Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in the face of growing opposition and the rise of the far right? These victories for sexual and reproductive rights and health are the result of relentless grassroots work and advocacy by our Member Associations, in partnership with community organizations, allied politicians, and the mobilization of public opinion.
Most Popular This Week

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in t
Kazakhstan
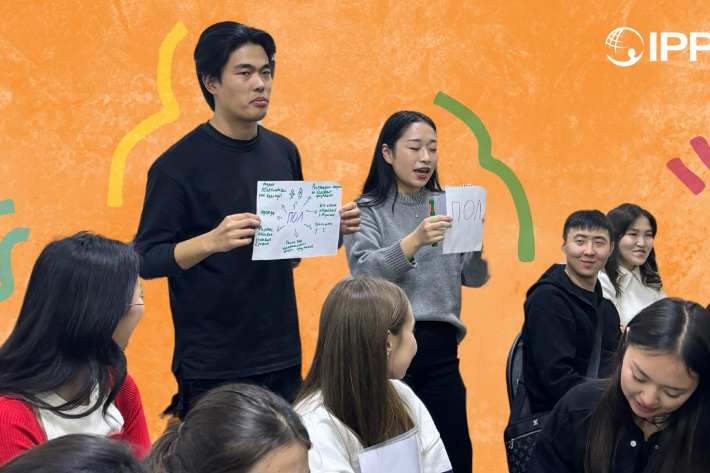

Kazakhstan's Rising HIV Crisis: A Call for Action
On World AIDS Day, we commemorate the remarkable achievements of IPPF Member Associations in their unwavering commitment to combating the HIV epidemic.

Ensuring SRHR in Humanitarian Crises: What You Need to Know
Over the past two decades, global forced displacement has consistently increased, affecting an estimated 114 million people as of mid-2023.
Estonia, Nepal, Namibia, Japan, Thailand

The Rainbow Wave for Marriage Equality
Love wins! The fight for marriage equality has seen incredible progress worldwide, with a recent surge in legalizations.
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
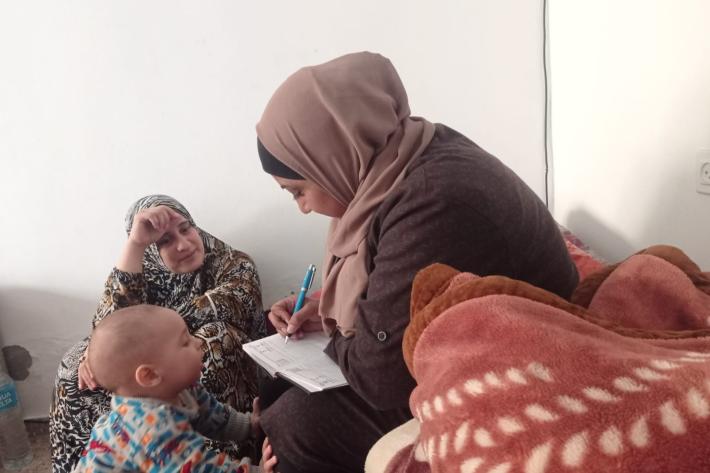

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Filter our stories by:
- Asociación Pro-Bienestar de la Familia Colombiana
- (-) Association Béninoise pour la Promotion de la Famille
- Association Tunisienne de la Santé de la Reproduction
- (-) Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia
- Family Planning Association of India
- Family Planning Association of Nepal
- Mouvement Français pour le Planning Familial
- Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA)
- Planned Parenthood Federation of America
- Pro Familia - Germany
- Reproductive Health Uganda


| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
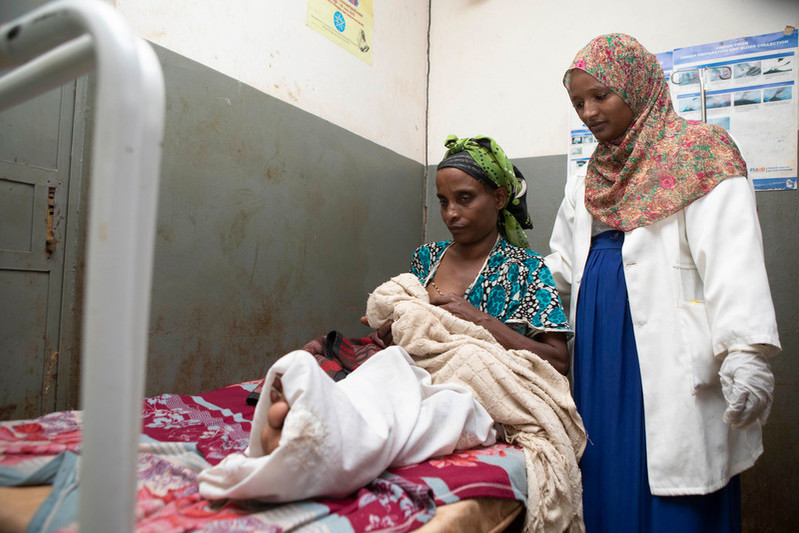
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 15 May 2025
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
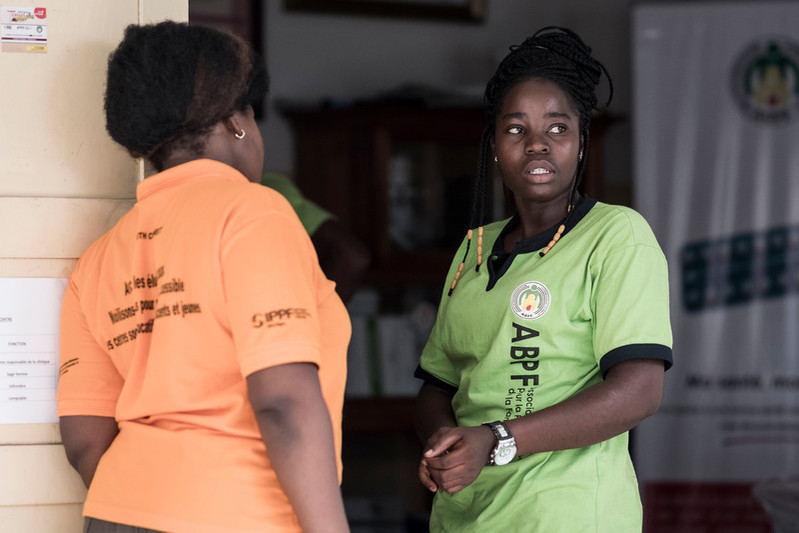
| 10 October 2018
In pictures: The Benin community working together to tackle abortion stigma
Geneviève Head of Youth and Stigma project and fundraising at the Association Beninoise pour la promotion de la famille (ABPF) Since joining ABPF in 1995, Geneviève has worked closely with community leaders to reduce stigma around abortion. Talking about the importance of young women having choice and access to abortion care, Geneviève says, “the law only applies in three circumstances, meanwhile everyday people need to access these services. Reproductive rights do exist, but that is something many people choose to ignore.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Hélène ABPF youth champion with the Young People’s Action Movement 27-year-old Hélène acts as a link between young people’s activities and the ABPF board. She has advocated for abortion rights at conferences locally and internationally. “In my school there were a fair number of pregnant girls so I was already looking for a way to help. Every week I went to different classes to educate them about abortion and stigma. When my mother found out, she told me this was a movement of depravity! But after a while my mum became a member of the association and came with me, and even my dad. Now they say they are proud of what I’ve achieved.