Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in the face of growing opposition and the rise of the far right? These victories for sexual and reproductive rights and health are the result of relentless grassroots work and advocacy by our Member Associations, in partnership with community organizations, allied politicians, and the mobilization of public opinion.
Most Popular This Week

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in t
Kazakhstan
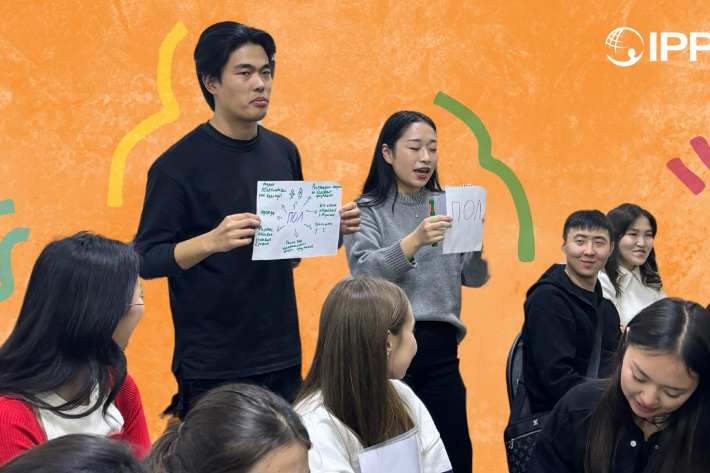

Kazakhstan's Rising HIV Crisis: A Call for Action
On World AIDS Day, we commemorate the remarkable achievements of IPPF Member Associations in their unwavering commitment to combating the HIV epidemic.

Ensuring SRHR in Humanitarian Crises: What You Need to Know
Over the past two decades, global forced displacement has consistently increased, affecting an estimated 114 million people as of mid-2023.
Estonia, Nepal, Namibia, Japan, Thailand

The Rainbow Wave for Marriage Equality
Love wins! The fight for marriage equality has seen incredible progress worldwide, with a recent surge in legalizations.
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
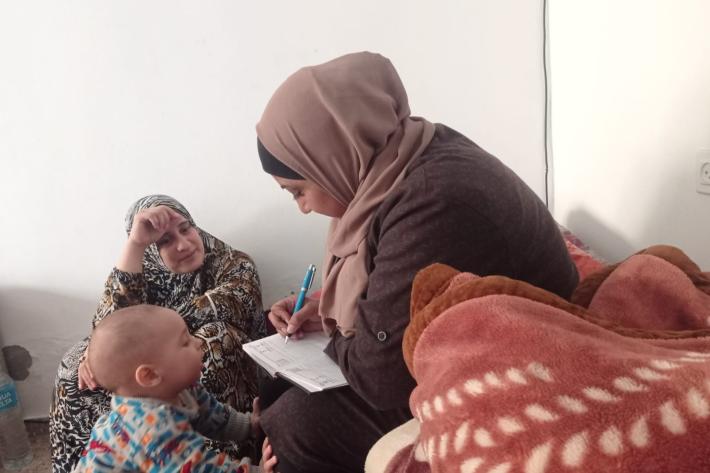

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu

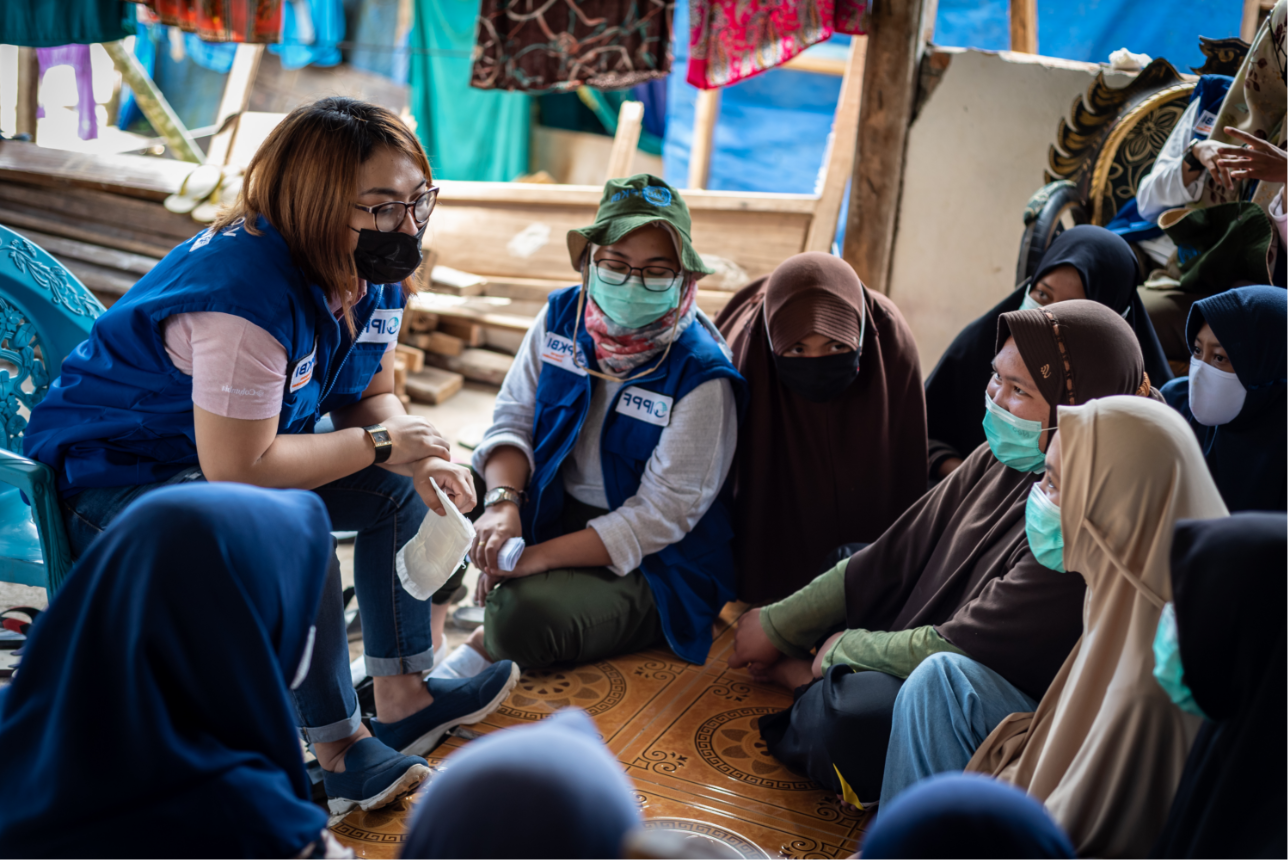
When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Filter our stories by:
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Aruba
- Bangladesh
- Benin
- Botswana
- (-) Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Colombia
- Congo, Dem. Rep.
