Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.
Most Popular This Week
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
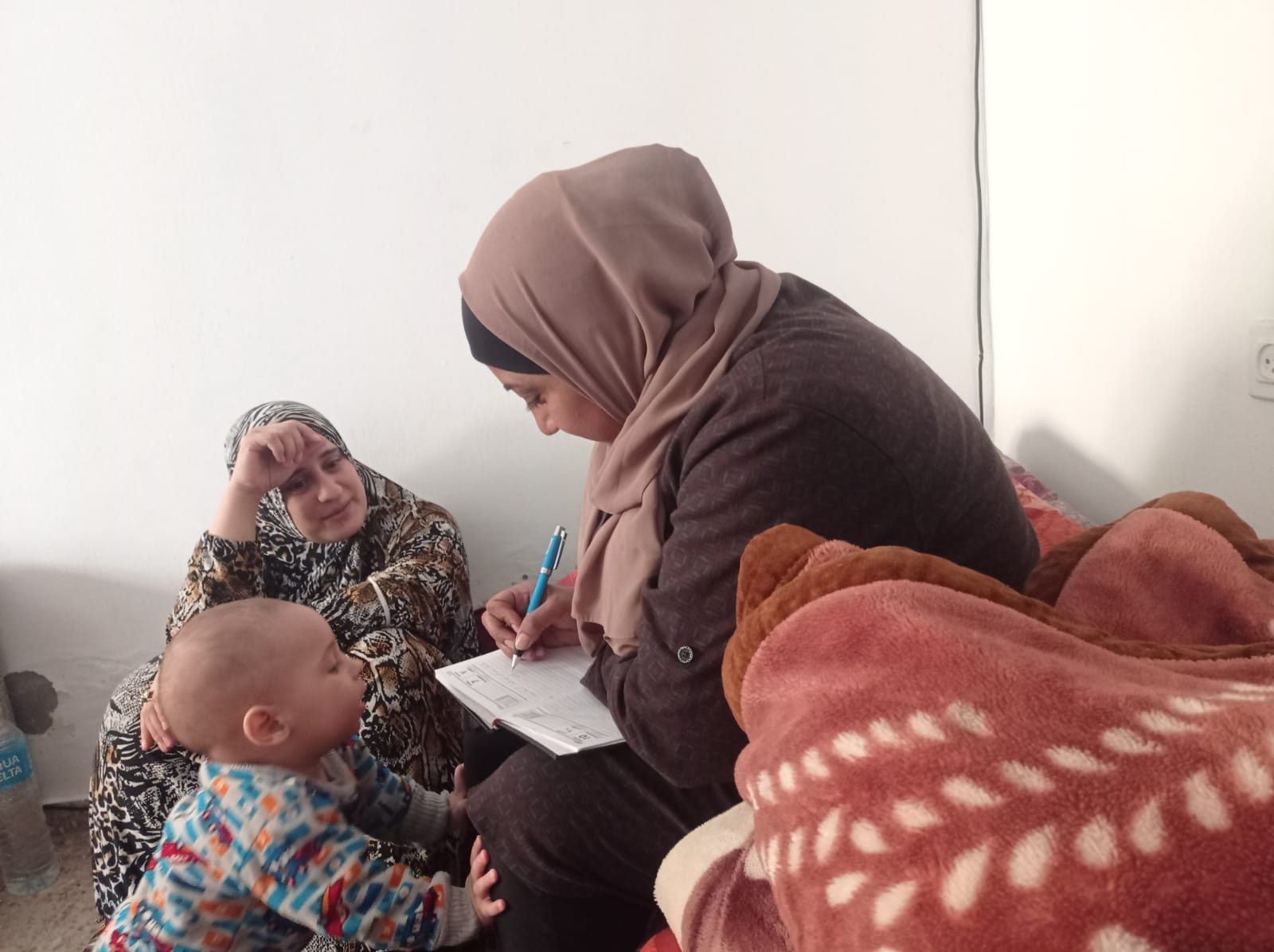

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
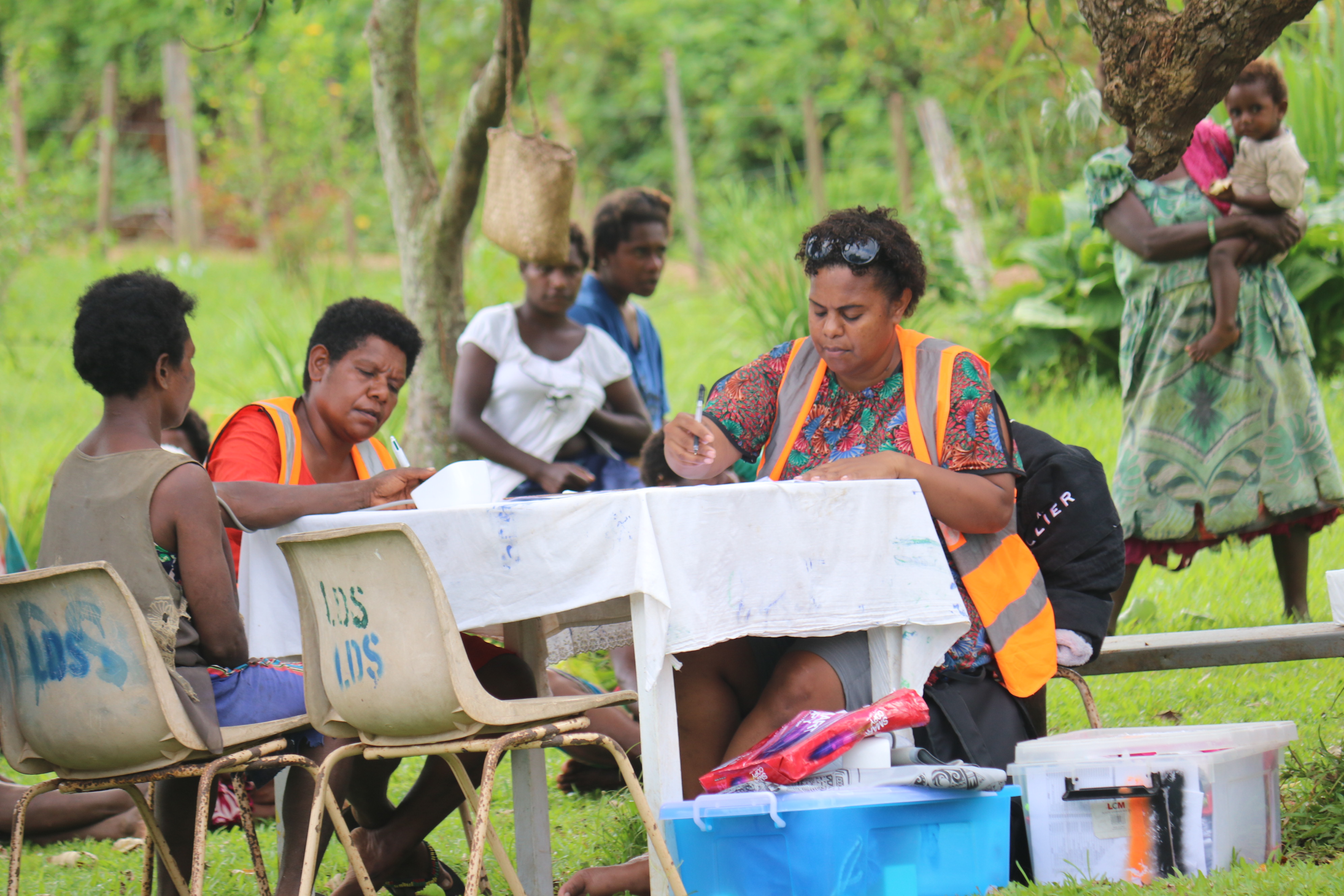