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Simon Gnansounou Community leader In the small town of Cocotomey-La Paix, Simon works closely with ABPF supporting their work to reduce abortion stigma within local communities. “It’s a project for social development, and I am all for that. It’s going to limit harm done to these girls. Parents don’t talk about this with their children. It’s taboo. This project helps us negotiate this difficult parent-child question. There is no development without health, and the politics of health are very complex.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Kader Youth champion 26-year-old Kader says his first youth meeting at ABPF was a positive experience. “They told me that there was a jam session at the event. What I liked is that it was run by young people. Everything that I know about reproductive health I learnt at the centre. A lot of young women I know got pregnant very early. I know people who have died because of unsafe abortion. We can avoid so much of it if people have the right information.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Souliya Mevo Tairou Midwife “Stigmatization complicates our work. Fourteen and 15-year olds come here without their parents and it’s hard to work with them. The girls are so scared that they can’t really explain what’s happening to them. They come here after going to the traditional healers when that hasn’t worked and they are bleeding or have an infection. Here, with the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, we have awareness sessions. The young people and those supervising give out their numbers and tell them to call if they have a problem.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Amour University student “Her friends told her to take laxatives and other products, to put things in her vagina, to wash with hot water, to move about a lot.” 21-year-old Amour talks about a friend who confided in him when she discovered she was pregnant. “When we talk about abortion in Benin, it’s something people don’t want to hear about. It’s not well seen. Talking about sex is a problem. It’s still taboo. Thanks to the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, I had benefited from training on how to talk to girls if they came to ask about abortion.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Flore Literature teacher Flore says some of her students go to her for support and advice: “They are quite shy because at home the subject of sex is always taboo. They are reticent; they think it’s a shame. We will only correct this problem over time. There is chatting and whispering in class ‘you know what she did?’ Can’t we support these children instead of stigmatizing them?” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ida University student 19-year-old Ida attended a workshop on abortion and stigma for teachers and students at the Fiyegnon collège d’enseignement général. “It really helped. If we take our own decisions we will make it to the end, we will get what is right for us.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
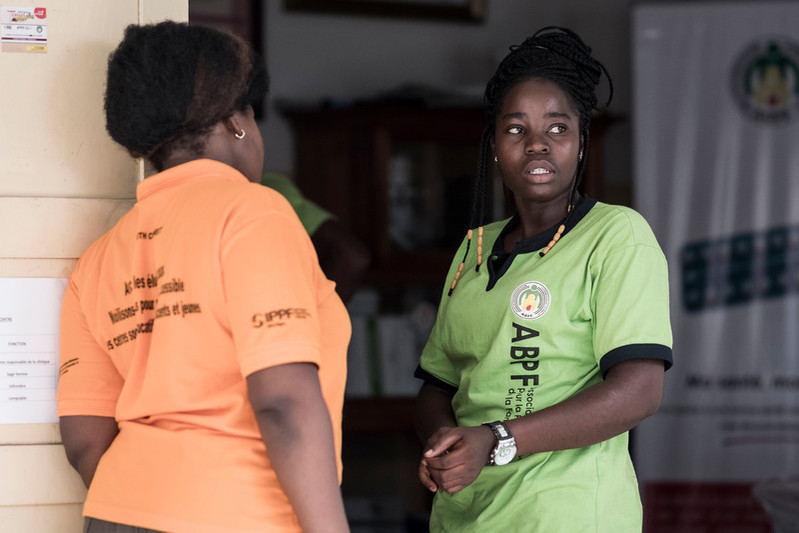
| 16 May 2025
In pictures: The Benin community working together to tackle abortion stigma
Geneviève Head of Youth and Stigma project and fundraising at the Association Beninoise pour la promotion de la famille (ABPF) Since joining ABPF in 1995, Geneviève has worked closely with community leaders to reduce stigma around abortion. Talking about the importance of young women having choice and access to abortion care, Geneviève says, “the law only applies in three circumstances, meanwhile everyday people need to access these services. Reproductive rights do exist, but that is something many people choose to ignore.