- Cook Islands
- El Salvador
- Estonia
- Ethiopia
- Fiji
- France
- Germany
- Ghana
- Guinea-Conakry
- India
- Ireland
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- (-) Kiribati
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Palestine
- Poland
- Senegal
- Somaliland
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Thailand
- Togo
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vanuatu
- Zambia


| 18 June 2020
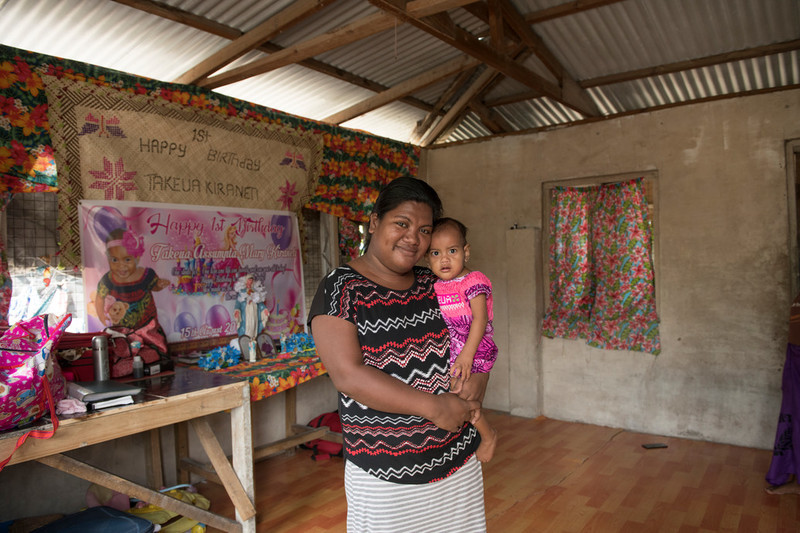
In pictures: Healthcare in the face of the climate crisis in Kiribati
Humanitarian crises Largely brought on by sudden onset and slow-onset natural disasters, humanitarian crises are increasingly prevalent in the Pacific. During responses to humanitarian crises in the Pacific, sexual and reproductive healthcare is often under-prioritised and under-resourced. As a result, women and girls of reproductive age and vulnerable and marginalized groups are disproportionately affected and facing increased health and psychosocial risks. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Fragile environments Low topography, rising sea levels and insufficient fresh water supply leaves Kiribati’s population vulnerable to the effects of the climate crisis. The fragility of the outer islands of Kiribati during natural disasters is compounded by their geographic isolation, which makes transportation and communication during post-disaster relief and response both expensive and difficult. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Coastal exposure The majority of the population of 115,000 people live a subsistence lifestyle. Communities are geographically dispersed across 33 atolls covering 3.5 million square kilometres in the central Pacific Ocean. The population and infrastructure within Kiribati are largely concentrated on the coast, where communities face increased exposure to climate threats and natural hazards such as tsunamis, earthquakes, king tides, flooding, droughts, and occasionally cyclones. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Takaria, leader and youth organizer in the Tebikenikua community Takaria will be running to be a Member of Parliament in Kiribati in 2020. “I assist the youth with family problems and family planning and disasters. In our community there are unforeseen pregnancies, domestic violence, and disasters such as high tide waters and strong winds, which can also affect this community. The Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) is the key point for us with outreach and training so people in this community know how to prevent and treat STIs, etc. They all know where the KFHA clinic is and that they can get counselling or services there. The problem now is you can’t survive with the sea rise levels. I want all members of my community to live better and have better health and peace.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Susan*, sex worker Susan receives care at the Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) including a pap smear. Susan*, 28, is a sex worker from the town of Betio on the main island of Kiribati. Originally from an outlying island, she moved into Tarawa to seek work. Unable to find employment that would fulfill her dream of sending money back to her two children, she was introduced to sex work. With other sex workers, she regularly travels out to the large cargo ships from China, Philippines and Korea anchored off the coast of Kiribati. Despite her new income, she still can’t speak with her children or see them due to the restrictive costs involved of travel between islands.*pseudonym Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Theta, 25-year-old mother and youth volunteer Theta is part of the Humanitarian Youth Club set up by the Kiribati Family Health Association in her village. “We face a lot of situations here, one of them is disasters and the second is unemployment and school drop out with our youth. I have helped the Humanitarian Youth Club to apply for financial grants from the Australian High Commission [for $1,000] I am recognized as the smartest member who can write in English. We have learned how to design a disaster plan for the community and share our ideas on sexual and reproductive issues such as STIs. We discuss what we can do for the next strong tide, where we can gather as a community and what we can do if even the maneabe (town hall) floods? If the tide and wind is too strong, we need to go to another safer place, such as another community’s town hall. For now, I want to enjoy the chance to be in our own beloved country. I won’t move until the majority have already left. I want my daughter to grow up in the same place I grew up in.