Ali. I have worked with Lady Mermaid’s Bureau (LMB) for eight years as a programme officer and I am also a consultant on safe abortion. LMB was founded by three sex workers in 2002. It is the oldest sex worker’s organisation in Eastern Africa. When it started, LMB arranged for sex workers to meet Parliament and expose all the problems that sex workers have to face. They originally thought the government would only take two years to legalise sex work. That was obviously not the case and as advisers we said it would take a lot of time talking about their sexual health and other problems. Before I became an adviser I was working with a garbage collection company. I was the night supervisor and I had a lot of friends who were sex workers. They would talk with me and tell me how they wanted a street where they would not be arrested. These were the workers who originally started Lady Mermaid’s Bureau. First it was for fellow sex workers to help them when they were arrested by the police. Then I came in to advise them in the set up and do what I could do to help them reach their goals. There were many problems. Talking about sex work was a taboo. When I became part of LMB nobody was talking about sex workers. The women’s movement was against sex workers. They thought it was exploitative to all women. So we had to engage most of them in our programmes until they came on board to realise sex workers rights. When the sex workers went to Parliament in 2004, that meeting acted to provide an amnesty to the women. Now they can take cases to the police. Previously, no sex worker would go to the police to report a client because she would just end up being arrested. Abortion among sex workers is still a very major issue that has to be looked at by the government. Many women are very vulnerable to becoming sex workers. They are poor, from slums and a lot of them are students. They face a lot of violence: rape, the police themselves use them (ask for sex) and then there are clients who rape the women. So there are a lot of incidences of violence that turn into unwanted pregnancies. Most of the women will resort to aborting if they face such violence because they don’t know the father of the child. If you go to a private clinic it can cost 120,000 to 250,000 Uganda shillings. Also, service providers will not tell the sex workers that there is a cheaper way of doing abortions. They try to escalate the costs. Sex workers aren't told about how they can take misoprostol from home and then they can follow up onto the clinic. So the service is perceived to be high although it could be cheaper to abort. We have seen women who have not been able to access safe abortion. We have a young lady here who tried to abort unsafely because it was too expensive for her to have a safe abortion. Again she was afraid that she would be arrested, she was afraid that nurses at the clinic would stigmatise her. So she tried to abort the local way but it didn’t work and now she has a child. Countrywide the problem is lack of contraceptives: you find that some women have aborted two or three times, and then there's the problem of not counselling on contraceptive use and the lack of contraceptives in private and public health institutions. In many cases the men don’t want to use the male condoms and there aren't many female condoms on the market and they are extremely expensive. It is really very important for women to have information about contraceptives and can access contraceptive methods. These days we have sex workers ranging from 14 year to 38 years. Most of these young girls have been trafficked from the villages. Some come from the villages where they are promised some work in the city and they end up into sex work. Some are refugees who have come from Congo, others have come from Rwanda and others have come from South Sudan. We also have sex workers who are students from the colleges. And then we have young ladies who have grown up in slum areas of Kawempe, Katanag in Makerere, Natete who have been orphaned and left to fend for their families. There are the older ladies who work on the streets to sell tomatoes. They give out their numbers to clients or men who can raise them on call. And another group of older women work from their homes in slum areas where pimps take customers to them. There are also some high-class sex workers from 20-32 years old. They work in posh shops in Kampala where they give out business cards. There are sex workers who have pimps that use social media like Facebook and badoo to expose the women. Men just call the pimp who will bring the sex worker. Getting contraceptives to girls under 14 is also a big issue which parliament needs to look at. Now a lot of young ladies find themselves in distress. Most of them come from the villages and most of them have lost parents. They enter into sex work from 14 and they find themselves becoming pregnant. Since contraceptives are restricted to these ages, it is increasing the problem rather than solving it. There is need for counselling on contraceptives at least from ages of 14 and then there is need for a contraceptive referral centre. Another issue is a lot of rumours that contraceptives damage the body of the women and that it changes the hormones, causing infertility. So these women in the end don’t talk about these problems when they visit health centres and the doctor will not follow up. The women end up concluding that every contraceptive is damaging to their bodies. This project started to have an impact in its second and the third year. Sex workers had learnt about safe services, and how to tell a health institution that they had had a miscarriage. The majority of the feedback has been positive. Abortion should be legalised. The legislators should learn about the stories and they can get a precise picture of the level of deaths caused by unsafe abortion. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 April 2024
From garbage collector to sexual health counsellor
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Ali. I have worked with Lady Mermaid’s Bureau (LMB) for eight years as a programme officer and I am also a consultant on safe abortion. LMB was founded by three sex workers in 2002. It is the oldest sex worker’s organisation in Eastern Africa. When it started, LMB arranged for sex workers to meet Parliament and expose all the problems that sex workers have to face. They originally thought the government would only take two years to legalise sex work. That was obviously not the case and as advisers we said it would take a lot of time talking about their sexual health and other problems. Before I became an adviser I was working with a garbage collection company. I was the night supervisor and I had a lot of friends who were sex workers. They would talk with me and tell me how they wanted a street where they would not be arrested. These were the workers who originally started Lady Mermaid’s Bureau. First it was for fellow sex workers to help them when they were arrested by the police. Then I came in to advise them in the set up and do what I could do to help them reach their goals. There were many problems. Talking about sex work was a taboo. When I became part of LMB nobody was talking about sex workers. The women’s movement was against sex workers. They thought it was exploitative to all women. So we had to engage most of them in our programmes until they came on board to realise sex workers rights. When the sex workers went to Parliament in 2004, that meeting acted to provide an amnesty to the women. Now they can take cases to the police. Previously, no sex worker would go to the police to report a client because she