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Vanuatu

Sex: changing minds and winning hearts in Tanna, Vanuatu
“Very traditional.” These two words are often used to describe the people of Tanna in Vanuatu, one of the most populated islands in the small country in the Pacific.
Vanuatu
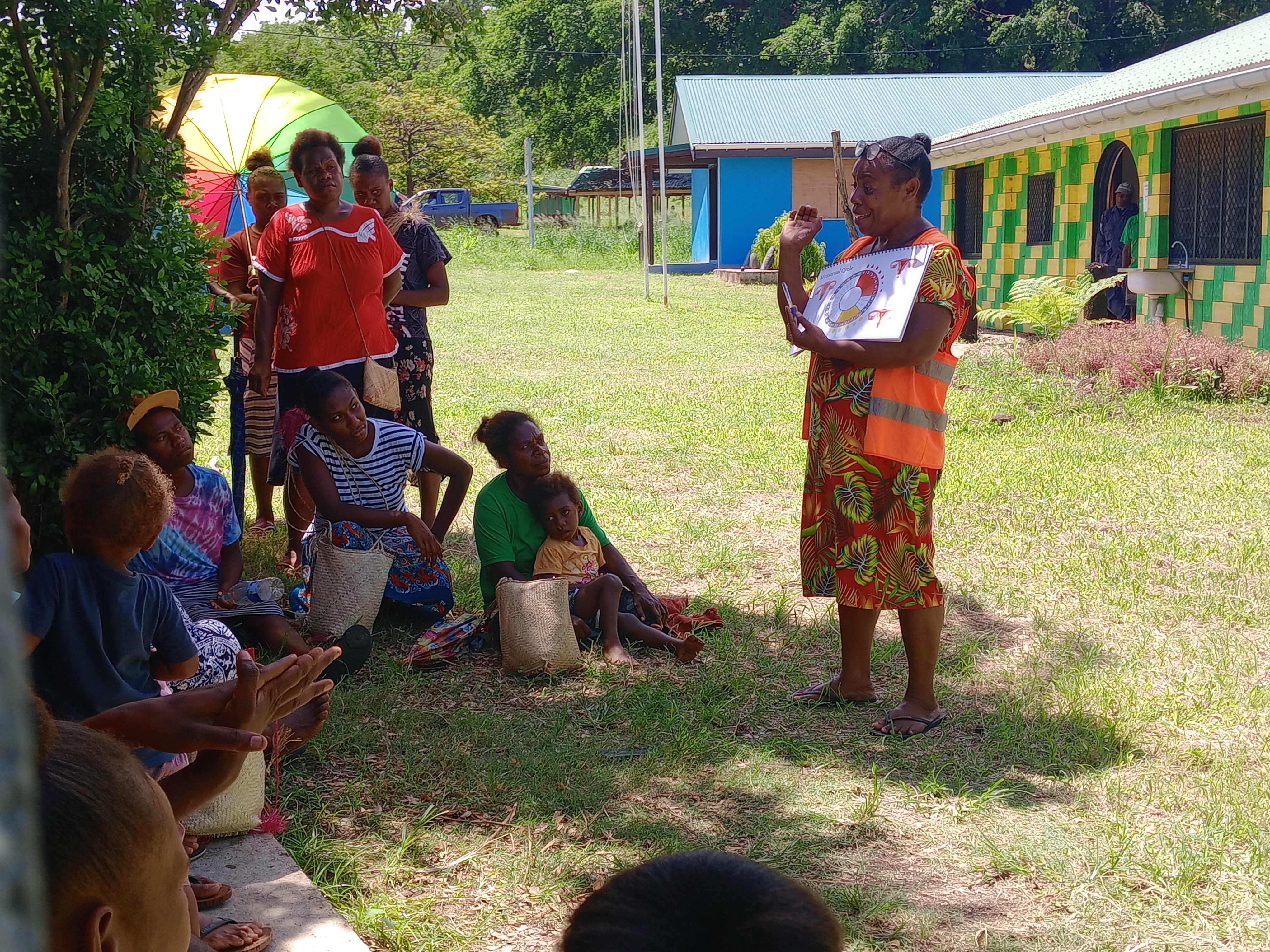

Vanuatu cyclone response: The mental health toll on humanitarian providers
Girls and women from nearby villages flock to mobile health clinics set up by the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA).
Cook Islands

Trans & Proud: Being Transgender in the Cook Islands
It’s a scene like many others around the world: a loving family pour over childhood photos, giggling and reminiscing about the memories.
Cook Islands

In Pictures: The activists who helped win LGBTI+ rights in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands has removed a law that criminalizes homosexuality, in a huge victory for the local LGBTI+ community.
Filter our stories by:
- Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille
- Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia
- Family Planning Association of Nepal
- Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA)
- Reproductive & Family Health Association of Fiji
- Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC)
- Reproductive Health Uganda
- Somaliland Family Health Association
- Tonga Family Health Association
- Vanuatu Family Health Association
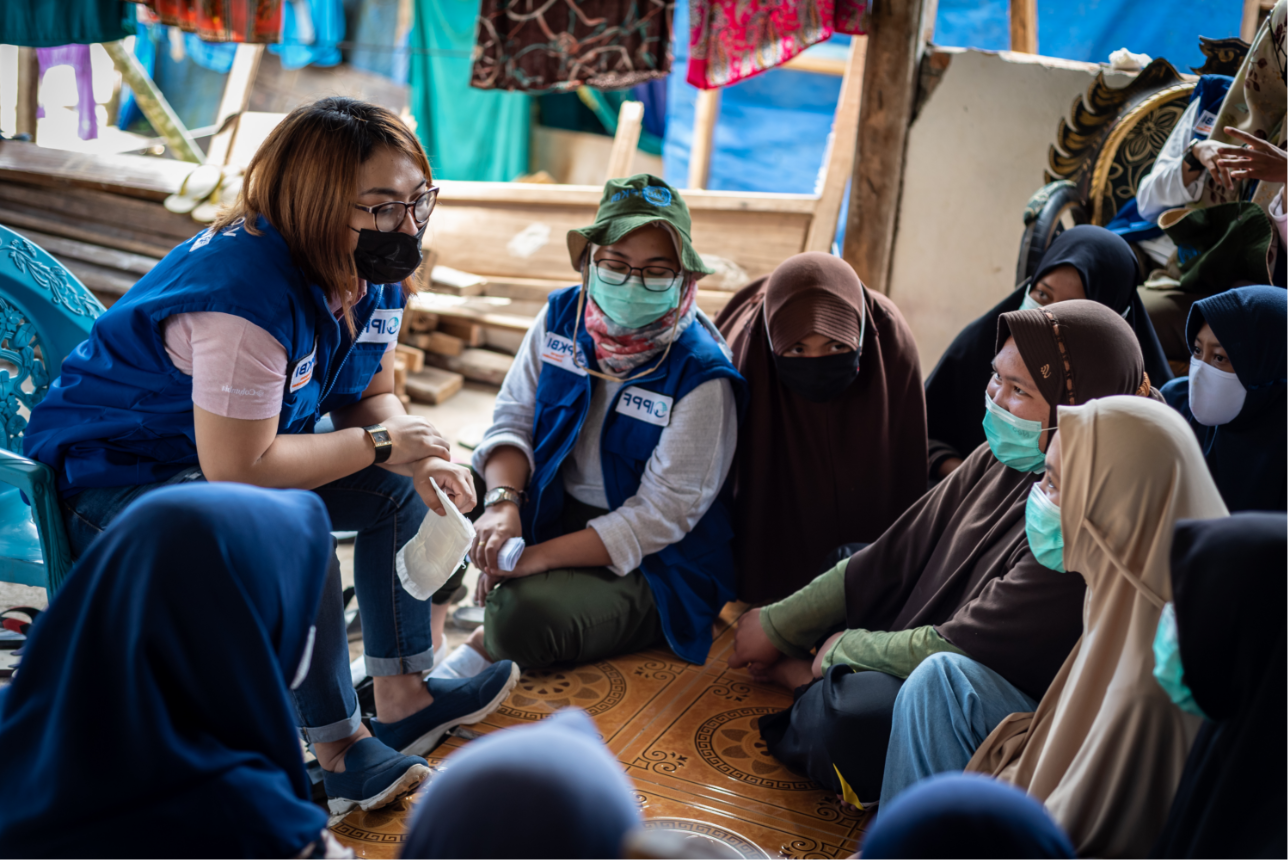


| 08 January 2021
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.