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Hélène ABPF youth champion with the Young People’s Action Movement 27-year-old Hélène acts as a link between young people’s activities and the ABPF board. She has advocated for abortion rights at conferences locally and internationally. “In my school there were a fair number of pregnant girls so I was already looking for a way to help. Every week I went to different classes to educate them about abortion and stigma. When my mother found out, she told me this was a movement of depravity! But after a while my mum became a member of the association and came with me, and even my dad. Now they say they are proud of what I’ve achieved.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Simon Gnansounou Community leader In the small town of Cocotomey-La Paix, Simon works closely with ABPF supporting their work to reduce abortion stigma within local communities. “It’s a project for social development, and I am all for that. It’s going to limit harm done to these girls. Parents don’t talk about this with their children. It’s taboo. This project helps us negotiate this difficult parent-child question. There is no development without health, and the politics of health are very complex.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Kader Youth champion 26-year-old Kader says his first youth meeting at ABPF was a positive experience. “They told me that there was a jam session at the event. What I liked is that it was run by young people. Everything that I know about reproductive health I learnt at the centre. A lot of young women I know got pregnant very early. I know people who have died because of unsafe abortion. We can avoid so much of it if people have the right information.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Souliya Mevo Tairou Midwife “Stigmatization complicates our work. Fourteen and 15-year olds come here without their parents and it’s hard to work with them. The girls are so scared that they can’t really explain what’s happening to them. They come here after going to the traditional healers when that hasn’t worked and they are bleeding or have an infection. Here, with the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, we have awareness sessions. The young people and those supervising give out their numbers and tell them to call if they have a problem.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Amour University student “Her friends told her to take laxatives and other products, to put things in her vagina, to wash with hot water, to move about a lot.” 21-year-old Amour talks about a friend who confided in him when she discovered she was pregnant. “When we talk about abortion in Benin, it’s something people don’t want to hear about. It’s not well seen. Talking about sex is a problem. It’s still taboo. Thanks to the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, I had benefited from training on how to talk to girls if they came to ask about abortion.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Flore Literature teacher Flore says some of her students go to her for support and advice: “They are quite shy because at home the subject of sex is always taboo. They are reticent; they think it’s a shame. We will only correct this problem over time. There is chatting and whispering in class ‘you know what she did?’ Can’t we support these children instead of stigmatizing them?” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ida University student 19-year-old Ida attended a workshop on abortion and stigma for teachers and students at the Fiyegnon collège d’enseignement général. “It really helped. If we take our own decisions we will make it to the end, we will get what is right for us.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 16 July 2020