would just end up being arrested. Abortion among sex workers is still a very major issue that has to be looked at by the government. Many women are very vulnerable to becoming sex workers. They are poor, from slums and a lot of them are students. They face a lot of violence: rape, the police themselves use them (ask for sex) and then there are clients who rape the women. So there are a lot of incidences of violence that turn into unwanted pregnancies. Most of the women will resort to aborting if they face such violence because they don’t know the father of the child. If you go to a private clinic it can cost 120,000 to 250,000 Uganda shillings. Also, service providers will not tell the sex workers that there is a cheaper way of doing abortions. They try to escalate the costs. Sex workers aren't told about how they can take misoprostol from home and then they can follow up onto the clinic. So the service is perceived to be high although it could be cheaper to abort. We have seen women who have not been able to access safe abortion. We have a young lady here who tried to abort unsafely because it was too expensive for her to have a safe abortion. Again she was afraid that she would be arrested, she was afraid that nurses at the clinic would stigmatise her. So she tried to abort the local way but it didn’t work and now she has a child. Countrywide the problem is lack of contraceptives: you find that some women have aborted two or three times, and then there's the problem of not counselling on contraceptive use and the lack of contraceptives in private and public health institutions. In many cases the men don’t want to use the male condoms and there aren't many female condoms on the market and they are extremely expensive. It is really very important for women to have information about contraceptives and can access contraceptive methods. These days we have sex workers ranging from 14 year to 38 years. Most of these young girls have been trafficked from the villages. Some come from the villages where they are promised some work in the city and they end up into sex work. Some are refugees who have come from Congo, others have come from Rwanda and others have come from South Sudan. We also have sex workers who are students from the colleges. And then we have young ladies who have grown up in slum areas of Kawempe, Katanag in Makerere, Natete who have been orphaned and left to fend for their families. There are the older ladies who work on the streets to sell tomatoes. They give out their numbers to clients or men who can raise them on call. And another group of older women work from their homes in slum areas where pimps take customers to them. There are also some high-class sex workers from 20-32 years old. They work in posh shops in Kampala where they give out business cards. There are sex workers who have pimps that use social media like Facebook and badoo to expose the women. Men just call the pimp who will bring the sex worker. Getting contraceptives to girls under 14 is also a big issue which parliament needs to look at. Now a lot of young ladies find themselves in distress. Most of them come from the villages and most of them have lost parents. They enter into sex work from 14 and they find themselves becoming pregnant. Since contraceptives are restricted to these ages, it is increasing the problem rather than solving it. There is need for counselling on contraceptives at least from ages of 14 and then there is need for a contraceptive referral centre. Another issue is a lot of rumours that contraceptives damage the body of the women and that it changes the hormones, causing infertility. So these women in the end don’t talk about these problems when they visit health centres and the doctor will not follow up. The women end up concluding that every contraceptive is damaging to their bodies. This project started to have an impact in its second and the third year. Sex workers had learnt about safe services, and how to tell a health institution that they had had a miscarriage. The majority of the feedback has been positive. Abortion should be legalised. The legislators should learn about the stories and they can get a precise picture of the level of deaths caused by unsafe abortion. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
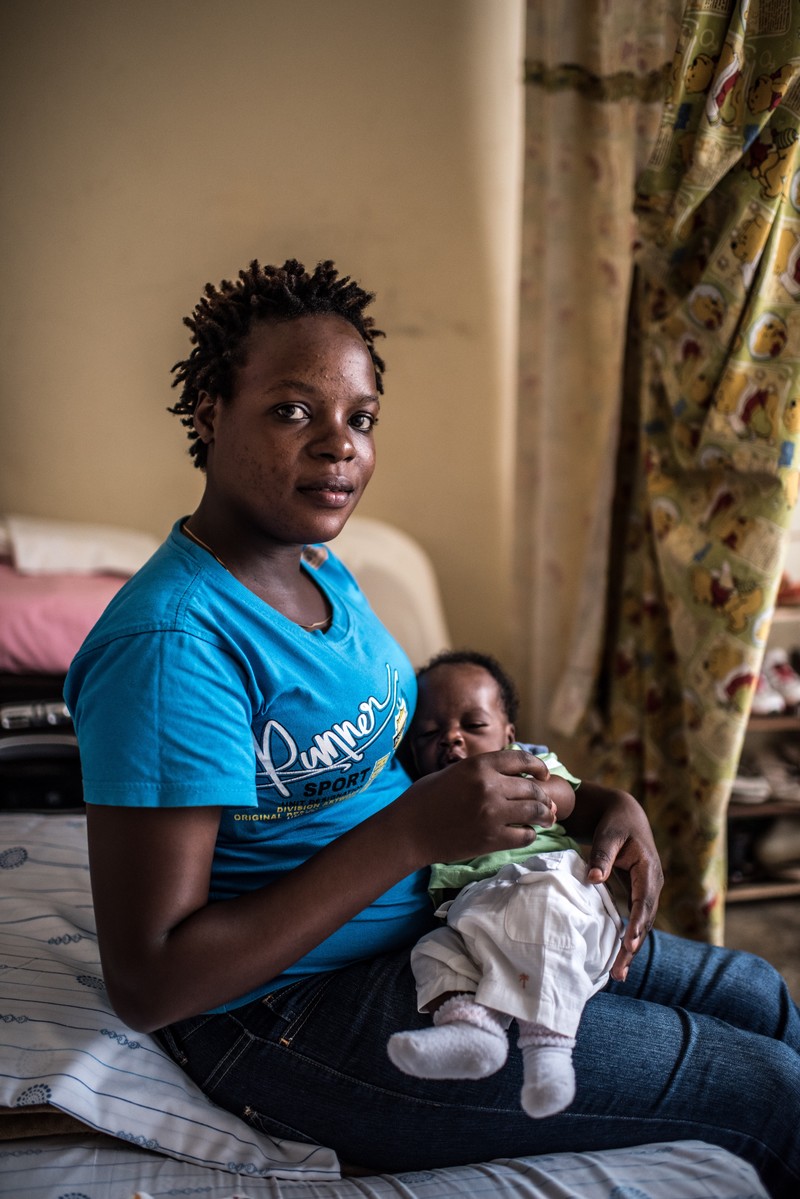
| 20 May 2017
Life-changing post-abortion care for sex workers
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Masitula. I’m a single mother of two sons and I'm a sex worker. I live in Nansana Wakiso district, it is near Kampala. Every evening I travel 10 kilometres to Natete, a Kampala city suburb where I am a sex worker. I got pregnant after a client refused to wear a condom. I attempted to abort using some unsafe abortion practices but I was unsuccessful. I now have a two-month old baby whose father I do not know. My eldest son is seven years, he is in primary school. The other one is two months. I became a sex worker after a friend advised me that this job can provide me with some income. My husband left me six years ago for another woman when my eldest was only one. He doesn’t give me a single penny for taking care of his son. I used to be a teacher but the income is little. So I have been a sex worker for six years. There are many problems for sex workers here. One is with the police. The police catch us, take our money and sometimes force us to have sex. The other problem is that those men who buy us, some of them don’t pay. They just use us and they don’t pay. It affects me because when you go to work and you don’t get any income, it is bad. They use you for free. And I don’t have anyone to take care of my kids. So sometimes I don’t work I just stay at home because no one will take care of my kids. I live only with my children. I don’t have anyone else. Sometimes I have to take my baby with me and if I get a job, then I give him to my friend until I finish. It is difficult with such a little baby but there is nothing I can do. I don’t even know the father. He just forced me. He said that he will not put on a condom. So that is why I tried to abort with herbs, but it didn't work.They caused me a lot of pain and I was about to die. I didn’t go for a safe abortion because with this government of ours, it is not easy to go to the hospital and tell them that I want to abort. You just go and tell them that you want medicine for ulcers. But Lady Mermaid's Bureau, supported by SAAF, has helped me and other sex workers. When you call them they come immediately. When you are sick they take you to hospital. In everything they are good. When I get some problems, I just go and tell them. They do what other people can’t do. It has changed my life because I now have a friend. They are my friends. I take them as part of my family because I don’t have any family. My father died, I don’t have a mother and my husband left me. They are my family now. Abortion should be legal and also sex work because it is a job. We don’t want to do it. It's just because we don’t have anything else and that is why we do it. So the government should also take us as human beings. No one treats us as human beings. And to prevent women from having unsafe abortions the government should provide people with jobs and factories to work in. So that they don't have to do sex work because it affects these girls, and some of them are like me. We don’t have jobs, you go and look for a job, you don’t find the job and you just find yourself doing this sex working job instead. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
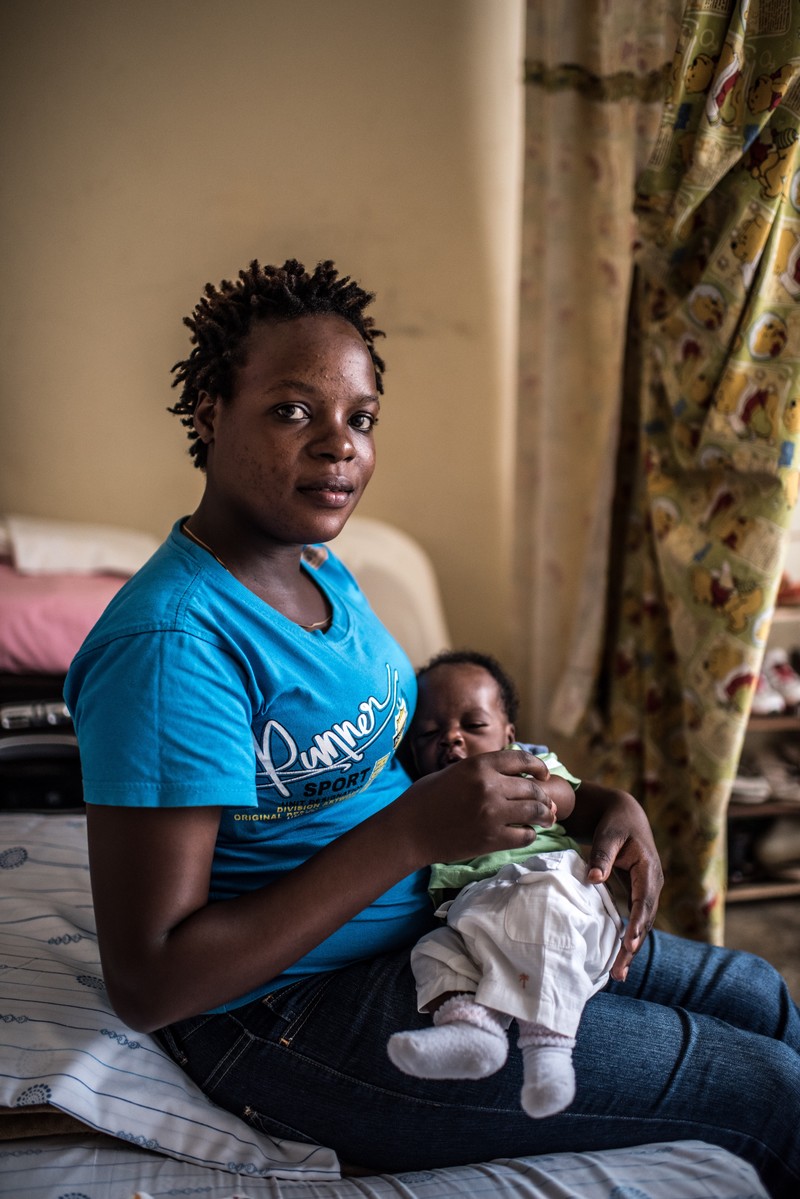
| 16 April 2024
Life-changing post-abortion care for sex workers