| 24 April 2024
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.
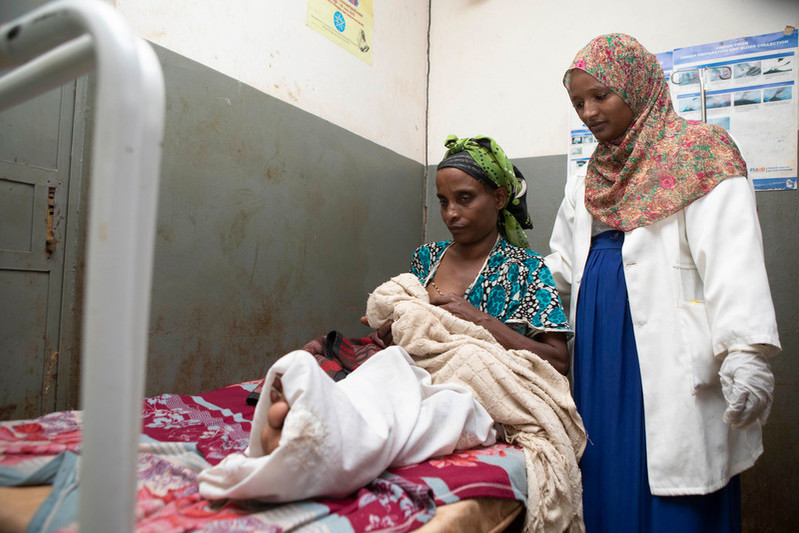

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 24 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
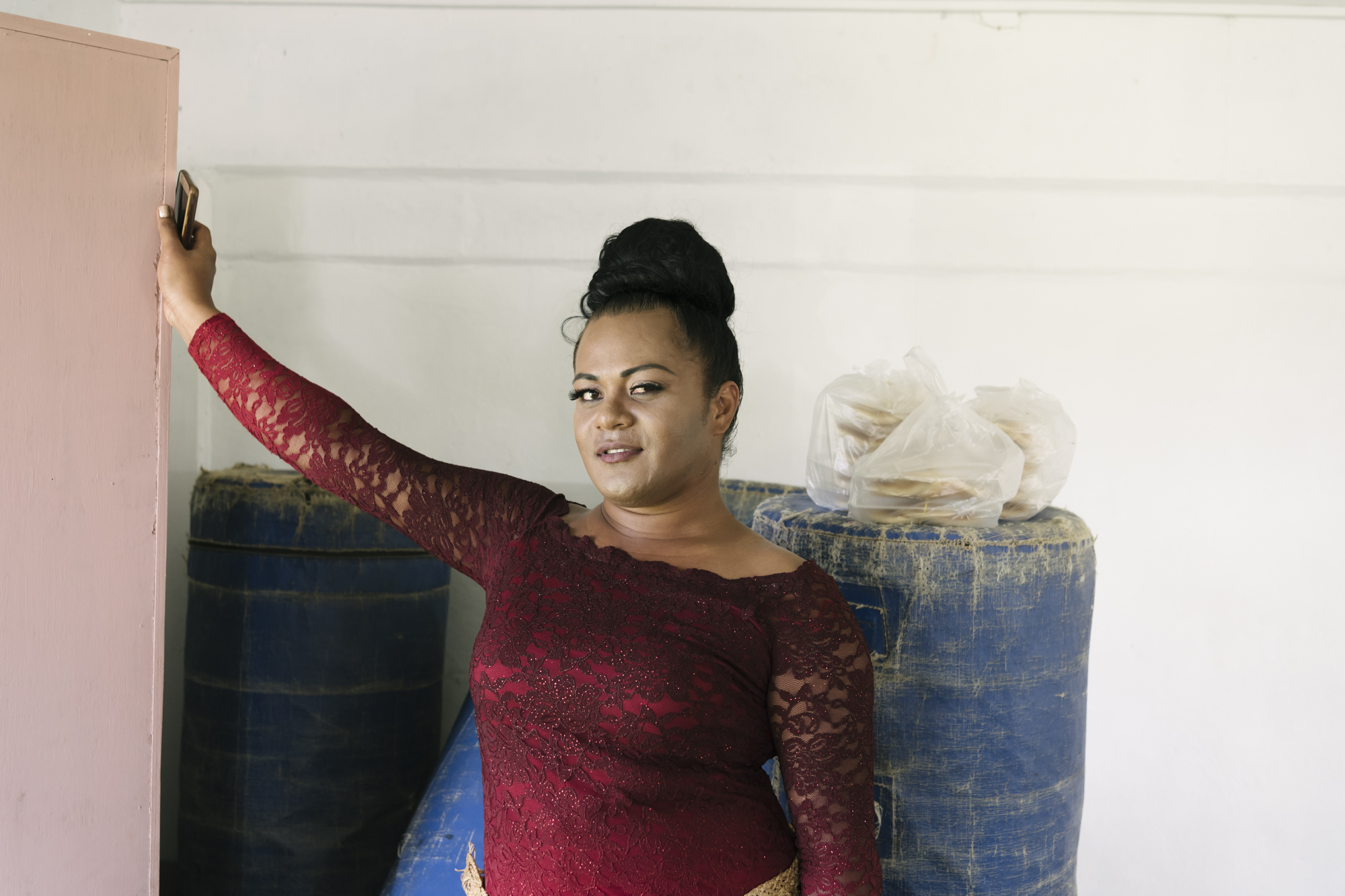
| 29 March 2018
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita
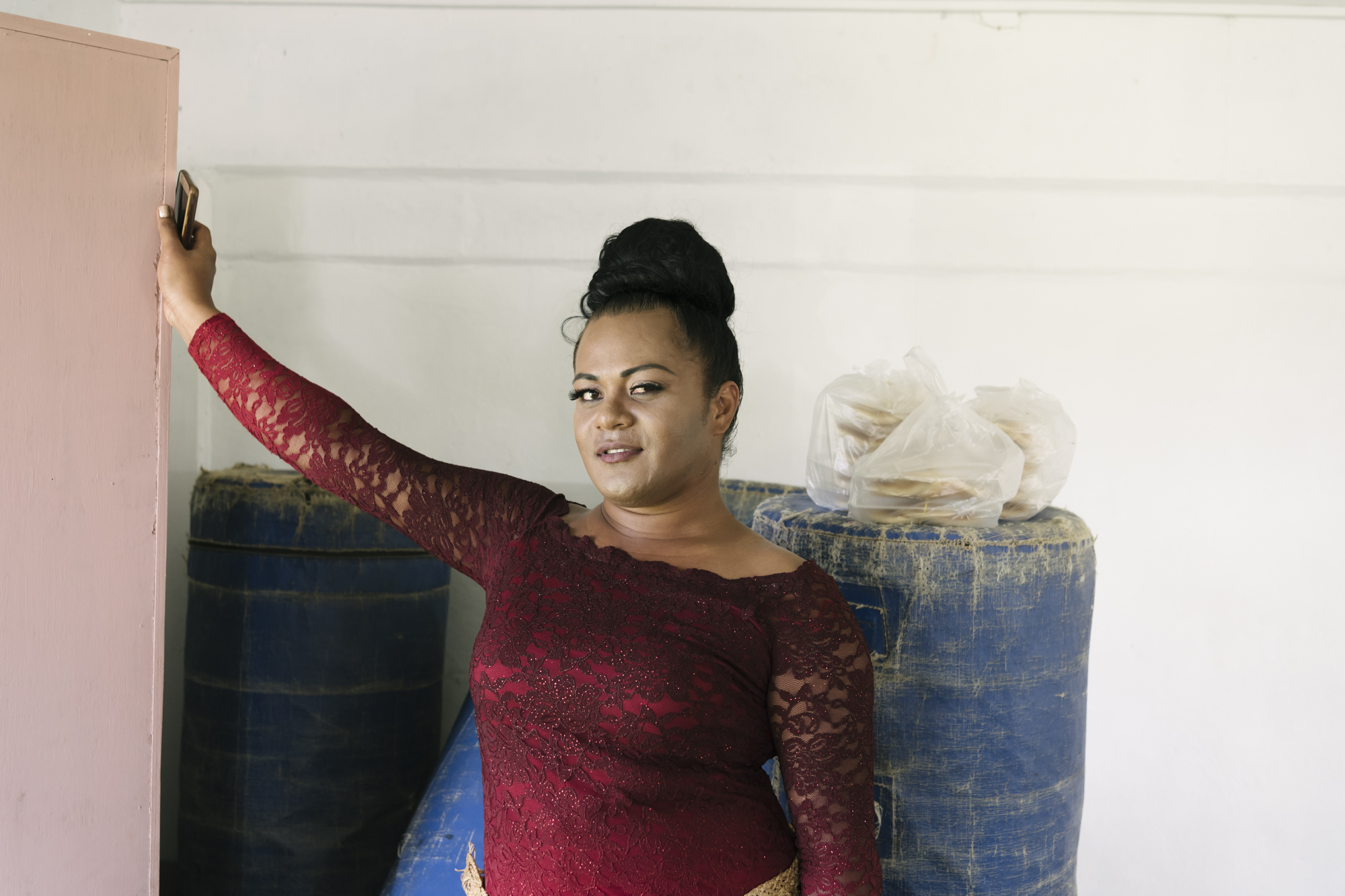
| 24 April 2024
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita