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Beitau, youth volunteer Beitau is the Chairperson of the Humanitarian Youth Club. “I was lucky to be selected as Chairperson as the Humanitarian Youth Club. I feel like I get more respect from the community now I am in this position. I would love advanced training on leadership now, to further assist the club. As I am the Chairperson of the HYC, my main target is to help people during a disaster. I have attended training through KFHA. What I took from this is that when a disaster strikes, we have to do our best for pregnant women, small children and people with disabilities. They more vulnerable and less able to survive a disaster.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abe, youth officer Abe was involved with KFHA since 2012. “I was inspired by what they KFHA was doing and the issues they were addressing that affects youth. I was surprised to see how many young people come to the clinic as they are affected by STIs, HIV and teenage pregnancy. The lack of education here is a big problem, most people here have a lot of children and yet can’t afford to send them to school. Sexual and reproductive health is our responsibility and we must talk about it with young people. Climate change affects many countries, but Kiribati is small and low lying. I used to go visit a very nice beach with a lot of nice trees and plants. Now, the trees are gone, and the waves have taken over, and the houses have disappeared so no one can build there. In my role as a youth worker and activist, I tell people to fight climate change: to grow more mangroves, to clean up the beach, because we love our Kiribati.”©IPPF/Hannah Maule-Ffinch/Kiribati Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 17 May 2025
In pictures: Healthcare in the face of the climate crisis in Kiribati
Humanitarian crises Largely brought on by sudden onset and slow-onset natural disasters, humanitarian crises are increasingly prevalent in the Pacific. During responses to humanitarian crises in the Pacific, sexual and reproductive healthcare is often under-prioritised and under-resourced. As a result, women and girls of reproductive age and vulnerable and marginalized groups are disproportionately affected and facing increased health and psychosocial risks. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Fragile environments Low topography, rising sea levels and insufficient fresh water supply leaves Kiribati’s population vulnerable to the effects of the climate crisis. The fragility of the outer islands of Kiribati during natural disasters is compounded by their geographic isolation, which makes transportation and communication during post-disaster relief and response both expensive and difficult. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Coastal exposure The majority of the population of 115,000 people live a subsistence lifestyle. Communities are geographically dispersed across 33 atolls covering 3.5 million square kilometres in the central Pacific Ocean. The population and infrastructure within Kiribati are largely concentrated on the coast, where communities face increased exposure to climate threats and natural hazards such as tsunamis, earthquakes, king tides, flooding, droughts, and occasionally cyclones. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Takaria, leader and youth organizer in the Tebikenikua community Takaria will be running to be a Member of Parliament in Kiribati in 2020. “I assist the youth with family problems and family planning and disasters. In our community there are unforeseen pregnancies, domestic violence, and disasters such as high tide waters and strong winds, which can also affect this community. The Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) is the key point for us with outreach and training so people in this community know how to prevent and treat STIs, etc. They all know where the KFHA clinic is and that they can get counselling or services there. The problem now is you can’t survive with the sea rise levels. I want all members of my community to live better and have better health and peace.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Susan*, sex worker Susan receives care at the Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) including a pap smear. Susan*, 28, is a sex worker from the town of Betio on the main island of Kiribati. Originally from an outlying island, she moved into Tarawa to seek work. Unable to find employment that would fulfill her dream of sending money back to her two children, she was introduced to sex work. With other sex workers, she regularly travels out to the large cargo ships from China, Philippines and Korea anchored off the coast of Kiribati. Despite her new income, she still can’t speak with her children or see them due to the restrictive costs involved of travel between islands.