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Masitula. I’m a single mother of two sons and I'm a sex worker. I live in Nansana Wakiso district, it is near Kampala. Every evening I travel 10 kilometres to Natete, a Kampala city suburb where I am a sex worker. I got pregnant after a client refused to wear a condom. I attempted to abort using some unsafe abortion practices but I was unsuccessful. I now have a two-month old baby whose father I do not know. My eldest son is seven years, he is in primary school. The other one is two months. I became a sex worker after a friend advised me that this job can provide me with some income. My husband left me six years ago for another woman when my eldest was only one. He doesn’t give me a single penny for taking care of his son. I used to be a teacher but the income is little. So I have been a sex worker for six years. There are many problems for sex workers here. One is with the police. The police catch us, take our money and sometimes force us to have sex. The other problem is that those men who buy us, some of them don’t pay. They just use us and they don’t pay. It affects me because when you go to work and you don’t get any income, it is bad. They use you for free. And I don’t have anyone to take care of my kids. So sometimes I don’t work I just stay at home because no one will take care of my kids. I live only with my children. I don’t have anyone else. Sometimes I have to take my baby with me and if I get a job, then I give him to my friend until I finish. It is difficult with such a little baby but there is nothing I can do. I don’t even know the father. He just forced me. He said that he will not put on a condom. So that is why I tried to abort with herbs, but it didn't work.They caused me a lot of pain and I was about to die. I didn’t go for a safe abortion because with this government of ours, it is not easy to go to the hospital and tell them that I want to abort. You just go and tell them that you want medicine for ulcers. But Lady Mermaid's Bureau, supported by SAAF, has helped me and other sex workers. When you call them they come immediately. When you are sick they take you to hospital. In everything they are good. When I get some problems, I just go and tell them. They do what other people can’t do. It has changed my life because I now have a friend. They are my friends. I take them as part of my family because I don’t have any family. My father died, I don’t have a mother and my husband left me. They are my family now. Abortion should be legal and also sex work because it is a job. We don’t want to do it. It's just because we don’t have anything else and that is why we do it. So the government should also take us as human beings. No one treats us as human beings. And to prevent women from having unsafe abortions the government should provide people with jobs and factories to work in. So that they don't have to do sex work because it affects these girls, and some of them are like me. We don’t have jobs, you go and look for a job, you don’t find the job and you just find yourself doing this sex working job instead. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
| 20 April 2017
Sex workers in Uganda find hope
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. Joanne is a sex-worker who has been involved in the project run by Lady Mermaid's Bureau, funded by SAAF. "My name is Joanne, I have been a sex-worker for two years." Joanne was abused as a child and became pregnant at a very young age. She was forced to leave school with only a primary education and could not speak English very well. When she moved to Kampala from her village she was told she could get a good job but she had nowhere to stay and ended up becoming a sex-worker in order to support herself and her two children. While sex-work offers some financial support, the fact that it is illegal and that gender inequality is high in Uganda make sex workers very vulnerable to rape and violence. "The problems are very many. Men don’t want to pay. Someone uses you but he does not want to pay. We are being beaten, and there's a lot of stress and competition." "There is a lot of competition between sex workers. Sometimes you go on the streets and no man is going to buy you and you end up not earning a single coin. Other times, when that man buys you, he tells you the money, you negotiate when you go to the lodge the man does not pay you. That is the most hard thing because you need to feed your children, but someone does not pay you. The men beat us when we are in the lodges. They are rough, they don’t want to use condoms, you tell him to use a condom, and he does not want to use a condom. So they end up infecting you sometimes. My other sex workers most of them got infected through that. We are even being raped by policemen sometimes. They come on the streets to chase us away and if we stay on the streets to work, the policemen force you. When a policeman arrests you, he takes you to a police station because you don’t have money. He asks what you can offer if you want to leave jail. You will say, "I have nothing I don’t have money." So the only thing you can do is to have sex with him. Then he will release you. Women cells are not the same as the ones for men - sometimes you are there alone at night. So police cells are being used to rape women. He has not paid you so that is rape - he has just forced you. There are many women who got pregnant because of this rape. Even me. I have had two abortions." Joanne used local herbs to terminate her pregnancy which led to complications. Then her friend told her about Lady Mermaid's Bureau and they referred her to IPPF's Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) who were able to help her. Since being involved with Lady Mermaid's Bureau Joanne has been taught English and computer skills and has also got access to contraception and legal support. She thinks that both sex-work and abortion should be legalised in Uganda to reduce the stigma that leads to violence and abuse. "At times men don't respect us as sex-workers. Because it is illegal they abuse you. If they legalise it, it will be good." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
| 16 April 2024
Sex workers in Uganda find hope
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. Joanne is a sex-worker who has been involved in the project run by Lady Mermaid's Bureau, funded by SAAF. "My name is Joanne, I have been a sex-worker for two years." Joanne was abused as a child and became pregnant at a very young age. She was forced to leave school with only a primary education and could not speak English very well. When she moved to Kampala from her village she was told she could get a good job but she had nowhere to stay and ended up becoming a sex-worker in order to support herself and her two children. While sex-work offers some financial support, the fact that it is illegal and that gender inequality is high in Uganda make sex workers very vulnerable to rape and violence. "The problems are very many. Men don’t want to pay. Someone uses you but he does not want to pay. We are being beaten, and there's a lot of stress and competition." "There is a lot of competition between sex workers. Sometimes you go on the streets and no man is going to buy you and you end up not earning a single coin. Other times, when that man buys you, he tells you the money, you negotiate when you go to the lodge the man does not pay you. That is the most hard thing because you need to feed your children, but someone does not pay you. The men beat us when we are in the lodges. They are rough, they don’t want to use condoms, you tell him to use a condom, and he