| 05 February 2018
"Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation (FGM)"
I left Somaliland when I was 9 years old with my mother, brother, uncles, aunts and cousins. It was the civil war and we were lucky enough to reach Canada as refugees. I remember that time as a pleasant, warm, loving time where my cousins and I had a lot of freedom to play, walk to school and daydream. I am from Somaliland so of course I am part of the 97-98% or so of girls who undergo the female genital cut. I think it happened when I was around seven years old. I remember being restrained. I remember strangers being around and I remember peeing standing up and it burning. These memories don’t come up often and they don’t cause me pain. It’s a distant, childhood event. A cousin and a niece my age were there and we went through it together and afterwards our mothers and aunts took care of us. I grew up, went to school, questioned the world and my role in it for a time, got married, had kids and eventually went back to Somaliland. There I met Edna Adan Ismail and asked to volunteer with her. She opened her office, hospital and life to me and I became immersed in the maternal health issues of the women in my home country. The effort to end FGM Most were not as lucky as I had been. Because of FGM/C (female genital mutilation/circumcision), most had experienced recurring infections and difficulties in child birth. Some had formed cysts, some became infertile, and some had obstetric fistula. But few linked these problem to the cutting. At SOFHA (Somaliland Family Health Association) we’ve been working to help women (and men) understand these links and get the help they need. That’s only a part of the work. The effort to end FGM/C in Somaliland goes back almost 40 years. FGM/C programs and projects have been happening for at least the last 25 years. We’re now at the point where it’s recognized as a legitimate, critical, health and social issue. We’re on the cusp of a law against the practice and I have personally witnessed a transformation among the individuals who engage in this work. NGO and government staff tasked with working on FGM/C used to go into communities apologetically, “Sorry but we have to talk to you about this ‘issue’, we know it’s unpleasant but bear with us” to “I have 2 daughters and I have not cut them. This is a terrible practice and we must stop it now”. It fills me with great joy to see young women and men taking this personal stance and doing it confidently and proudly. But it’s not easy for most people to do this. It certainly wasn’t for me. This is personal. This is private. Before I got into the work I might have said, “What business is it of yours anyway? Do you really want me digging into your private life? Into your past and history? I am not a victim. I may be a survivor but not in the way you think and not for the reasons you imagine. I am bigger than this. This doesn’t define me.” Dignity, bravery, respect And it may not define most Somali women. I think that’s what confuses many people. Maybe it’s because it happens in childhood and those memories are lost or hidden or maybe because mothers and grandmothers have such good intentions or maybe because it’s so universal within the community? That’s why it’s a completely different experience for a young Somali girl born and brought up somewhere else. The experience is very personal and it varies from person to person. Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation. In Somaliland, a dynamic young generation connected to the world through the internet, and integrated multi-pronged FGM/C programming, is helping us to influence a generation of Somalis to abandon the cut and break the cycle. It’s still some distance away but we see the end in sight. Words Amal Ahmed, the executive director of our Member Association in Somaliland (SOFHA)

| 24 April 2024
"Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation (FGM)"
I left Somaliland when I was 9 years old with my mother, brother, uncles, aunts and cousins. It was the civil war and we were lucky enough to reach Canada as refugees. I remember that time as a pleasant, warm, loving time where my cousins and I had a lot of freedom to play, walk to school and daydream. I am from Somaliland so of course I am part of the 97-98% or so of girls who undergo the female genital cut. I think it happened when I was around seven years old. I remember being restrained. I remember strangers being around and I remember peeing standing up and it burning. These memories don’t come up often and they don’t cause me pain. It’s a distant, childhood event. A cousin and a niece my age were there and we went through it together and afterwards our mothers and aunts took care of us. I grew up, went to school, questioned the world and my role in it for a time, got married, had kids and eventually went back to Somaliland. There I met Edna Adan Ismail and asked to volunteer with her. She opened her office, hospital and life to me and I became immersed in the maternal health issues of the women in my home country. The effort to end FGM Most were not as lucky as I had been. Because of FGM/C (female genital mutilation/circumcision), most had experienced recurring infections and difficulties in child birth. Some had formed cysts, some became infertile, and some had obstetric fistula. But few linked these problem to the cutting. At SOFHA (Somaliland Family Health Association) we’ve been working to help women (and men) understand these links and get the help they need. That’s only a part of the work. The effort to end FGM/C in Somaliland goes back almost 40 years. FGM/C programs and projects have been happening for at least the last 25 years. We’re now at the point where it’s recognized as a legitimate, critical, health and social issue. We’re on the cusp of a law against the practice and I have personally witnessed a transformation among the individuals who engage in this work. NGO and government staff tasked with working on FGM/C used to go into communities apologetically, “Sorry but we have to talk to you about this ‘issue’, we know it’s unpleasant but bear with us” to “I have 2 daughters and I have not cut them. This is a terrible practice and we must stop it now”. It fills me with great joy to see young women and men taking this personal stance and doing it confidently and proudly. But it’s not easy for most people to do this. It certainly wasn’t for me. This is personal. This is private. Before I got into the work I might have said, “What business is it of yours anyway? Do you really want me digging into your private life? Into your past and history? I am not a victim. I may be a survivor but not in the way you think and not for the reasons you imagine. I am bigger than this. This doesn’t define me.” Dignity, bravery, respect And it may not define most Somali women. I think that’s what confuses many people. Maybe it’s because it happens in childhood and those memories are lost or hidden or maybe because mothers and grandmothers have such good intentions or maybe because it’s so universal within the community? That’s why it’s a completely different experience for a young Somali girl born and brought up somewhere else. The experience is very personal and it varies from person to person. Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation. In Somaliland, a dynamic young generation connected to the world through the internet, and integrated multi-pronged FGM/C programming, is helping us to influence a generation of Somalis to abandon the cut and break the cycle. It’s still some distance away but we see the end in sight. Words Amal Ahmed, the executive director of our Member Association in Somaliland (SOFHA)
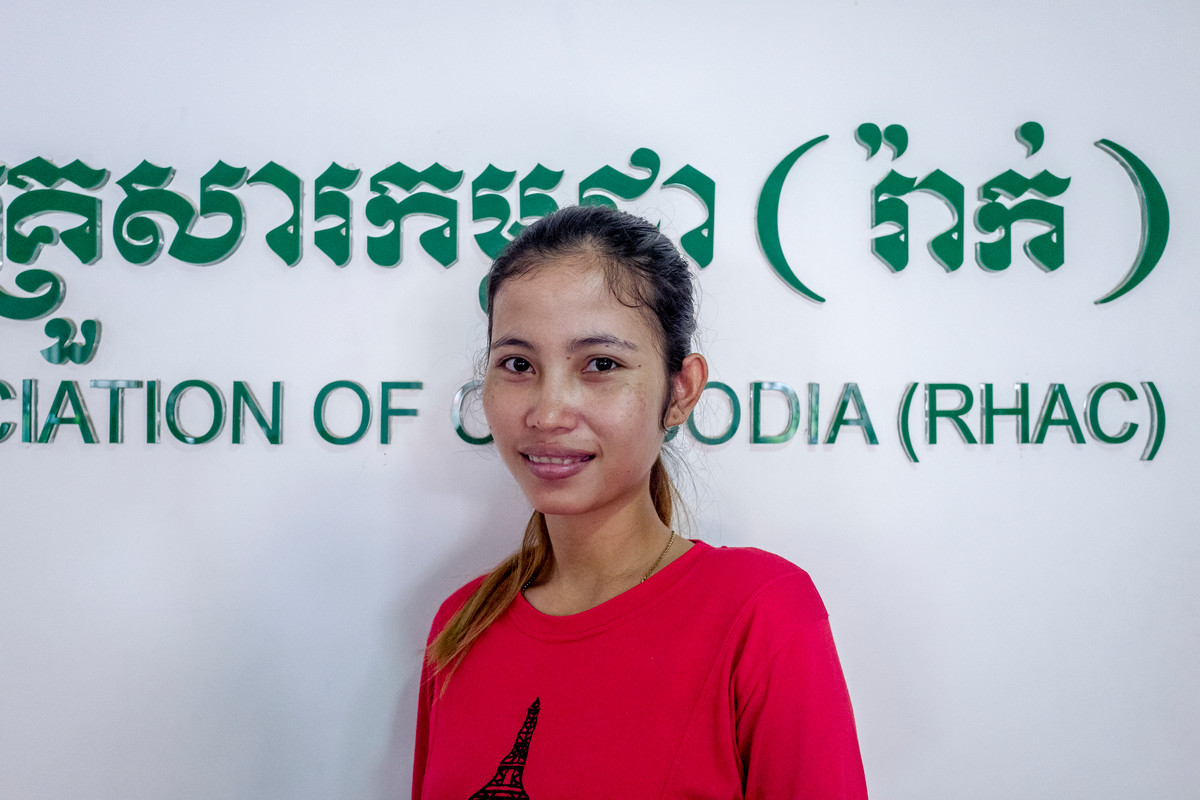