*pseudonym Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Theta, 25-year-old mother and youth volunteer Theta is part of the Humanitarian Youth Club set up by the Kiribati Family Health Association in her village. “We face a lot of situations here, one of them is disasters and the second is unemployment and school drop out with our youth. I have helped the Humanitarian Youth Club to apply for financial grants from the Australian High Commission [for $1,000] I am recognized as the smartest member who can write in English. We have learned how to design a disaster plan for the community and share our ideas on sexual and reproductive issues such as STIs. We discuss what we can do for the next strong tide, where we can gather as a community and what we can do if even the maneabe (town hall) floods? If the tide and wind is too strong, we need to go to another safer place, such as another community’s town hall. For now, I want to enjoy the chance to be in our own beloved country. I won’t move until the majority have already left. I want my daughter to grow up in the same place I grew up in.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Beitau, youth volunteer Beitau is the Chairperson of the Humanitarian Youth Club. “I was lucky to be selected as Chairperson as the Humanitarian Youth Club. I feel like I get more respect from the community now I am in this position. I would love advanced training on leadership now, to further assist the club. As I am the Chairperson of the HYC, my main target is to help people during a disaster. I have attended training through KFHA. What I took from this is that when a disaster strikes, we have to do our best for pregnant women, small children and people with disabilities. They more vulnerable and less able to survive a disaster.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abe, youth officer Abe was involved with KFHA since 2012. “I was inspired by what they KFHA was doing and the issues they were addressing that affects youth. I was surprised to see how many young people come to the clinic as they are affected by STIs, HIV and teenage pregnancy. The lack of education here is a big problem, most people here have a lot of children and yet can’t afford to send them to school. Sexual and reproductive health is our responsibility and we must talk about it with young people. Climate change affects many countries, but Kiribati is small and low lying. I used to go visit a very nice beach with a lot of nice trees and plants. Now, the trees are gone, and the waves have taken over, and the houses have disappeared so no one can build there. In my role as a youth worker and activist, I tell people to fight climate change: to grow more mangroves, to clean up the beach, because we love our Kiribati.”©IPPF/Hannah Maule-Ffinch/Kiribati Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
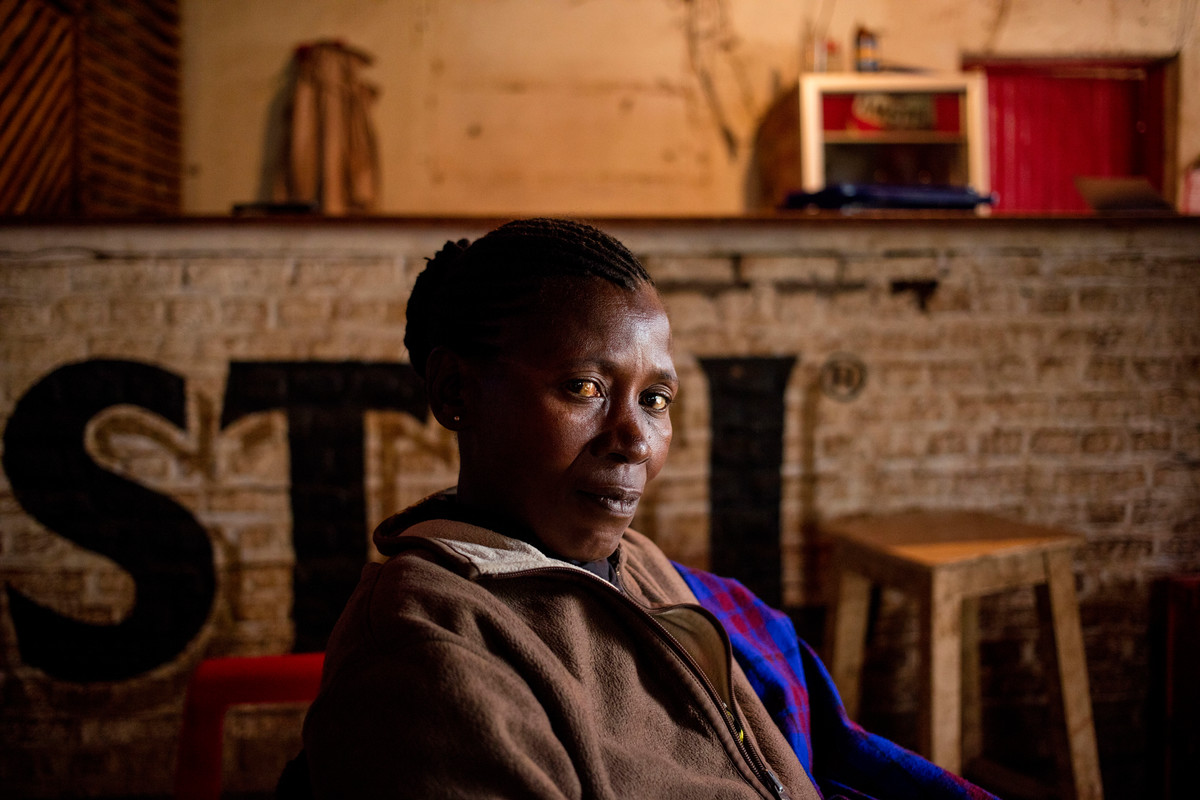

| 22 January 2018
"I am a living example of having a good life..."
At a local bar, we meet nine women from Kirundo. They’re all sex workers who became friends through Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial's (ABUBEF) peer educator project. Yvonne is 40 and has known that she’s HIV-positive for 22 years. After her diagnosis she was isolated from her friends and stigmatized both in public and at home, where she was even given separate plates to eat from. “I started to get drunk every day,” she says. “I hoped death would take me in my sleep. I didn’t believe in tomorrow. I was lost and lonely. Until I got to the ABUBEF clinic.” ABUBEF has supported her treatment for the past six years. “I take my pill every day and I am living example of having a good life even with a previous death sentence,” Yvonne explains. “But I see that the awareness of HIV, protection and testing provided by ABUBEF is still very small.” Yvonne became a peer educator, speaking in public about HIV awareness, wearing an ABUBEF T-shirt. The project spread to the wider region, and volunteers were given travel expenses, materials and training, along with condoms for distribution. But funding cuts mean those expenses are no longer available. Yvonne says she’ll carry on in Kirundo even if she can’t travel more widely like she used to. Her friend, 29-year-old Perusi, shares her experience of ABUBEF as a safe space where her privacy will be respected. It often happens, she says, that her clients rape her, and run away, failing to pay. Since sex work is illegal, she says, and there’s no protection from the authorities, and sex workers like her often feel rejected by society. But at ABUBEF’s clinics, they are welcomed.

| 16 May 2025
"I am a living example of having a good life..."