does not want to use a condom. So they end up infecting you sometimes. My other sex workers most of them got infected through that. We are even being raped by policemen sometimes. They come on the streets to chase us away and if we stay on the streets to work, the policemen force you. When a policeman arrests you, he takes you to a police station because you don’t have money. He asks what you can offer if you want to leave jail. You will say, "I have nothing I don’t have money." So the only thing you can do is to have sex with him. Then he will release you. Women cells are not the same as the ones for men - sometimes you are there alone at night. So police cells are being used to rape women. He has not paid you so that is rape - he has just forced you. There are many women who got pregnant because of this rape. Even me. I have had two abortions." Joanne used local herbs to terminate her pregnancy which led to complications. Then her friend told her about Lady Mermaid's Bureau and they referred her to IPPF's Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) who were able to help her. Since being involved with Lady Mermaid's Bureau Joanne has been taught English and computer skills and has also got access to contraception and legal support. She thinks that both sex-work and abortion should be legalised in Uganda to reduce the stigma that leads to violence and abuse. "At times men don't respect us as sex-workers. Because it is illegal they abuse you. If they legalise it, it will be good." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
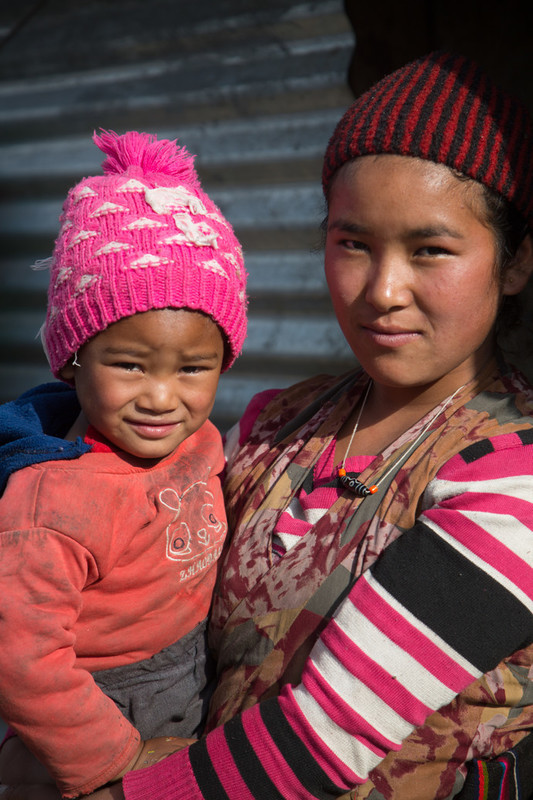

| 05 March 2017
Forced into marriage at 16
High up in the mountains of Rasuwa in northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border, is the village of Gatlang. This tight-knit village of traditional stone houses and Buddhist stupas is home to the Tamang people: a Buddhist indigenous group for whom family life is strictly patriarchal. Marriage traditions here can be oppressive: when a man chooses a wife, the girls – many are as young as 14 – have little choice but to marry. Most then go on to have large families, meaning food, money and education are spread sparsely. Jomini Tamang was just 16 years old when her parents forced her to marry. “I don’t want to get married,” she told them, but the wedding went ahead anyway. Jomini lives in Gatlang, a remote village of traditional stone and carved wooden houses, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border. The people here are Tamang, a Buddhist ethnic group, and family life is strictly patriarchal. Many Tamang marry young – from around 14 years old – and girls tend to be pushed into marriage by both their parents and the young men who choose them. “It’s not easy being married, it’s difficult,” says Jomini, whose husband is eight years older than her. “When I got married, I didn’t know anything about what happens after marriage, about the physical side.” After a year of marriage, Jomini had her first child, a boy called Gauran, who is now two. Women like Jomini are expected to combine childcare with household chores and long shifts farming vegetables in the village fields. “After the birth, I had many difficulties. Bringing up a child in this remote village was frightening and challenging, and Gauran was ill a lot". Giving birth at a young age can lead to severe physical complications or death, and maternal mortality is one of the leading causes of death for women in Nepal. Only 60% of women receive skilled antenatal support. Luckily for Jomini, shortly after Gauran’s birth, the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), Nepal’s leading family planning NGO, stepped in to help. Jomini met Pasang Tamang, a local woman who works as a reproductive health female volunteer for FPAN. Through Pasang, Jomini learned about different contraceptive methods and, with careful advice and support, was able to think through which might be best for her. She opted for the contraceptive injection, and says she is much happier now: contraception has given her more freedom, and the space to think clearly about when to have another child. Jomini’s experiences have convinced her to do everything possible to enable her children to live happier lives, less constrained by patriarchy and marriage. If she has a daughter, “I will tell her not to get married at an early age like her mum, and that if she does, she will suffer,” she says. “I will advise her to study more so she can work.” “And I will advise my son the same! Study more and wait til you are more mature to get married.” Stories Read more stories from Nepal

| 16 April 2024
Forced into marriage at 16
High up in the mountains of Rasuwa in northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border, is the village of Gatlang. This tight-knit village of traditional stone houses and Buddhist stupas is home to the Tamang people: a Buddhist indigenous group for whom family life is strictly patriarchal. Marriage traditions here can be oppressive: when a man chooses a wife, the girls – many are as young as 14 – have little choice but to marry. Most then go on to have large families, meaning food, money and education are spread sparsely. Jomini Tamang was just 16 years old when her parents forced her to marry. “I don’t want to get married,” she told them, but the wedding went ahead anyway. Jomini lives in Gatlang, a remote village of traditional stone and carved wooden houses, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border. The people here are Tamang, a Buddhist ethnic group, and family life is strictly patriarchal. Many Tamang marry young – from around 14 years old – and girls tend to be pushed into marriage by both their parents and the young men who choose them. “It’s not easy being married, it’s difficult,” says Jomini, whose husband is eight years older than her. “When I got married, I didn’t know anything about what happens after marriage, about the physical side.” After a year of marriage, Jomini had her first child, a boy called Gauran, who is now two. Women like Jomini are expected to combine childcare with household chores and long shifts farming vegetables in the village fields. “After the birth, I had many difficulties. Bringing up a child in this remote village was frightening and challenging, and Gauran was ill a lot". Giving birth at a young age can lead to severe physical complications or death, and maternal mortality is one of the leading causes of death for women in Nepal. Only 60% of women receive skilled antenatal support. Luckily for Jomini, shortly after Gauran’s birth, the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), Nepal’s leading family planning NGO, stepped in to help. Jomini met Pasang Tamang, a local woman who works as a reproductive health female volunteer for FPAN. Through Pasang, Jomini learned about different contraceptive methods and, with careful advice and support, was able to think through which might be best for her. She opted for the contraceptive injection, and says she is much happier now: contraception has given her more freedom, and the space to think clearly about when to have another child. Jomini’s experiences have convinced her to do everything possible to enable her children to live happier lives, less constrained by patriarchy and marriage. If she has a daughter, “I will tell her not to get married at an early age like her mum, and that if she does, she will suffer,” she says. “I will advise her to study more so she can work.” “And I will advise my son the same! Study more and wait til you are more mature to get married.” Stories Read more stories from Nepal

| 20 May 2017
From garbage collector to sexual health counsellor
