Spotlight
A selection of resources from across the Federation

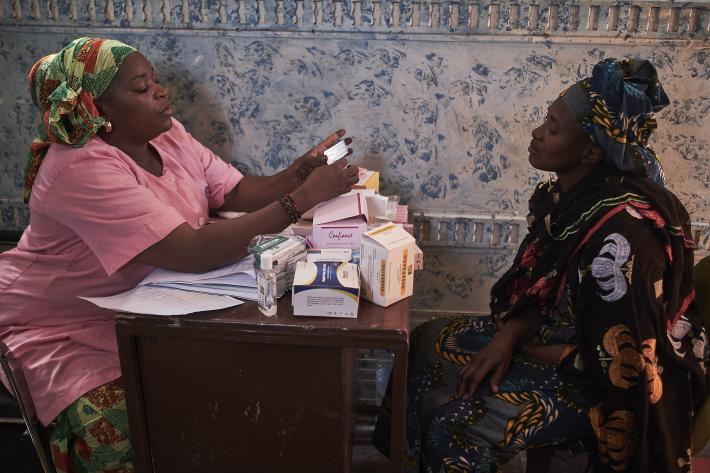
IMAP Statement on advances in emergency contraception
The purpose of this statement is to review newly published data on increasing the effectiveness of levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive pills by using pre‑coital administration or combined with a non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drug; the potential use of LNG‑ECP as a regular contraceptive method for infrequent sex; ulipristal acetate which is an established EC method and is now being studied combined with misoprostol for termination of early pregnancy; and the underutilization of low dose mifepristone as an EC method.
Filter our resources by:


| 06 December 2019
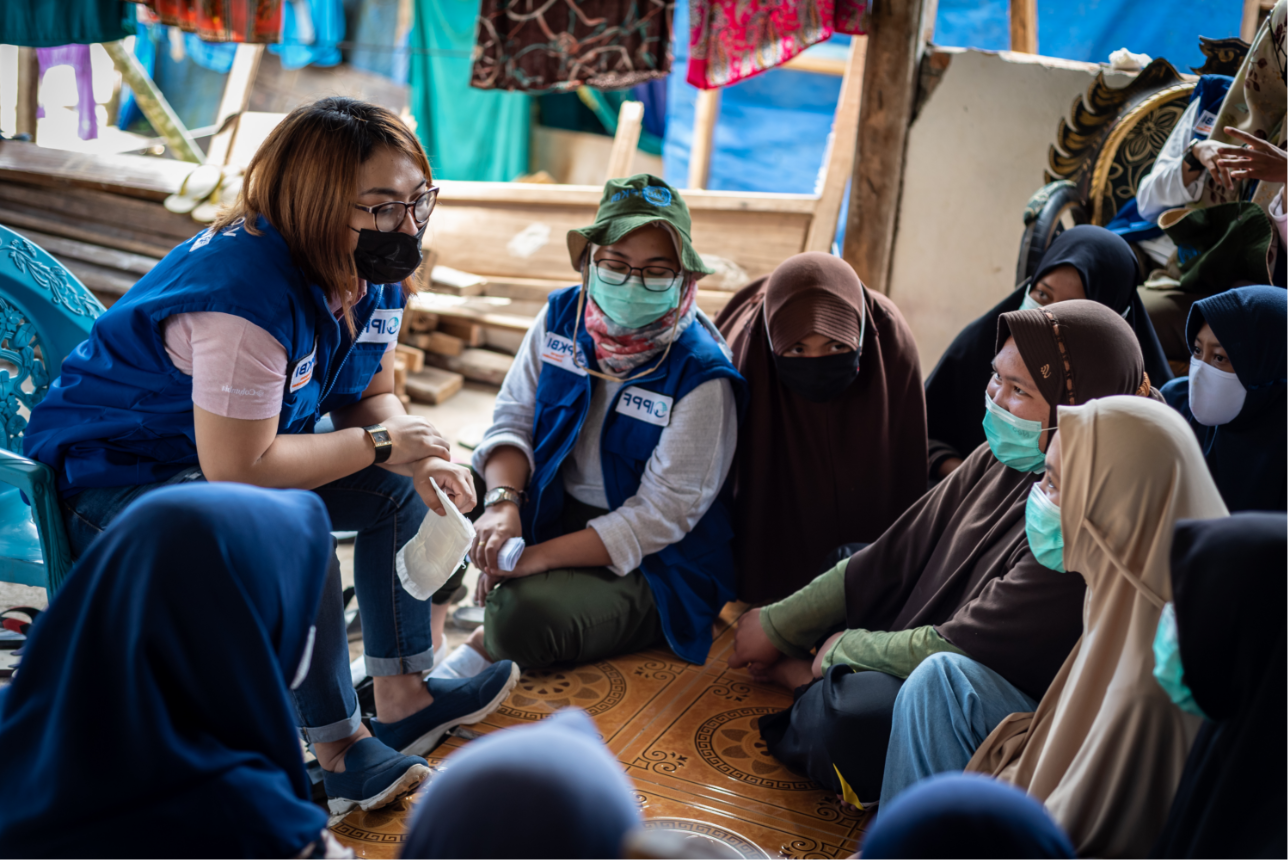
IMAP statement on expanding access and contraceptive choice through integrated sexual and reproductive health services
In 2018, IPPF endorsed the WHO/UNFPA Call to Action to Attain Universal Health Coverage Through Linked Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights and HIV Interventions.13 This IMAP statement serves as a reminder of this call to action to ensure all people have access to comprehensive SRH services, including integrated contraceptive and HIV/STI services, provided through primary healthcare.

| 28 October 2019
After the ECHO trial – Expanding access and choice through integrated services
Since the early 1990s, the evidence has been inconclusive as to whether using hormonal contraception increases women’s risk of acquiring HIV, particularly among progestogen-only injectable users. Observational studies indicated that women using progestogen-only injectable contraceptive methods may be at higher risk of acquiring human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The Evidence for Contraceptive Options and HIV Outcomes (ECHO) trial finds no link between HIV acquisition and the use of DMPA-IM, progestogen implant, and non-hormonal copper IUD. For more information please see the technical brief on the ECHO trial. Following the release of the result of the ECHO trial and the WHO latest guidance statement and revised Medical Eligibility Criteria (MEC) for contraceptive use, IPPF developed a follow-up technical brief to support IPPF MAs and frontline service providers’ work regarding the provision of the integrated contraceptive, HIV and other STI programmes to expand access and contraceptive choice. For more information, please see the attached technical brief After the ECHO trial – Expanding access and choice through integrated services, available in English and French.

| 09 July 2019
IPPF Technical Brief on the ECHO trial
Since the early 1990s, the evidence has been inconclusive as to whether using hormonal contraception increases women’s risk of acquiring HIV, particularly among progestogen-only injectable users. Observational studies indicated that women using progestogen-only injectable contraceptive methods may be at higher risk of acquiring human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The ECHO trial finds no link between HIV acquisition and the use of DMPA-IM, progestogen implant, and non-hormonal copper IUD.