| 17 November 2017
“The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby"
When garment worker Ny thought she might be pregnant with her first child, a home test kit quickly confirmed her suspicions. But the 23-year-old – who is originally from Takeo province but moved to Phnom Penh to take up a job in the garment industry – did not know where to go to seek prenatal care. After a cousin recommended that she visit a nearby Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia clinic, Ny took her relative’s advice – and has gone back eight times to date. “I come here every month to check on the baby,” she says, cradling her belly. “I had never been before I got pregnant.” During her visits to the medical clinic, Ny says, she has had a raft of standard tests and procedures as part of her prenatal care, including two ultrasounds, blood and urine tests, and vaccinations. “The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby [such as] to eat nutritious food and not to carry heavy things,” she says. As well as caring for the health of mother and unborn child, RHAC staff have also offered up valuable family planning information. “I did not know about how to plan to have children before I came to the clinic,” Ny says. “The doctors here told me that there are three different methods of [long-term] contraception: medication, an implant and an IUD.” Ny, who sews winter clothing at a factory while her husband also works in a nearby garment factory, says she was very glad to learn about her options. “This child was unplanned, but I don’t feel any regret because I had already been married for two years. But after having the baby I plan to use birth control, though I don’t know what method I will use,” she says. “I know that I don’t want to have another child straight away. It may be two or three years until I have the next one, as I want to wait until my family’s finances improve.”

| 24 April 2024
“The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby"
When garment worker Ny thought she might be pregnant with her first child, a home test kit quickly confirmed her suspicions. But the 23-year-old – who is originally from Takeo province but moved to Phnom Penh to take up a job in the garment industry – did not know where to go to seek prenatal care. After a cousin recommended that she visit a nearby Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia clinic, Ny took her relative’s advice – and has gone back eight times to date. “I come here every month to check on the baby,” she says, cradling her belly. “I had never been before I got pregnant.” During her visits to the medical clinic, Ny says, she has had a raft of standard tests and procedures as part of her prenatal care, including two ultrasounds, blood and urine tests, and vaccinations. “The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby [such as] to eat nutritious food and not to carry heavy things,” she says. As well as caring for the health of mother and unborn child, RHAC staff have also offered up valuable family planning information. “I did not know about how to plan to have children before I came to the clinic,” Ny says. “The doctors here told me that there are three different methods of [long-term] contraception: medication, an implant and an IUD.” Ny, who sews winter clothing at a factory while her husband also works in a nearby garment factory, says she was very glad to learn about her options. “This child was unplanned, but I don’t feel any regret because I had already been married for two years. But after having the baby I plan to use birth control, though I don’t know what method I will use,” she says. “I know that I don’t want to have another child straight away. It may be two or three years until I have the next one, as I want to wait until my family’s finances improve.”
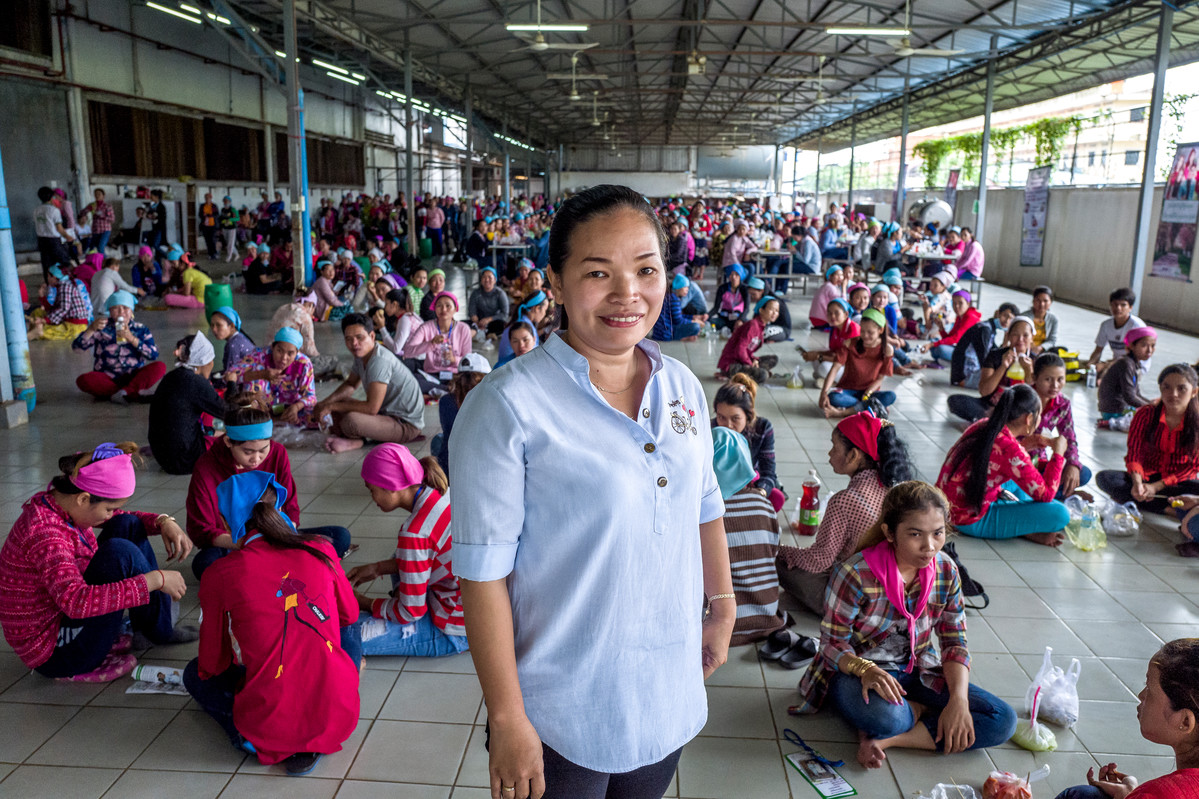

| 16 November 2017
“When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need"
Female workers, many of them undereducated migrants from rural areas, dominate the garment sector in Cambodia. And Propitious garment factory in Takhmao, a small city that lies just south of the capital Phnom Penh, is no exception. Women make up more than 90 percent of the factory’s workforce. Helping to oversee the 3,700-strong workforce is human resources manager Kouch Davy, who has worked at Propitious since it opened four years ago. Seeing a need to improve the workers’ sexual and reproductive health knowledge, she says she decided to work with the Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC) because of its reputation for providing high-quality services. “I raised it in a management meeting, and the board was happy to explore it,” she says. For almost two years, trained staff from RHAC have been visiting the factory twice a month to meet with workers during their lunch break. They answer questions on topics ranging from birth control to STIs and abortion. The organisation has also provided training to the nurses who work in the factory’s on-site medical clinic. Davy says the factory’s female garment workers have changed as a result. “They are more open to asking questions about sexual health and they have also become more informed about the subject,” she says. “When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need, so they tend to exaggerate their problems and ask for sick leave. But when they go to see an RHAC clinic and get proper treatment, there is less sick leave. “Now that they understand about contraception, there are fewer women getting pregnant and taking maternity leave, so that also helps with the workflow. ” Davy says the factory has seen requests for sick leave drop by an average of between 100 to 200 cases a month – and any decrease in absenteeism is a major boon for productivity. “The factory works like a chain: if just one person on the production line takes a day off, it affects the overall productivity,” she says. “And if a worker comes to work sick, they have problems concentrating.” Even Davy says she has gone to RHAC to seek medical care, visiting one of their clinics a few months ago for a breast examination. Meanwhile, the company that owns Propitious has extended its partnership with RHAC to a second factory in Phnom Penh. The firm has even requested that the NGO starts visiting its largest factory, which is situated in a rural province and has 10,000 workers, in the future.