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Ali. I have worked with Lady Mermaid’s Bureau (LMB) for eight years as a programme officer and I am also a consultant on safe abortion. LMB was founded by three sex workers in 2002. It is the oldest sex worker’s organisation in Eastern Africa. When it started, LMB arranged for sex workers to meet Parliament and expose all the problems that sex workers have to face. They originally thought the government would only take two years to legalise sex work. That was obviously not the case and as advisers we said it would take a lot of time talking about their sexual health and other problems. Before I became an adviser I was working with a garbage collection company. I was the night supervisor and I had a lot of friends who were sex workers. They would talk with me and tell me how they wanted a street where they would not be arrested. These were the workers who originally started Lady Mermaid’s Bureau. First it was for fellow sex workers to help them when they were arrested by the police. Then I came in to advise them in the set up and do what I could do to help them reach their goals. There were many problems. Talking about sex work was a taboo. When I became part of LMB nobody was talking about sex workers. The women’s movement was against sex workers. They thought it was exploitative to all women. So we had to engage most of them in our programmes until they came on board to realise sex workers rights. When the sex workers went to Parliament in 2004, that meeting acted to provide an amnesty to the women. Now they can take cases to the police. Previously, no sex worker would go to the police to report a client because she would just end up being arrested. Abortion among sex workers is still a very major issue that has to be looked at by the government. Many women are very vulnerable to becoming sex workers. They are poor, from slums and a lot of them are students. They face a lot of violence: rape, the police themselves use them (ask for sex) and then there are clients who rape the women. So there are a lot of incidences of violence that turn into unwanted pregnancies. Most of the women will resort to aborting if they face such violence because they don’t know the father of the child. If you go to a private clinic it can cost 120,000 to 250,000 Uganda shillings. Also, service providers will not tell the sex workers that there is a cheaper way of doing abortions. They try to escalate the costs. Sex workers aren't told about how they can take misoprostol from home and then they can follow up onto the clinic. So the service is perceived to be high although it could be cheaper to abort. We have seen women who have not been able to access safe abortion. We have a young lady here who tried to abort unsafely because it was too expensive for her to have a safe abortion. Again she was afraid that she would be arrested, she was afraid that nurses at the clinic would stigmatise her. So she tried to abort the local way but it didn’t work and now she has a child. Countrywide the problem is lack of contraceptives: you find that some women have aborted two or three times, and then there's the problem of not counselling on contraceptive use and the lack of contraceptives in private and public health institutions. In many cases the men don’t want to use the male condoms and there aren't many female condoms on the market and they are extremely expensive. It is really very important for women to have information about contraceptives and can access contraceptive methods. These days we have sex workers ranging from 14 year to 38 years. Most of these young girls have been trafficked from the villages. Some come from the villages where they are promised some work in the city and they end up into sex work. Some are refugees who have come from Congo, others have come from Rwanda and others have come from South Sudan. We also have sex workers who are students from the colleges. And then we have young ladies who have grown up in slum areas of Kawempe, Katanag in Makerere, Natete who have been orphaned and left to fend for their families. There are the older ladies who work on the streets to sell tomatoes. They give out their numbers to clients or men who can raise them on call. And another group of older women work from their homes in slum areas where pimps take customers to them. There are also some high-class sex workers from 20-32 years old. They work in posh shops in Kampala where they give out business cards. There are sex workers who have pimps that use social media like Facebook and badoo to expose the women. Men just call the pimp who will bring the sex worker. Getting contraceptives to girls under 14 is also a big issue which parliament needs to look at. Now a lot of young ladies find themselves in distress. Most of them come from the villages and most of them have lost parents. They enter into sex work from 14 and they find themselves becoming pregnant. Since contraceptives are restricted to these ages, it is increasing the problem rather than solving it. There is need for counselling on contraceptives at least from ages of 14 and then there is need for a contraceptive referral centre. Another issue is a lot of rumours that contraceptives damage the body of the women and that it changes the hormones, causing infertility. So these women in the end don’t talk about these problems when they visit health centres and the doctor will not follow up. The women end up concluding that every contraceptive is damaging to their bodies. This project started to have an impact in its second and the third year. Sex workers had learnt about safe services, and how to tell a health institution that they had had a miscarriage. The majority of the feedback has been positive. Abortion should be legalised. The legislators should learn about the stories and they can get a precise picture of the level of deaths caused by unsafe abortion. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 April 2024
From garbage collector to sexual health counsellor
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Ali. I have worked with Lady Mermaid’s Bureau (LMB) for eight years as a programme officer and I am also a consultant on safe abortion. LMB was founded by three sex workers in 2002. It is the oldest sex worker’s organisation in Eastern Africa. When it started, LMB arranged for sex workers to meet Parliament and expose all the problems that sex workers have to face. They originally thought the government would only take two years to legalise sex work. That was obviously not the case and as advisers we said it would take a lot of time talking about their sexual health and other problems. Before I became an adviser I was working with a garbage collection company. I was the night supervisor and I had a lot of friends who were sex workers. They would talk with me and tell me how they wanted a street where they would not be arrested. These were the workers who originally started Lady Mermaid’s Bureau. First it was for fellow sex workers to help them when they were arrested by the police. Then I came in to advise them in the set up and do what I could do to help them reach their goals. There were many problems. Talking about sex work was a taboo. When I became part of LMB nobody was talking about sex workers. The women’s movement was against sex workers. They thought it was exploitative to all women. So we had to engage most of them in our programmes until they came on board to realise sex workers rights. When the sex workers went to Parliament in 2004, that meeting acted to provide an amnesty to the women. Now they can take cases to the police. Previously, no