At a local bar, we meet nine women from Kirundo. They’re all sex workers who became friends through Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial's (ABUBEF) peer educator project. Yvonne is 40 and has known that she’s HIV-positive for 22 years. After her diagnosis she was isolated from her friends and stigmatized both in public and at home, where she was even given separate plates to eat from. “I started to get drunk every day,” she says. “I hoped death would take me in my sleep. I didn’t believe in tomorrow. I was lost and lonely. Until I got to the ABUBEF clinic.” ABUBEF has supported her treatment for the past six years. “I take my pill every day and I am living example of having a good life even with a previous death sentence,” Yvonne explains. “But I see that the awareness of HIV, protection and testing provided by ABUBEF is still very small.” Yvonne became a peer educator, speaking in public about HIV awareness, wearing an ABUBEF T-shirt. The project spread to the wider region, and volunteers were given travel expenses, materials and training, along with condoms for distribution. But funding cuts mean those expenses are no longer available. Yvonne says she’ll carry on in Kirundo even if she can’t travel more widely like she used to. Her friend, 29-year-old Perusi, shares her experience of ABUBEF as a safe space where her privacy will be respected. It often happens, she says, that her clients rape her, and run away, failing to pay. Since sex work is illegal, she says, and there’s no protection from the authorities, and sex workers like her often feel rejected by society. But at ABUBEF’s clinics, they are welcomed.
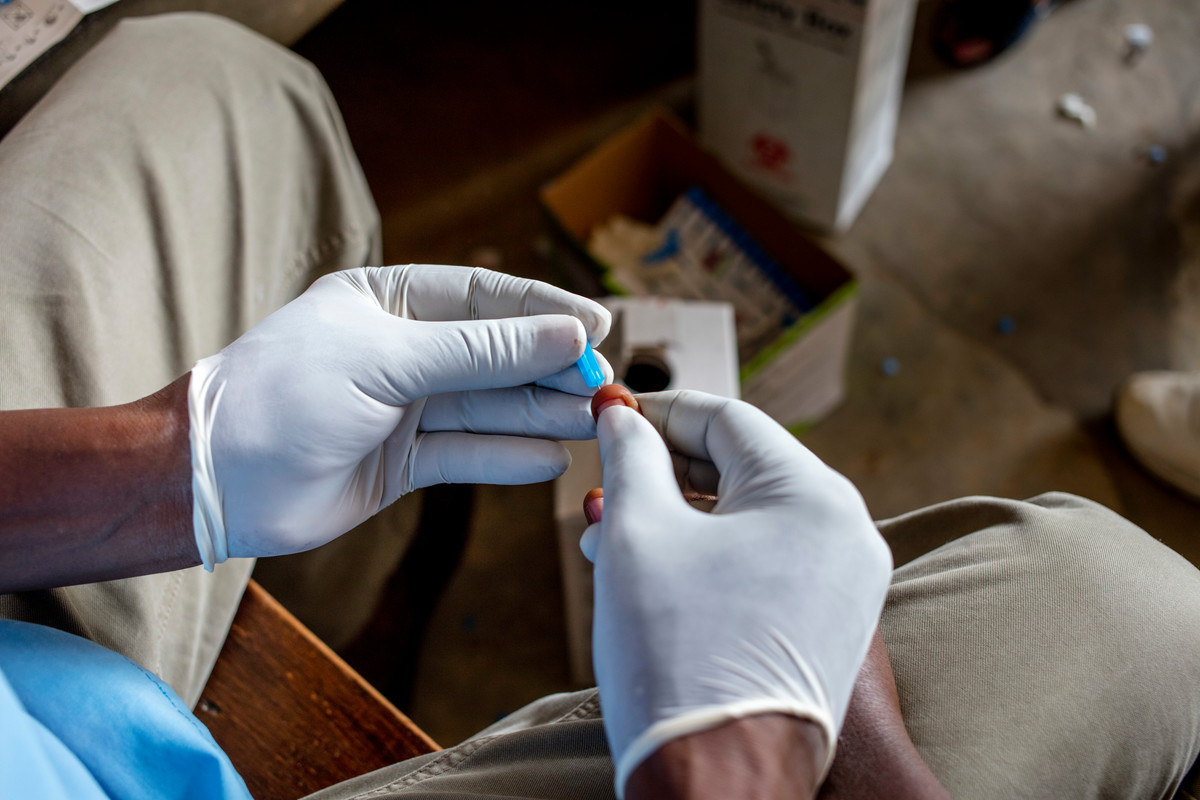
| 22 January 2018
“They saved the life of me and my child”
Monica has never told anyone about the attack. She was pregnant at the time, already had two teenage sons, and rape is a taboo subject in her community in Burundi. Knowing that her attacker was HIV-positive, and fearing that her husband would accuse her of provocation - or worse still, leave her - she turned to a place she knew would help. ABUBEF is the Association Burundaise Pour Le Bien-Etre Familial. Their clinic in Kirundo offered Monica HIV counselling and treatment for the duration of her pregnancy. Above all, ABUBEF offered privacy. Neither Monica nor her daughter has tested positive for HIV. “They saved the life of me and my child,” Monica says. “I hope they get an award for their psychological and health support for women.” Three years on from the attack, Monica, now 45, raises her children and tends the family farm where she grows beans, cassava, potatoes and rice. She’s proud of her eldest son who’s due to start university this year. She educates her boys against violence, and spreads the word about ABUBEF. Monica speaks to other women to make sure they know where to seek help if they need it. Her attacker still lives in the neighbourhood, and she worries that he’s transmitting HIV. But the ABUBEF clinic that helped Monica is under threat from funding cuts. The possibility that it could close prompted her to tell her story. “This is a disaster for our community,” she says. “I know how much the clinic needs support from donors, how much they need new equipment and money for new staff. I want people to know that this facility is one of a kind - and without it many people will be lost.”