| 24 April 2024
“When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need"
Female workers, many of them undereducated migrants from rural areas, dominate the garment sector in Cambodia. And Propitious garment factory in Takhmao, a small city that lies just south of the capital Phnom Penh, is no exception. Women make up more than 90 percent of the factory’s workforce. Helping to oversee the 3,700-strong workforce is human resources manager Kouch Davy, who has worked at Propitious since it opened four years ago. Seeing a need to improve the workers’ sexual and reproductive health knowledge, she says she decided to work with the Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC) because of its reputation for providing high-quality services. “I raised it in a management meeting, and the board was happy to explore it,” she says. For almost two years, trained staff from RHAC have been visiting the factory twice a month to meet with workers during their lunch break. They answer questions on topics ranging from birth control to STIs and abortion. The organisation has also provided training to the nurses who work in the factory’s on-site medical clinic. Davy says the factory’s female garment workers have changed as a result. “They are more open to asking questions about sexual health and they have also become more informed about the subject,” she says. “When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need, so they tend to exaggerate their problems and ask for sick leave. But when they go to see an RHAC clinic and get proper treatment, there is less sick leave. “Now that they understand about contraception, there are fewer women getting pregnant and taking maternity leave, so that also helps with the workflow. ” Davy says the factory has seen requests for sick leave drop by an average of between 100 to 200 cases a month – and any decrease in absenteeism is a major boon for productivity. “The factory works like a chain: if just one person on the production line takes a day off, it affects the overall productivity,” she says. “And if a worker comes to work sick, they have problems concentrating.” Even Davy says she has gone to RHAC to seek medical care, visiting one of their clinics a few months ago for a breast examination. Meanwhile, the company that owns Propitious has extended its partnership with RHAC to a second factory in Phnom Penh. The firm has even requested that the NGO starts visiting its largest factory, which is situated in a rural province and has 10,000 workers, in the future.

| 08 January 2021
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.

| 24 April 2024
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 24 April 2024
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
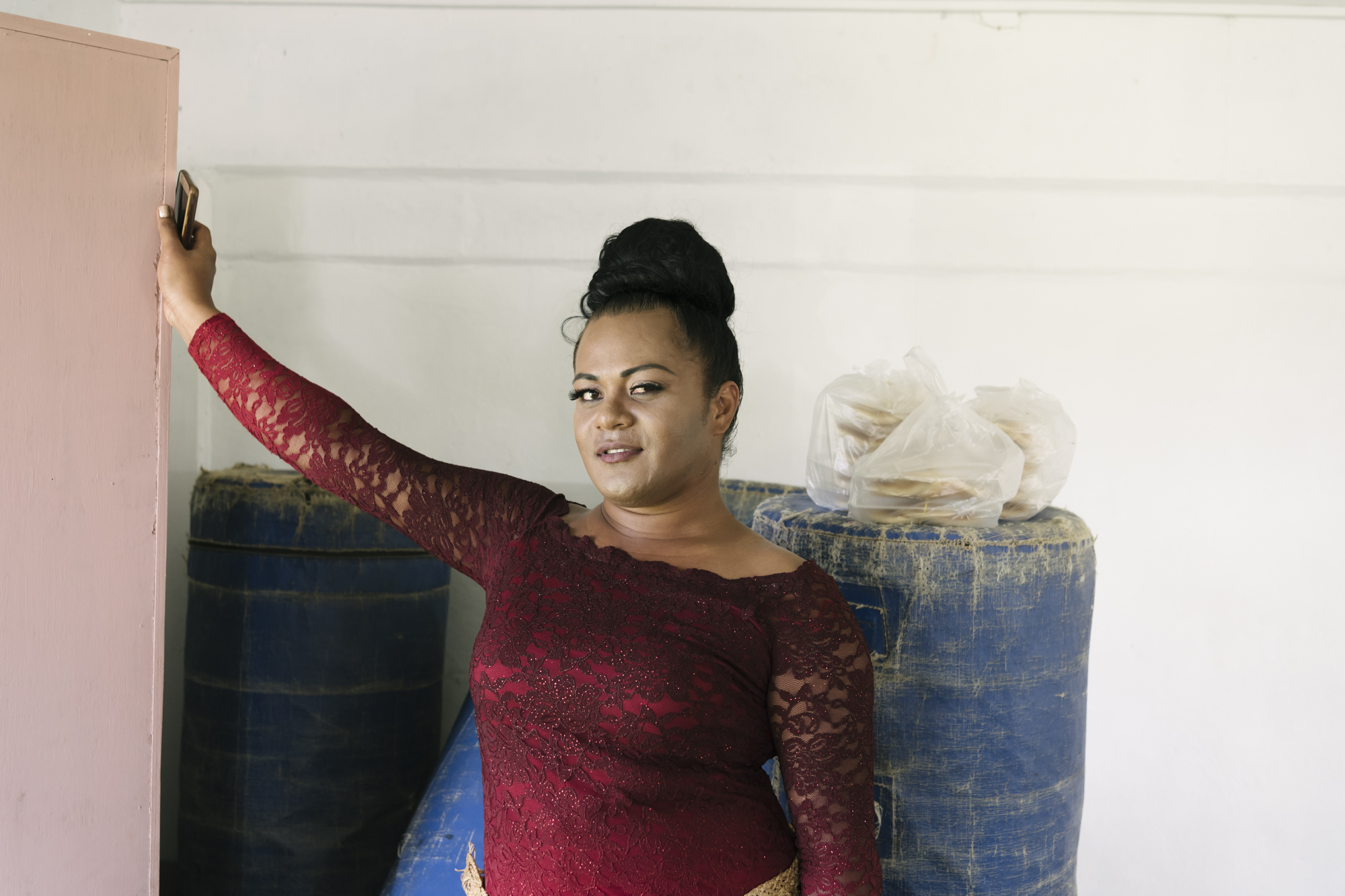
| 29 March 2018
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita
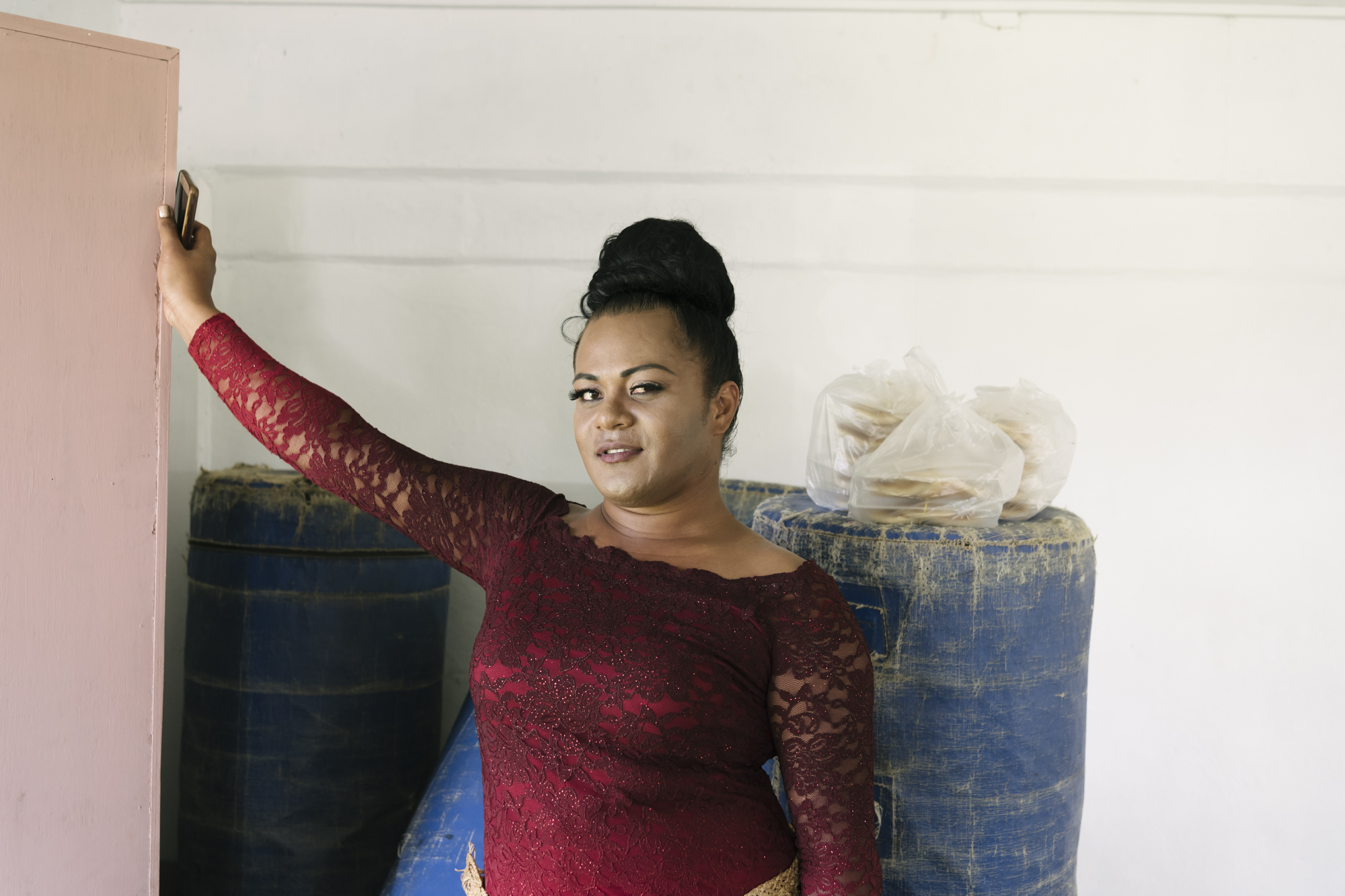
| 24 April 2024
"I have a feeling the future will be better"
Leiti is a Tongan word to describe transgender women, it comes from the English word “lady”. In Tonga the transgender community is organized by the Tonga Leiti Association (TLA), and with the support of Tonga Family Health Association (TFHA). Together they are educating people to help stop the discrimination and stigma surrounding the Leiti community. Leilani, who identifies as a leiti, has been working with the Tonga Leiti Association, supported by Tonga Health Family Association to battle the stigma surrounding the leiti and LGBTI+ community in Tonga. She says "I started to dress like a leiti at a very young age. Being a leiti in a Tongan family is very difficult because being a leiti or having a son who’s a leiti are considered shameful, so for the family (it) is very difficult to accept us. Many leitis run away from their families." Frequently facing abuse Access to health care and sexual and reproductive health service is another difficulty the leiti community face: going to public clinics, they often face abuse and are more likely to be ignored or dismissed by staff. When they are turned away from other clinics, Leilani knows she can always rely on Tonga Health Family Association for help. 'I think Tonga Family Health has done a lot up to now. They always come and do our annual HIV testing and they supply us (with) some condom because we do the condom distribution here in Tonga and if we have a case in our members or anybody come to our office we refer them to Tonga Family Health. They really, really help us a lot. They (are the) only one that can understand us." Tonga Family Health Association and Tonga Leiti Association partnership allows for both organisations to attend training workshops run by one another. A valuable opportunity not only for clinic staff but for volunteers like Leilani. "When the Tonga Family Health run the training they always ask some members from TLA to come and train with them and we do the same with them. When I give a presentation at the TFHA's clinic, I share with people what we do; I ask them for to change their mindset and how they look about us." Overcoming stigma and discrimination With her training, Leilani visits schools to help educate, inform and overcome the stigma and discrimination surrounding the leiti community. Many young leiti's drop out of school at an early age due to verbal, physical and in some cases sexual abuse. Slowly, Leilani is seeing a positive change in the schools she visits. “We go to school because there a lot of discrimination of the leiti's in high school and primary school too. I have been going from school to school for two years. My plan to visit all the schools in Tonga. We mostly go to all-boys schools is because discrimination in school is mostly done by boys. I was very happy last year when I went to a boys school and so how they really appreciate the work and how well they treated the Leiti's in the school." In February, Tonga was hit by tropical cyclone Gita, the worst cyclone to hit the island in over 60 years. Leilani worries that not enough is being done to ensure the needs of the Leiti and LGBTI+ community is being met during and post humanitarian disasters. "We are one of the vulnerable groups, after the cyclone Gita we should be one of the first priority for the government, or the hospital or any donations. Cause our life is very unique and we are easy to harm." Despite the hardships surrounding the leiti community, Leilani is hopeful for the future, "I can see a lot of families that now accept leiti's in their house and they treat them well. I have a feeling the future will be better. Please stop discriminating against us, but love us. We are here to stay, we are not here to chase away." Watch the Humanitarian teams response to Cyclone Gita