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”

| 15 May 2025
"Before, there was no safe abortion"
Rewda Kedir works as a midwife in a rural area of the Oromia region in southwest Ethiopia. Only 14% of married women are using any method of contraception here. The government hospital Rewda works in is supported to provide a full range of sexual and reproductive healthcare, which includes providing free contraceptives and comprehensive abortion care. In January 2017, the maternal healthcare clinic faced shortages of contraceptives after the US administration reactivated and expanded the Global Gag Rule, which does not allow any funding to go to organizations associated with providing abortion care. Fortunately in this case, the shortages only lasted a month due to the government of the Netherlands stepping in and matching lost funding. “Before, we had a shortage of contraceptive pills and emergency contraceptives. We would have to give people prescriptions and they would go to private clinics and where they had to pay," Rewda tells us. "When I first came to this clinic, there was a real shortage of people trained in family planning. I was the only one. Now there are many people trained on family planning, and when I’m not here, people can help." "There used to be a shortage of choice and alternatives, and now there are many. And the implant procedures are better because there are newer products that are much smaller so putting them in is less invasive.” Opening a dialogue on contraception The hospital has been providing medical abortions for six years. “Before, there was no safe abortion," says Rewda. She explains how people would go to 'traditional' healers and then come to the clinic with complications like sepsis, bleeding, anaemia and toxic shock. If they had complications or infections above nine weeks, Rewda and her colleagues would send them to Jimma, the regional capital. "Before, it was very difficult to persuade them to use family planning, and we had to have a lot of conversations. Now, they come 45 days after delivery to speak to us about this and get their babies immunised," she explains. "They want contraceptives to space out their children. Sometimes their husbands don’t like them coming to get family planning so we have to lock their appointment cards away. Their husbands want more children and they think that women who do not keep having their children will go with other men." "More kids, more wealth" Rewda tells us that they've used family counselling to try and persuade men to reconsider their ideas about contraception, by explaining to them that continuously giving birth under unsafe circumstances can affect a woman's health and might lead to maternal death, damage the uterus and lead to long-term complications. "Here, people believe that more kids means more wealth, and religion restricts family planning services. Before, they did not have good training on family planning and abortion. Now, women that have abortions get proper care and the counseling and education has improved. There are still unsafe abortions but they have really reduced. We used to see about 40 a year and now it’s one or two." However, problems still exist. "There are some complications, like irregular bleeding from some contraceptives," Rewda says, and that "women still face conflict with their husbands over family planning and sometimes have to go to court to fight this or divorce them.”