sex worker would go to the police to report a client because she would just end up being arrested. Abortion among sex workers is still a very major issue that has to be looked at by the government. Many women are very vulnerable to becoming sex workers. They are poor, from slums and a lot of them are students. They face a lot of violence: rape, the police themselves use them (ask for sex) and then there are clients who rape the women. So there are a lot of incidences of violence that turn into unwanted pregnancies. Most of the women will resort to aborting if they face such violence because they don’t know the father of the child. If you go to a private clinic it can cost 120,000 to 250,000 Uganda shillings. Also, service providers will not tell the sex workers that there is a cheaper way of doing abortions. They try to escalate the costs. Sex workers aren't told about how they can take misoprostol from home and then they can follow up onto the clinic. So the service is perceived to be high although it could be cheaper to abort. We have seen women who have not been able to access safe abortion. We have a young lady here who tried to abort unsafely because it was too expensive for her to have a safe abortion. Again she was afraid that she would be arrested, she was afraid that nurses at the clinic would stigmatise her. So she tried to abort the local way but it didn’t work and now she has a child. Countrywide the problem is lack of contraceptives: you find that some women have aborted two or three times, and then there's the problem of not counselling on contraceptive use and the lack of contraceptives in private and public health institutions. In many cases the men don’t want to use the male condoms and there aren't many female condoms on the market and they are extremely expensive. It is really very important for women to have information about contraceptives and can access contraceptive methods. These days we have sex workers ranging from 14 year to 38 years. Most of these young girls have been trafficked from the villages. Some come from the villages where they are promised some work in the city and they end up into sex work. Some are refugees who have come from Congo, others have come from Rwanda and others have come from South Sudan. We also have sex workers who are students from the colleges. And then we have young ladies who have grown up in slum areas of Kawempe, Katanag in Makerere, Natete who have been orphaned and left to fend for their families. There are the older ladies who work on the streets to sell tomatoes. They give out their numbers to clients or men who can raise them on call. And another group of older women work from their homes in slum areas where pimps take customers to them. There are also some high-class sex workers from 20-32 years old. They work in posh shops in Kampala where they give out business cards. There are sex workers who have pimps that use social media like Facebook and badoo to expose the women. Men just call the pimp who will bring the sex worker. Getting contraceptives to girls under 14 is also a big issue which parliament needs to look at. Now a lot of young ladies find themselves in distress. Most of them come from the villages and most of them have lost parents. They enter into sex work from 14 and they find themselves becoming pregnant. Since contraceptives are restricted to these ages, it is increasing the problem rather than solving it. There is need for counselling on contraceptives at least from ages of 14 and then there is need for a contraceptive referral centre. Another issue is a lot of rumours that contraceptives damage the body of the women and that it changes the hormones, causing infertility. So these women in the end don’t talk about these problems when they visit health centres and the doctor will not follow up. The women end up concluding that every contraceptive is damaging to their bodies. This project started to have an impact in its second and the third year. Sex workers had learnt about safe services, and how to tell a health institution that they had had a miscarriage. The majority of the feedback has been positive. Abortion should be legalised. The legislators should learn about the stories and they can get a precise picture of the level of deaths caused by unsafe abortion. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
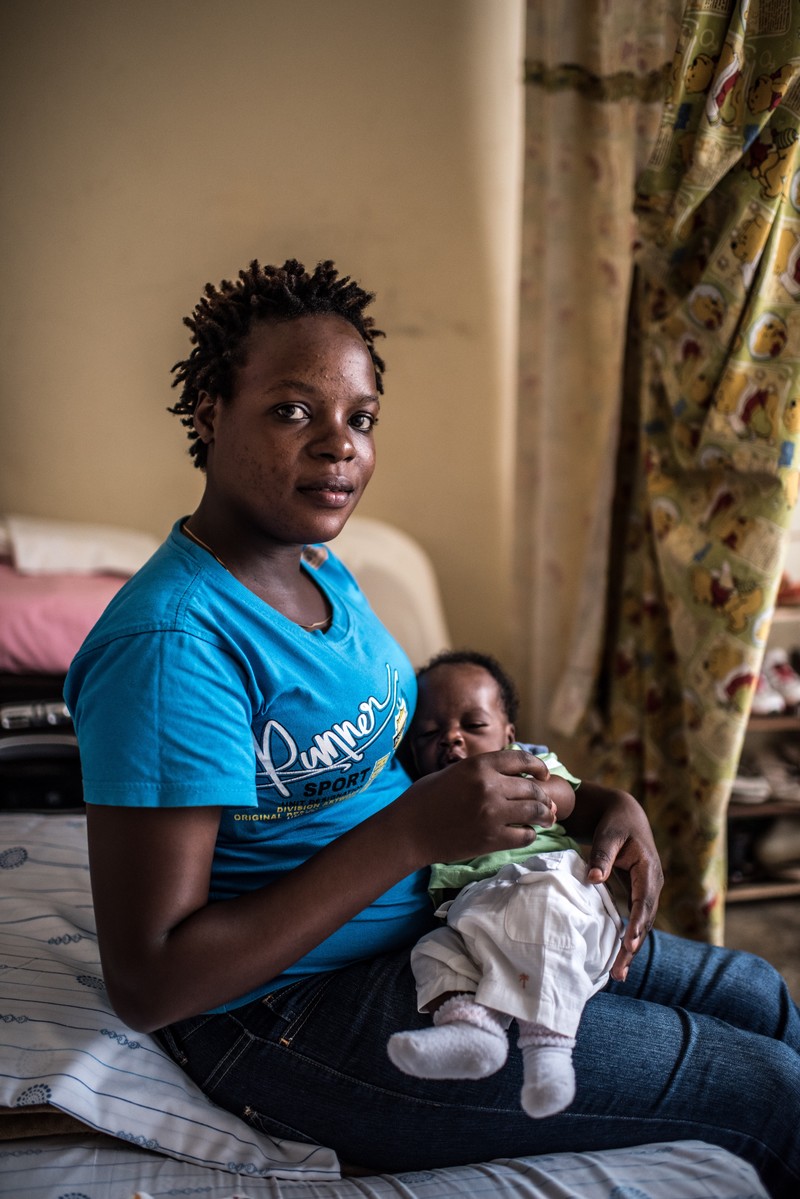
| 20 May 2017
Life-changing post-abortion care for sex workers
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Masitula. I’m a single mother of two sons and I'm a sex worker. I live in Nansana Wakiso district, it is near Kampala. Every evening I travel 10 kilometres to Natete, a Kampala city suburb where I am a sex worker. I got pregnant after a client refused to wear a condom. I attempted to abort using some unsafe abortion practices but I was unsuccessful. I now have a two-month old baby whose father I do not know. My eldest son is seven years, he is in primary school. The other one is two months. I became a sex worker after a friend advised me that this job can provide me with some income. My husband left me six years ago for another woman when my eldest was only one. He doesn’t give me a single penny for taking care of his son. I used to be a teacher but the income is little. So I have been a sex worker for six years. There are many problems for sex workers here. One is with the police. The police catch us, take our money and sometimes force us to have sex. The other problem is that those men who buy us, some of them don’t pay. They just use us and they don’t pay. It affects me because when you go to work and you don’t get any income, it is bad. They use you for free. And I don’t have anyone to take care of my kids. So sometimes I don’t work I just stay at home because no one will take care of my kids. I live only with my children. I don’t have anyone else. Sometimes I have to take my baby with me and if I get a job, then I give him to my friend until I finish. It is difficult with such a little baby but there is nothing I can do. I don’t even know the father. He just forced me. He said that he will not put on a condom. So that is why I tried to abort with herbs, but it didn't work.They caused me a lot of pain and I was about to die. I didn’t go for a safe abortion because with this government of ours, it is not easy to go to the hospital and tell them that I want to abort. You just go and tell them that you want medicine for ulcers. But Lady Mermaid's Bureau, supported by SAAF, has helped me and other sex workers. When you call them they come immediately. When you are sick they take you to hospital. In everything they are good. When I get some problems, I just go and tell them. They do what other people can’t do. It has changed my life because I now have a friend. They are my friends. I take them as part of my family because I don’t have any family. My father died, I don’t have a mother and my husband left me. They are my family now. Abortion should be legal and also sex work because it is a job. We don’t want to do it. It's just because we don’t have anything else and that is why we do it. So the government should also take us as human beings. No one treats us as human beings. And to prevent women from having unsafe abortions the government should provide people with jobs and factories to work in. So that they don't have to do sex work because it affects these girls, and some of them are like me. We don’t have jobs, you go and look for a job, you don’t find the job and you just find yourself doing this sex working job instead. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
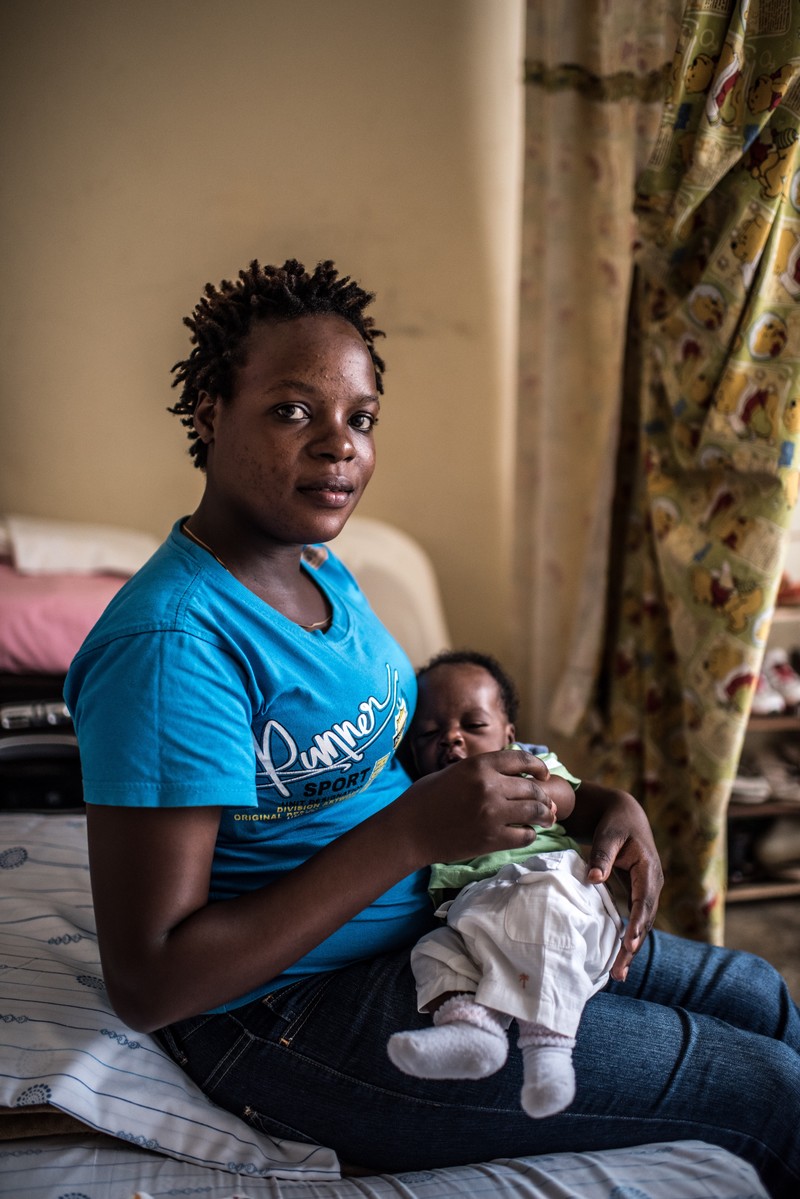