| 05 February 2018
"Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation (FGM)"
I left Somaliland when I was 9 years old with my mother, brother, uncles, aunts and cousins. It was the civil war and we were lucky enough to reach Canada as refugees. I remember that time as a pleasant, warm, loving time where my cousins and I had a lot of freedom to play, walk to school and daydream. I am from Somaliland so of course I am part of the 97-98% or so of girls who undergo the female genital cut. I think it happened when I was around seven years old. I remember being restrained. I remember strangers being around and I remember peeing standing up and it burning. These memories don’t come up often and they don’t cause me pain. It’s a distant, childhood event. A cousin and a niece my age were there and we went through it together and afterwards our mothers and aunts took care of us. I grew up, went to school, questioned the world and my role in it for a time, got married, had kids and eventually went back to Somaliland. There I met Edna Adan Ismail and asked to volunteer with her. She opened her office, hospital and life to me and I became immersed in the maternal health issues of the women in my home country. The effort to end FGM Most were not as lucky as I had been. Because of FGM/C (female genital mutilation/circumcision), most had experienced recurring infections and difficulties in child birth. Some had formed cysts, some became infertile, and some had obstetric fistula. But few linked these problem to the cutting. At SOFHA (Somaliland Family Health Association) we’ve been working to help women (and men) understand these links and get the help they need. That’s only a part of the work. The effort to end FGM/C in Somaliland goes back almost 40 years. FGM/C programs and projects have been happening for at least the last 25 years. We’re now at the point where it’s recognized as a legitimate, critical, health and social issue. We’re on the cusp of a law against the practice and I have personally witnessed a transformation among the individuals who engage in this work. NGO and government staff tasked with working on FGM/C used to go into communities apologetically, “Sorry but we have to talk to you about this ‘issue’, we know it’s unpleasant but bear with us” to “I have 2 daughters and I have not cut them. This is a terrible practice and we must stop it now”. It fills me with great joy to see young women and men taking this personal stance and doing it confidently and proudly. But it’s not easy for most people to do this. It certainly wasn’t for me. This is personal. This is private. Before I got into the work I might have said, “What business is it of yours anyway? Do you really want me digging into your private life? Into your past and history? I am not a victim. I may be a survivor but not in the way you think and not for the reasons you imagine. I am bigger than this. This doesn’t define me.” Dignity, bravery, respect And it may not define most Somali women. I think that’s what confuses many people. Maybe it’s because it happens in childhood and those memories are lost or hidden or maybe because mothers and grandmothers have such good intentions or maybe because it’s so universal within the community? That’s why it’s a completely different experience for a young Somali girl born and brought up somewhere else. The experience is very personal and it varies from person to person. Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation. In Somaliland, a dynamic young generation connected to the world through the internet, and integrated multi-pronged FGM/C programming, is helping us to influence a generation of Somalis to abandon the cut and break the cycle. It’s still some distance away but we see the end in sight. Words Amal Ahmed, the executive director of our Member Association in Somaliland (SOFHA)