| 16 May 2025
“They saved the life of me and my child”
Monica has never told anyone about the attack. She was pregnant at the time, already had two teenage sons, and rape is a taboo subject in her community in Burundi. Knowing that her attacker was HIV-positive, and fearing that her husband would accuse her of provocation - or worse still, leave her - she turned to a place she knew would help. ABUBEF is the Association Burundaise Pour Le Bien-Etre Familial. Their clinic in Kirundo offered Monica HIV counselling and treatment for the duration of her pregnancy. Above all, ABUBEF offered privacy. Neither Monica nor her daughter has tested positive for HIV. “They saved the life of me and my child,” Monica says. “I hope they get an award for their psychological and health support for women.” Three years on from the attack, Monica, now 45, raises her children and tends the family farm where she grows beans, cassava, potatoes and rice. She’s proud of her eldest son who’s due to start university this year. She educates her boys against violence, and spreads the word about ABUBEF. Monica speaks to other women to make sure they know where to seek help if they need it. Her attacker still lives in the neighbourhood, and she worries that he’s transmitting HIV. But the ABUBEF clinic that helped Monica is under threat from funding cuts. The possibility that it could close prompted her to tell her story. “This is a disaster for our community,” she says. “I know how much the clinic needs support from donors, how much they need new equipment and money for new staff. I want people to know that this facility is one of a kind - and without it many people will be lost.”
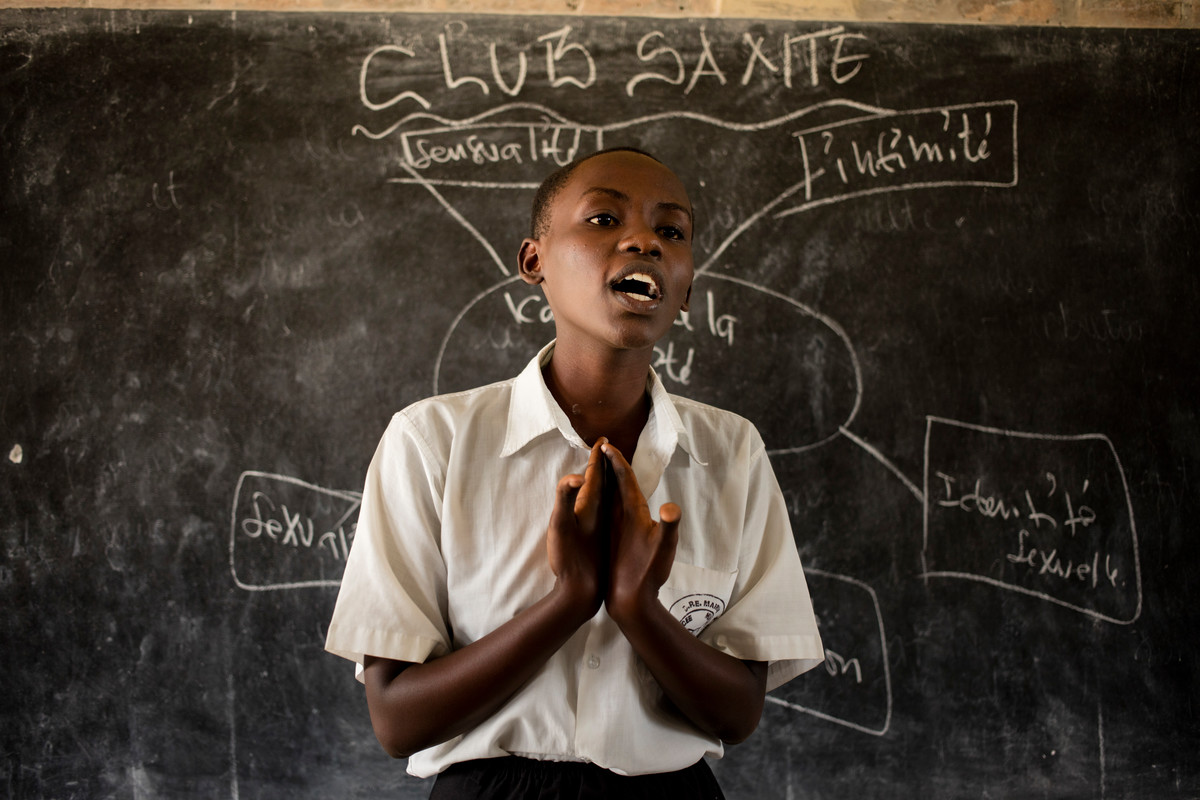

| 19 January 2018
“I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one"
On Friday afternoon in Municipal Lycee of Nyakabiga, Burundi, headmistress Chantal Keza is introducing her students to the medical staff from Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ABUBEF). Peer educators at the school, trained by ABUBEF, will perform a short drama based around sexual health and will answer questions about contraception methods from students. One of the actresses is peer educator Ammande Berlyne Dushime. Ammande, who is 17 years old is one of three peer educators at the school. Ammande, together with her friends, perform their short drama on the stage based on a young girls quest for information on contraception. It ends on a positive note, with the girl receiving useful and correct information from a peer educator at her school. A story that could be a very real life scenario at her school. Peer programmes that trained Ammande, are under threat of closure due to the Global Gag rule. Ammande says, “I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one. I am ready to go on with work as peer educator, but if there are not going to be regular visits by the medical stuff from the clinic, then we will have no one to seek information and advice from. I am just a teenager, I know so little. Not only I will lose my support, but also I will not be taken serious by my schoolmates. With such important topic like sexual education and contraception, I am not the authority. I can only show the right way to go. And this road leads to ABUBEF.” She says “As peer educator I am responsible for Saturday morning meetings at the clinic. We sing songs, play games, have fun and learn new things about sex education, contraception, HIV protection and others. Visiting the clinic is then very easy, and no student has to be afraid, that showing up at the clinic that treats HIV positive people, will ruin their reputation. Now they know that we can meet there openly, and undercover of these meetings seek for help, information, professional advice and contraception methods” Peer educator classes are a safe and open place for students to openly talk about their sexual health. The Global Gage Rule will force peer educator programmes like this to close due to lack of funding. Help us bridge the funding gap Learn more about the Global Gag Rule

| 16 May 2025
“I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one"
On Friday afternoon in Municipal Lycee of Nyakabiga, Burundi, headmistress Chantal Keza is introducing her students to the medical staff from Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ABUBEF). Peer educators at the school, trained by ABUBEF, will perform a short drama based around sexual health and will answer questions about contraception methods from students. One of the actresses is peer educator Ammande Berlyne Dushime. Ammande, who is 17 years old is one of three peer educators at the school. Ammande, together with her friends, perform their short drama on the stage based on a young girls quest for information on contraception. It ends on a positive note, with the girl receiving useful and correct information from a peer educator at her school. A story that could be a very real life scenario at her school. Peer programmes that trained Ammande, are under threat of closure due to the Global Gag rule. Ammande says, “I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one. I am ready to go on with work as peer educator, but if there are not going to be regular visits by the medical stuff from the clinic, then we will have no one to seek information and advice from. I am just a teenager, I know so little. Not only I will lose my support, but also I will not be taken serious by my schoolmates. With such important topic like sexual education and contraception, I am not the authority. I can only show the right way to go. And this road leads to ABUBEF.” She says “As peer educator I am responsible for Saturday morning meetings at the clinic. We sing songs, play games, have fun and learn new things about sex education, contraception, HIV protection and others. Visiting the clinic is then very easy, and no student has to be afraid, that showing up at the clinic that treats HIV positive people, will ruin their reputation. Now they know that we can meet there openly, and undercover of these meetings seek for help, information, professional advice and contraception methods” Peer educator classes are a safe and open place for students to openly talk about their sexual health. The Global Gage Rule will force peer educator programmes like this to close due to lack of funding. Help us bridge the funding gap Learn more about the Global Gag Rule