| 16 April 2024
Life-changing post-abortion care for sex workers
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. My name is Masitula. I’m a single mother of two sons and I'm a sex worker. I live in Nansana Wakiso district, it is near Kampala. Every evening I travel 10 kilometres to Natete, a Kampala city suburb where I am a sex worker. I got pregnant after a client refused to wear a condom. I attempted to abort using some unsafe abortion practices but I was unsuccessful. I now have a two-month old baby whose father I do not know. My eldest son is seven years, he is in primary school. The other one is two months. I became a sex worker after a friend advised me that this job can provide me with some income. My husband left me six years ago for another woman when my eldest was only one. He doesn’t give me a single penny for taking care of his son. I used to be a teacher but the income is little. So I have been a sex worker for six years. There are many problems for sex workers here. One is with the police. The police catch us, take our money and sometimes force us to have sex. The other problem is that those men who buy us, some of them don’t pay. They just use us and they don’t pay. It affects me because when you go to work and you don’t get any income, it is bad. They use you for free. And I don’t have anyone to take care of my kids. So sometimes I don’t work I just stay at home because no one will take care of my kids. I live only with my children. I don’t have anyone else. Sometimes I have to take my baby with me and if I get a job, then I give him to my friend until I finish. It is difficult with such a little baby but there is nothing I can do. I don’t even know the father. He just forced me. He said that he will not put on a condom. So that is why I tried to abort with herbs, but it didn't work.They caused me a lot of pain and I was about to die. I didn’t go for a safe abortion because with this government of ours, it is not easy to go to the hospital and tell them that I want to abort. You just go and tell them that you want medicine for ulcers. But Lady Mermaid's Bureau, supported by SAAF, has helped me and other sex workers. When you call them they come immediately. When you are sick they take you to hospital. In everything they are good. When I get some problems, I just go and tell them. They do what other people can’t do. It has changed my life because I now have a friend. They are my friends. I take them as part of my family because I don’t have any family. My father died, I don’t have a mother and my husband left me. They are my family now. Abortion should be legal and also sex work because it is a job. We don’t want to do it. It's just because we don’t have anything else and that is why we do it. So the government should also take us as human beings. No one treats us as human beings. And to prevent women from having unsafe abortions the government should provide people with jobs and factories to work in. So that they don't have to do sex work because it affects these girls, and some of them are like me. We don’t have jobs, you go and look for a job, you don’t find the job and you just find yourself doing this sex working job instead. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
| 20 April 2017
Sex workers in Uganda find hope
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. Joanne is a sex-worker who has been involved in the project run by Lady Mermaid's Bureau, funded by SAAF. "My name is Joanne, I have been a sex-worker for two years." Joanne was abused as a child and became pregnant at a very young age. She was forced to leave school with only a primary education and could not speak English very well. When she moved to Kampala from her village she was told she could get a good job but she had nowhere to stay and ended up becoming a sex-worker in order to support herself and her two children. While sex-work offers some financial support, the fact that it is illegal and that gender inequality is high in Uganda make sex workers very vulnerable to rape and violence. "The problems are very many. Men don’t want to pay. Someone uses you but he does not want to pay. We are being beaten, and there's a lot of stress and competition." "There is a lot of competition between sex workers. Sometimes you go on the streets and no man is going to buy you and you end up not earning a single coin. Other times, when that man buys you, he tells you the money, you negotiate when you go to the lodge the man does not pay you. That is the most hard thing because you need to feed your children, but someone does not pay you. The men beat us when we are in the lodges. They are rough, they don’t want to use condoms, you tell him to use a condom, and he does not want to use a condom. So they end up infecting you sometimes. My other sex workers most of them got infected through that. We are even being raped by policemen sometimes. They come on the streets to chase us away and if we stay on the streets to work, the policemen force you. When a policeman arrests you, he takes you to a police station because you don’t have money. He asks what you can offer if you want to leave jail. You will say, "I have nothing I don’t have money." So the only thing you can do is to have sex with him. Then he will release you. Women cells are not the same as the ones for men - sometimes you are there alone at night. So police cells are being used to rape women. He has not paid you so that is rape - he has just forced you. There are many women who got pregnant because of this rape. Even me. I have had two abortions." Joanne used local herbs to terminate her pregnancy which led to complications. Then her friend told her about Lady Mermaid's Bureau and they referred her to IPPF's Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) who were able to help her. Since being involved with Lady Mermaid's Bureau Joanne has been taught English and computer skills and has also got access to contraception and legal support. She thinks that both sex-work and abortion should be legalised in Uganda to reduce the stigma that leads to violence and abuse. "At times men don't respect us as sex-workers. Because it is illegal they abuse you. If they legalise it, it will be good." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
| 16 April 2024
Sex workers in Uganda find hope
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. Joanne is a sex-worker who has been involved in the project run by Lady Mermaid's Bureau, funded by SAAF. "My name is Joanne, I have been a sex-worker for two years." Joanne was abused as a child and became pregnant at a very young age. She was forced to leave school with only a primary education and could not speak English very well. When she moved to Kampala from her village she was told she could get a good job but she had nowhere to stay and ended up becoming a sex-worker in order to support herself and her two children. While sex-work offers some financial support, the fact that it is illegal and that gender inequality is high in Uganda make sex workers very vulnerable to rape and violence. "The problems are very many. Men don’t want to pay. Someone uses you but he does not want to pay. We are being beaten, and there's a lot of stress and competition." "There is a lot of competition between sex workers. Sometimes you go on the streets and no man is going to buy you and you end up not earning a single coin. Other times, when that man buys you, he tells you the money, you negotiate when you go to the lodge the man does not pay you. That is the most hard thing because you need to feed your children, but someone does not pay you. The men beat us when we are in the lodges. They are