| 24 April 2024
"Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation (FGM)"
I left Somaliland when I was 9 years old with my mother, brother, uncles, aunts and cousins. It was the civil war and we were lucky enough to reach Canada as refugees. I remember that time as a pleasant, warm, loving time where my cousins and I had a lot of freedom to play, walk to school and daydream. I am from Somaliland so of course I am part of the 97-98% or so of girls who undergo the female genital cut. I think it happened when I was around seven years old. I remember being restrained. I remember strangers being around and I remember peeing standing up and it burning. These memories don’t come up often and they don’t cause me pain. It’s a distant, childhood event. A cousin and a niece my age were there and we went through it together and afterwards our mothers and aunts took care of us. I grew up, went to school, questioned the world and my role in it for a time, got married, had kids and eventually went back to Somaliland. There I met Edna Adan Ismail and asked to volunteer with her. She opened her office, hospital and life to me and I became immersed in the maternal health issues of the women in my home country. The effort to end FGM Most were not as lucky as I had been. Because of FGM/C (female genital mutilation/circumcision), most had experienced recurring infections and difficulties in child birth. Some had formed cysts, some became infertile, and some had obstetric fistula. But few linked these problem to the cutting. At SOFHA (Somaliland Family Health Association) we’ve been working to help women (and men) understand these links and get the help they need. That’s only a part of the work. The effort to end FGM/C in Somaliland goes back almost 40 years. FGM/C programs and projects have been happening for at least the last 25 years. We’re now at the point where it’s recognized as a legitimate, critical, health and social issue. We’re on the cusp of a law against the practice and I have personally witnessed a transformation among the individuals who engage in this work. NGO and government staff tasked with working on FGM/C used to go into communities apologetically, “Sorry but we have to talk to you about this ‘issue’, we know it’s unpleasant but bear with us” to “I have 2 daughters and I have not cut them. This is a terrible practice and we must stop it now”. It fills me with great joy to see young women and men taking this personal stance and doing it confidently and proudly. But it’s not easy for most people to do this. It certainly wasn’t for me. This is personal. This is private. Before I got into the work I might have said, “What business is it of yours anyway? Do you really want me digging into your private life? Into your past and history? I am not a victim. I may be a survivor but not in the way you think and not for the reasons you imagine. I am bigger than this. This doesn’t define me.” Dignity, bravery, respect And it may not define most Somali women. I think that’s what confuses many people. Maybe it’s because it happens in childhood and those memories are lost or hidden or maybe because mothers and grandmothers have such good intentions or maybe because it’s so universal within the community? That’s why it’s a completely different experience for a young Somali girl born and brought up somewhere else. The experience is very personal and it varies from person to person. Dignity, respect and bravery are guiding principles for our work on female genital mutilation. In Somaliland, a dynamic young generation connected to the world through the internet, and integrated multi-pronged FGM/C programming, is helping us to influence a generation of Somalis to abandon the cut and break the cycle. It’s still some distance away but we see the end in sight. Words Amal Ahmed, the executive director of our Member Association in Somaliland (SOFHA)

| 17 November 2017
“The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby"
When garment worker Ny thought she might be pregnant with her first child, a home test kit quickly confirmed her suspicions. But the 23-year-old – who is originally from Takeo province but moved to Phnom Penh to take up a job in the garment industry – did not know where to go to seek prenatal care. After a cousin recommended that she visit a nearby Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia clinic, Ny took her relative’s advice – and has gone back eight times to date. “I come here every month to check on the baby,” she says, cradling her belly. “I had never been before I got pregnant.” During her visits to the medical clinic, Ny says, she has had a raft of standard tests and procedures as part of her prenatal care, including two ultrasounds, blood and urine tests, and vaccinations. “The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby [such as] to eat nutritious food and not to carry heavy things,” she says. As well as caring for the health of mother and unborn child, RHAC staff have also offered up valuable family planning information. “I did not know about how to plan to have children before I came to the clinic,” Ny says. “The doctors here told me that there are three different methods of [long-term] contraception: medication, an implant and an IUD.” Ny, who sews winter clothing at a factory while her husband also works in a nearby garment factory, says she was very glad to learn about her options. “This child was unplanned, but I don’t feel any regret because I had already been married for two years. But after having the baby I plan to use birth control, though I don’t know what method I will use,” she says. “I know that I don’t want to have another child straight away. It may be two or three years until I have the next one, as I want to wait until my family’s finances improve.”

| 24 April 2024
“The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby"
When garment worker Ny thought she might be pregnant with her first child, a home test kit quickly confirmed her suspicions. But the 23-year-old – who is originally from Takeo province but moved to Phnom Penh to take up a job in the garment industry – did not know where to go to seek prenatal care. After a cousin recommended that she visit a nearby Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia clinic, Ny took her relative’s advice – and has gone back eight times to date. “I come here every month to check on the baby,” she says, cradling her belly. “I had never been before I got pregnant.” During her visits to the medical clinic, Ny says, she has had a raft of standard tests and procedures as part of her prenatal care, including two ultrasounds, blood and urine tests, and vaccinations. “The doctors have also been giving me advice on how to look after myself and the baby [such as] to eat nutritious food and not to carry heavy things,” she says. As well as caring for the health of mother and unborn child, RHAC staff have also offered up valuable family planning information. “I did not know about how to plan to have children before I came to the clinic,” Ny says. “The doctors here told me that there are three different methods of [long-term] contraception: medication, an implant and an IUD.” Ny, who sews winter clothing at a factory while her husband also works in a nearby garment factory, says she was very glad to learn about her options. “This child was unplanned, but I don’t feel any regret because I had already been married for two years. But after having the baby I plan to use birth control, though I don’t know what method I will use,” she says. “I know that I don’t want to have another child straight away. It may be two or three years until I have the next one, as I want to wait until my family’s finances improve.”

| 16 November 2017
“When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need"
Female workers, many of them undereducated migrants from rural areas, dominate the garment sector in Cambodia. And Propitious garment factory in Takhmao, a small city that lies just south of the capital Phnom Penh, is no exception. Women make up more than 90 percent of the factory’s workforce. Helping to oversee the 3,700-strong workforce is human resources manager Kouch Davy, who has worked at Propitious since it opened four years ago. Seeing a need to improve the workers’ sexual and reproductive health knowledge, she says she decided to work with the Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC) because of its reputation for providing high-quality services. “I raised it in a management meeting, and the board was happy to explore it,” she says. For almost two years, trained staff from RHAC have been visiting the factory twice a month to meet with workers during their lunch break. They answer questions on topics ranging from birth control to STIs and abortion. The organisation has also provided training to the nurses who work in the factory’s on-site medical clinic. Davy says the factory’s female garment workers have changed as a result. “They are more open to asking questions about sexual health and they have also become more informed about the subject,” she says. “When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need, so they tend to exaggerate their problems and ask for sick leave. But when they go to see an RHAC clinic and get proper treatment, there is less sick leave. “Now that they understand about contraception, there are fewer women getting pregnant and taking maternity leave, so that also helps with the workflow. ” Davy says the factory has seen requests for sick leave drop by an average of between 100 to 200 cases a month – and any decrease in absenteeism is a major boon for productivity. “The factory works like a chain: if just one person on the production line takes a day off, it affects the overall productivity,” she says. “And if a worker comes to work sick, they have problems concentrating.” Even Davy says she has gone to RHAC to seek medical care, visiting one of their clinics a few months ago for a breast examination. Meanwhile, the company that owns Propitious has extended its partnership with RHAC to a second factory in Phnom Penh. The firm has even requested that the NGO starts visiting its largest factory, which is situated in a rural province and has 10,000 workers, in the future.

| 24 April 2024
“When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need"
Female workers, many of them undereducated migrants from rural areas, dominate the garment sector in Cambodia. And Propitious garment factory in Takhmao, a small city that lies just south of the capital Phnom Penh, is no exception. Women make up more than 90 percent of the factory’s workforce. Helping to oversee the 3,700-strong workforce is human resources manager Kouch Davy, who has worked at Propitious since it opened four years ago. Seeing a need to improve the workers’ sexual and reproductive health knowledge, she says she decided to work with the Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC) because of its reputation for providing high-quality services. “I raised it in a management meeting, and the board was happy to explore it,” she says. For almost two years, trained staff from RHAC have been visiting the factory twice a month to meet with workers during their lunch break. They answer questions on topics ranging from birth control to STIs and abortion. The organisation has also provided training to the nurses who work in the factory’s on-site medical clinic. Davy says the factory’s female garment workers have changed as a result. “They are more open to asking questions about sexual health and they have also become more informed about the subject,” she says. “When they don’t dare to ask questions about sensitive health topics, they don’t have the information they need, so they tend to exaggerate their problems and ask for sick leave. But when they go to see an RHAC clinic and get proper treatment, there is less sick leave. “Now that they understand about contraception, there are fewer women getting pregnant and taking maternity leave, so that also helps with the workflow. ” Davy says the factory has seen requests for sick leave drop by an average of between 100 to 200 cases a month – and any decrease in absenteeism is a major boon for productivity. “The factory works like a chain: if just one person on the production line takes a day off, it affects the overall productivity,” she says. “And if a worker comes to work sick, they have problems concentrating.” Even Davy says she has gone to RHAC to seek medical care, visiting one of their clinics a few months ago for a breast examination. Meanwhile, the company that owns Propitious has extended its partnership with RHAC to a second factory in Phnom Penh. The firm has even requested that the NGO starts visiting its largest factory, which is situated in a rural province and has 10,000 workers, in the future.