| 18 June 2020
In pictures: Healthcare in the face of the climate crisis in Kiribati
Humanitarian crises Largely brought on by sudden onset and slow-onset natural disasters, humanitarian crises are increasingly prevalent in the Pacific. During responses to humanitarian crises in the Pacific, sexual and reproductive healthcare is often under-prioritised and under-resourced. As a result, women and girls of reproductive age and vulnerable and marginalized groups are disproportionately affected and facing increased health and psychosocial risks. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Fragile environments Low topography, rising sea levels and insufficient fresh water supply leaves Kiribati’s population vulnerable to the effects of the climate crisis. The fragility of the outer islands of Kiribati during natural disasters is compounded by their geographic isolation, which makes transportation and communication during post-disaster relief and response both expensive and difficult. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Coastal exposure The majority of the population of 115,000 people live a subsistence lifestyle. Communities are geographically dispersed across 33 atolls covering 3.5 million square kilometres in the central Pacific Ocean. The population and infrastructure within Kiribati are largely concentrated on the coast, where communities face increased exposure to climate threats and natural hazards such as tsunamis, earthquakes, king tides, flooding, droughts, and occasionally cyclones. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Takaria, leader and youth organizer in the Tebikenikua community Takaria will be running to be a Member of Parliament in Kiribati in 2020. “I assist the youth with family problems and family planning and disasters. In our community there are unforeseen pregnancies, domestic violence, and disasters such as high tide waters and strong winds, which can also affect this community. The Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) is the key point for us with outreach and training so people in this community know how to prevent and treat STIs, etc. They all know where the KFHA clinic is and that they can get counselling or services there. The problem now is you can’t survive with the sea rise levels. I want all members of my community to live better and have better health and peace.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Susan*, sex worker Susan receives care at the Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) including a pap smear. Susan*, 28, is a sex worker from the town of Betio on the main island of Kiribati. Originally from an outlying island, she moved into Tarawa to seek work. Unable to find employment that would fulfill her dream of sending money back to her two children, she was introduced to sex work. With other sex workers, she regularly travels out to the large cargo ships from China, Philippines and Korea anchored off the coast of Kiribati. Despite her new income, she still can’t speak with her children or see them due to the restrictive costs involved of travel between islands.*pseudonym Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Theta, 25-year-old mother and youth volunteer Theta is part of the Humanitarian Youth Club set up by the Kiribati Family Health Association in her village. “We face a lot of situations here, one of them is disasters and the second is unemployment and school drop out with our youth. I have helped the Humanitarian Youth Club to apply for financial grants from the Australian High Commission [for $1,000] I am recognized as the smartest member who can write in English. We have learned how to design a disaster plan for the community and share our ideas on sexual and reproductive issues such as STIs. We discuss what we can do for the next strong tide, where we can gather as a community and what we can do if even the maneabe (town hall) floods? If the tide and wind is too strong, we need to go to another safer place, such as another community’s town hall. For now, I want to enjoy the chance to be in our own beloved country. I won’t move until the majority have already left. I want my daughter to grow up in the same place I grew up in.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Beitau, youth volunteer Beitau is the Chairperson of the Humanitarian Youth Club. “I was lucky to be selected as Chairperson as the Humanitarian Youth Club. I feel like I get more respect from the community now I am in this position. I would love advanced training on leadership now, to further assist the club. As I am the Chairperson of the HYC, my main target is to help people during a disaster. I have attended training through KFHA. What I took from this is that when a disaster strikes, we have to do our best for pregnant women, small children and people with disabilities. They more vulnerable and less able to survive a disaster.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abe, youth officer Abe was involved with KFHA since 2012. “I was inspired by what they KFHA was doing and the issues they were addressing that affects youth. I was surprised to see how many young people come to the clinic as they are affected by STIs, HIV and teenage pregnancy. The lack of education here is a big problem, most people here have a lot of children and yet can’t afford to send them to school. Sexual and reproductive health is our responsibility and we must talk about it with young people. Climate change affects many countries, but Kiribati is small and low lying. I used to go visit a very nice beach with a lot of nice trees and plants. Now, the trees are gone, and the waves have taken over, and the houses have disappeared so no one can build there. In my role as a youth worker and activist, I tell people to fight climate change: to grow more mangroves, to clean up the beach, because we love our Kiribati.”©IPPF/Hannah Maule-Ffinch/Kiribati Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 17 May 2025