rough, they don’t want to use condoms, you tell him to use a condom, and he does not want to use a condom. So they end up infecting you sometimes. My other sex workers most of them got infected through that. We are even being raped by policemen sometimes. They come on the streets to chase us away and if we stay on the streets to work, the policemen force you. When a policeman arrests you, he takes you to a police station because you don’t have money. He asks what you can offer if you want to leave jail. You will say, "I have nothing I don’t have money." So the only thing you can do is to have sex with him. Then he will release you. Women cells are not the same as the ones for men - sometimes you are there alone at night. So police cells are being used to rape women. He has not paid you so that is rape - he has just forced you. There are many women who got pregnant because of this rape. Even me. I have had two abortions." Joanne used local herbs to terminate her pregnancy which led to complications. Then her friend told her about Lady Mermaid's Bureau and they referred her to IPPF's Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) who were able to help her. Since being involved with Lady Mermaid's Bureau Joanne has been taught English and computer skills and has also got access to contraception and legal support. She thinks that both sex-work and abortion should be legalised in Uganda to reduce the stigma that leads to violence and abuse. "At times men don't respect us as sex-workers. Because it is illegal they abuse you. If they legalise it, it will be good." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 05 March 2017
Forced into marriage at 16
High up in the mountains of Rasuwa in northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border, is the village of Gatlang. This tight-knit village of traditional stone houses and Buddhist stupas is home to the Tamang people: a Buddhist indigenous group for whom family life is strictly patriarchal. Marriage traditions here can be oppressive: when a man chooses a wife, the girls – many are as young as 14 – have little choice but to marry. Most then go on to have large families, meaning food, money and education are spread sparsely. Jomini Tamang was just 16 years old when her parents forced her to marry. “I don’t want to get married,” she told them, but the wedding went ahead anyway. Jomini lives in Gatlang, a remote village of traditional stone and carved wooden houses, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border. The people here are Tamang, a Buddhist ethnic group, and family life is strictly patriarchal. Many Tamang marry young – from around 14 years old – and girls tend to be pushed into marriage by both their parents and the young men who choose them. “It’s not easy being married, it’s difficult,” says Jomini, whose husband is eight years older than her. “When I got married, I didn’t know anything about what happens after marriage, about the physical side.” After a year of marriage, Jomini had her first child, a boy called Gauran, who is now two. Women like Jomini are expected to combine childcare with household chores and long shifts farming vegetables in the village fields. “After the birth, I had many difficulties. Bringing up a child in this remote village was frightening and challenging, and Gauran was ill a lot". Giving birth at a young age can lead to severe physical complications or death, and maternal mortality is one of the leading causes of death for women in Nepal. Only 60% of women receive skilled antenatal support. Luckily for Jomini, shortly after Gauran’s birth, the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), Nepal’s leading family planning NGO, stepped in to help. Jomini met Pasang Tamang, a local woman who works as a reproductive health female volunteer for FPAN. Through Pasang, Jomini learned about different contraceptive methods and, with careful advice and support, was able to think through which might be best for her. She opted for the contraceptive injection, and says she is much happier now: contraception has given her more freedom, and the space to think clearly about when to have another child. Jomini’s experiences have convinced her to do everything possible to enable her children to live happier lives, less constrained by patriarchy and marriage. If she has a daughter, “I will tell her not to get married at an early age like her mum, and that if she does, she will suffer,” she says. “I will advise her to study more so she can work.” “And I will advise my son the same! Study more and wait til you are more mature to get married.” Stories Read more stories from Nepal

| 16 April 2024
Forced into marriage at 16
High up in the mountains of Rasuwa in northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border, is the village of Gatlang. This tight-knit village of traditional stone houses and Buddhist stupas is home to the Tamang people: a Buddhist indigenous group for whom family life is strictly patriarchal. Marriage traditions here can be oppressive: when a man chooses a wife, the girls – many are as young as 14 – have little choice but to marry. Most then go on to have large families, meaning food, money and education are spread sparsely. Jomini Tamang was just 16 years old when her parents forced her to marry. “I don’t want to get married,” she told them, but the wedding went ahead anyway. Jomini lives in Gatlang, a remote village of traditional stone and carved wooden houses, high up in the mountains of northern Nepal, close to the Tibetan border. The people here are Tamang, a Buddhist ethnic group, and family life is strictly patriarchal. Many Tamang marry young – from around 14 years old – and girls tend to be pushed into marriage by both their parents and the young men who choose them. “It’s not easy being married, it’s difficult,” says Jomini, whose husband is eight years older than her. “When I got married, I didn’t know anything about what happens after marriage, about the physical side.” After a year of marriage, Jomini had her first child, a boy called Gauran, who is now two. Women like Jomini are expected to combine childcare with household chores and long shifts farming vegetables in the village fields. “After the birth, I had many difficulties. Bringing up a child in this remote village was frightening and challenging, and Gauran was ill a lot". Giving birth at a young age can lead to severe physical complications or death, and maternal mortality is one of the leading causes of death for women in Nepal. Only 60% of women receive skilled antenatal support. Luckily for Jomini, shortly after Gauran’s birth, the Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN), Nepal’s leading family planning NGO, stepped in to help. Jomini met Pasang Tamang, a local woman who works as a reproductive health female volunteer for FPAN. Through Pasang, Jomini learned about different contraceptive methods and, with careful advice and support, was able to think through which might be best for her. She opted for the contraceptive injection, and says she is much happier now: contraception has given her more freedom, and the space to think clearly about when to have another child. Jomini’s experiences have convinced her to do everything possible to enable her children to live happier lives, less constrained by patriarchy and marriage. If she has a daughter, “I will tell her not to get married at an early age like her mum, and that if she does, she will suffer,” she says. “I will advise her to study more so she can work.” “And I will advise my son the same! Study more and wait til you are more mature to get married.” Stories Read more stories from Nepal