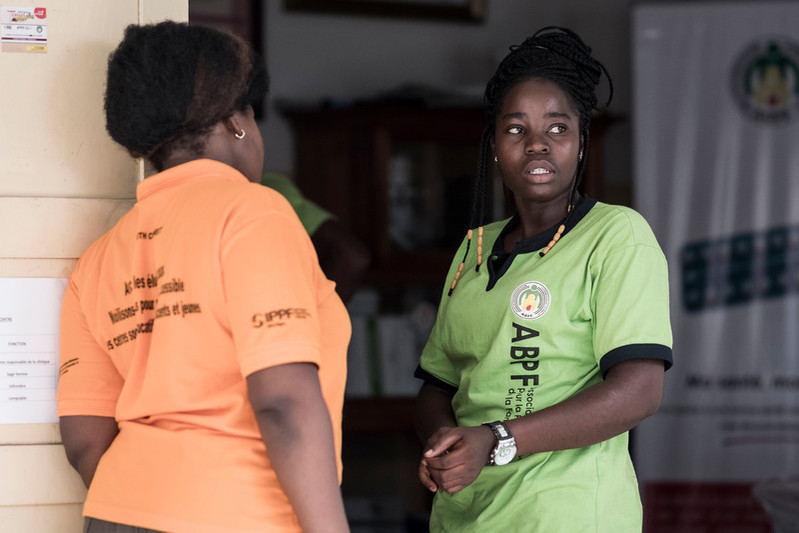
| 10 October 2018
In pictures: The Benin community working together to tackle abortion stigma
Geneviève Head of Youth and Stigma project and fundraising at the Association Beninoise pour la promotion de la famille (ABPF) Since joining ABPF in 1995, Geneviève has worked closely with community leaders to reduce stigma around abortion. Talking about the importance of young women having choice and access to abortion care, Geneviève says, “the law only applies in three circumstances, meanwhile everyday people need to access these services. Reproductive rights do exist, but that is something many people choose to ignore.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Hélène ABPF youth champion with the Young People’s Action Movement 27-year-old Hélène acts as a link between young people’s activities and the ABPF board. She has advocated for abortion rights at conferences locally and internationally. “In my school there were a fair number of pregnant girls so I was already looking for a way to help. Every week I went to different classes to educate them about abortion and stigma. When my mother found out, she told me this was a movement of depravity! But after a while my mum became a member of the association and came with me, and even my dad. Now they say they are proud of what I’ve achieved.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Simon Gnansounou Community leader In the small town of Cocotomey-La Paix, Simon works closely with ABPF supporting their work to reduce abortion stigma within local communities. “It’s a project for social development, and I am all for that. It’s going to limit harm done to these girls. Parents don’t talk about this with their children. It’s taboo. This project helps us negotiate this difficult parent-child question. There is no development without health, and the politics of health are very complex.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Kader Youth champion 26-year-old Kader says his first youth meeting at ABPF was a positive experience. “They told me that there was a jam session at the event. What I liked is that it was run by young people. Everything that I know about reproductive health I learnt at the centre. A lot of young women I know got pregnant very early. I know people who have died because of unsafe abortion. We can avoid so much of it if people have the right information.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Souliya Mevo Tairou Midwife “Stigmatization complicates our work. Fourteen and 15-year olds come here without their parents and it’s hard to work with them. The girls are so scared that they can’t really explain what’s happening to them. They come here after going to the traditional healers when that hasn’t worked and they are bleeding or have an infection. Here, with the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, we have awareness sessions. The young people and those supervising give out their numbers and tell them to call if they have a problem.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Amour University student “Her friends told her to take laxatives and other products, to put things in her vagina, to wash with hot water, to move about a lot.” 21-year-old Amour talks about a friend who confided in him when she discovered she was pregnant. “When we talk about abortion in Benin, it’s something people don’t want to hear about. It’s not well seen. Talking about sex is a problem. It’s still taboo. Thanks to the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, I had benefited from training on how to talk to girls if they came to ask about abortion.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Flore Literature teacher Flore says some of her students go to her for support and advice: “They are quite shy because at home the subject of sex is always taboo. They are reticent; they think it’s a shame. We will only correct this problem over time. There is chatting and whispering in class ‘you know what she did?’ Can’t we support these children instead of stigmatizing them?” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ida University student 19-year-old Ida attended a workshop on abortion and stigma for teachers and students at the Fiyegnon collège d’enseignement général. “It really helped. If we take our own decisions we will make it to the end, we will get what is right for us.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
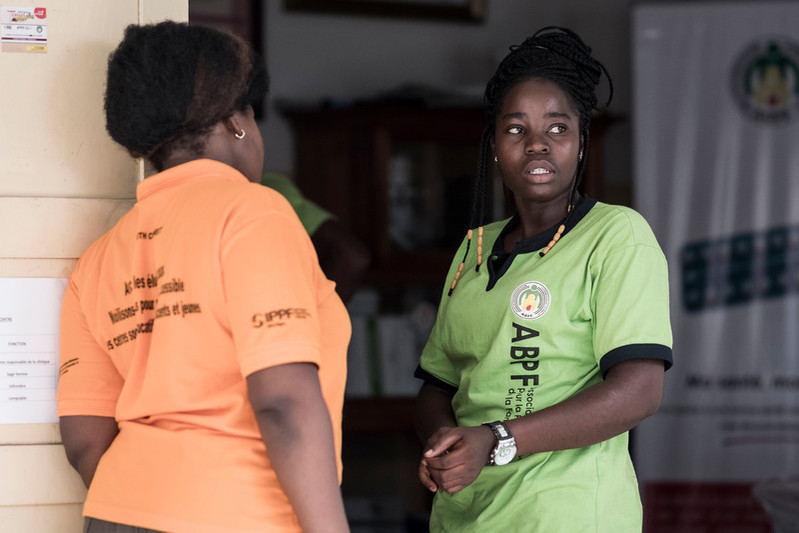
| 16 May 2025
In pictures: The Benin community working together to tackle abortion stigma
Geneviève Head of Youth and Stigma project and fundraising at the Association Beninoise pour la promotion de la famille (ABPF) Since joining ABPF in 1995, Geneviève has worked closely with community leaders to reduce stigma around abortion. Talking about the importance of young women having choice and access to abortion care, Geneviève says, “the law only applies in three circumstances, meanwhile everyday people need to access these services. Reproductive rights do exist, but that is something many people choose to ignore.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Hélène ABPF youth champion with the Young People’s Action Movement 27-year-old Hélène acts as a link between young people’s activities and the ABPF board. She has advocated for abortion rights at conferences locally and internationally. “In my school there were a fair number of pregnant girls so I was already looking for a way to help. Every week I went to different classes to educate them about abortion and stigma. When my mother found out, she told me this was a movement of depravity! But after a while my mum became a member of the association and came with me, and even my dad. Now they say they are proud of what I’ve achieved.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Simon Gnansounou Community leader In the small town of Cocotomey-La Paix, Simon works closely with ABPF supporting their work to reduce abortion stigma within local communities. “It’s a project for social development, and I am all for that. It’s going to limit harm done to these girls. Parents don’t talk about this with their children. It’s taboo. This project helps us negotiate this difficult parent-child question. There is no development without health, and the politics of health are very complex.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Kader Youth champion 26-year-old Kader says his first youth meeting at ABPF was a positive experience. “They told me that there was a jam session at the event. What I liked is that it was run by young people. Everything that I know about reproductive health I learnt at the centre. A lot of young women I know got pregnant very early. I know people who have died because of unsafe abortion. We can avoid so much of it if people have the right information.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Souliya Mevo Tairou Midwife “Stigmatization complicates our work. Fourteen and 15-year olds come here without their parents and it’s hard to work with them. The girls are so scared that they can’t really explain what’s happening to them. They come here after going to the traditional healers when that hasn’t worked and they are bleeding or have an infection. Here, with the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, we have awareness sessions. The young people and those supervising give out their numbers and tell them to call if they have a problem.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Amour University student “Her friends told her to take laxatives and other products, to put things in her vagina, to wash with hot water, to move about a lot.” 21-year-old Amour talks about a friend who confided in him when she discovered she was pregnant. “When we talk about abortion in Benin, it’s something people don’t want to hear about. It’s not well seen. Talking about sex is a problem. It’s still taboo. Thanks to the Youth and Abortion Stigma Project, I had benefited from training on how to talk to girls if they came to ask about abortion.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Flore Literature teacher Flore says some of her students go to her for support and advice: “They are quite shy because at home the subject of sex is always taboo. They are reticent; they think it’s a shame. We will only correct this problem over time. There is chatting and whispering in class ‘you know what she did?’ Can’t we support these children instead of stigmatizing them?” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Ida University student 19-year-old Ida attended a workshop on abortion and stigma for teachers and students at the Fiyegnon collège d’enseignement général. “It really helped. If we take our own decisions we will make it to the end, we will get what is right for us.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email