In pictures: Healthcare in the face of the climate crisis in Kiribati
Humanitarian crises Largely brought on by sudden onset and slow-onset natural disasters, humanitarian crises are increasingly prevalent in the Pacific. During responses to humanitarian crises in the Pacific, sexual and reproductive healthcare is often under-prioritised and under-resourced. As a result, women and girls of reproductive age and vulnerable and marginalized groups are disproportionately affected and facing increased health and psychosocial risks. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Fragile environments Low topography, rising sea levels and insufficient fresh water supply leaves Kiribati’s population vulnerable to the effects of the climate crisis. The fragility of the outer islands of Kiribati during natural disasters is compounded by their geographic isolation, which makes transportation and communication during post-disaster relief and response both expensive and difficult. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Coastal exposure The majority of the population of 115,000 people live a subsistence lifestyle. Communities are geographically dispersed across 33 atolls covering 3.5 million square kilometres in the central Pacific Ocean. The population and infrastructure within Kiribati are largely concentrated on the coast, where communities face increased exposure to climate threats and natural hazards such as tsunamis, earthquakes, king tides, flooding, droughts, and occasionally cyclones. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Takaria, leader and youth organizer in the Tebikenikua community Takaria will be running to be a Member of Parliament in Kiribati in 2020. “I assist the youth with family problems and family planning and disasters. In our community there are unforeseen pregnancies, domestic violence, and disasters such as high tide waters and strong winds, which can also affect this community. The Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) is the key point for us with outreach and training so people in this community know how to prevent and treat STIs, etc. They all know where the KFHA clinic is and that they can get counselling or services there. The problem now is you can’t survive with the sea rise levels. I want all members of my community to live better and have better health and peace.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Susan*, sex worker Susan receives care at the Kiribati Family Health Association (KFHA) including a pap smear. Susan*, 28, is a sex worker from the town of Betio on the main island of Kiribati. Originally from an outlying island, she moved into Tarawa to seek work. Unable to find employment that would fulfill her dream of sending money back to her two children, she was introduced to sex work. With other sex workers, she regularly travels out to the large cargo ships from China, Philippines and Korea anchored off the coast of Kiribati. Despite her new income, she still can’t speak with her children or see them due to the restrictive costs involved of travel between islands.*pseudonym Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Theta, 25-year-old mother and youth volunteer Theta is part of the Humanitarian Youth Club set up by the Kiribati Family Health Association in her village. “We face a lot of situations here, one of them is disasters and the second is unemployment and school drop out with our youth. I have helped the Humanitarian Youth Club to apply for financial grants from the Australian High Commission [for $1,000] I am recognized as the smartest member who can write in English. We have learned how to design a disaster plan for the community and share our ideas on sexual and reproductive issues such as STIs. We discuss what we can do for the next strong tide, where we can gather as a community and what we can do if even the maneabe (town hall) floods? If the tide and wind is too strong, we need to go to another safer place, such as another community’s town hall. For now, I want to enjoy the chance to be in our own beloved country. I won’t move until the majority have already left. I want my daughter to grow up in the same place I grew up in.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Beitau, youth volunteer Beitau is the Chairperson of the Humanitarian Youth Club. “I was lucky to be selected as Chairperson as the Humanitarian Youth Club. I feel like I get more respect from the community now I am in this position. I would love advanced training on leadership now, to further assist the club. As I am the Chairperson of the HYC, my main target is to help people during a disaster. I have attended training through KFHA. What I took from this is that when a disaster strikes, we have to do our best for pregnant women, small children and people with disabilities. They more vulnerable and less able to survive a disaster.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abe, youth officer Abe was involved with KFHA since 2012. “I was inspired by what they KFHA was doing and the issues they were addressing that affects youth. I was surprised to see how many young people come to the clinic as they are affected by STIs, HIV and teenage pregnancy. The lack of education here is a big problem, most people here have a lot of children and yet can’t afford to send them to school. Sexual and reproductive health is our responsibility and we must talk about it with young people. Climate change affects many countries, but Kiribati is small and low lying. I used to go visit a very nice beach with a lot of nice trees and plants. Now, the trees are gone, and the waves have taken over, and the houses have disappeared so no one can build there. In my role as a youth worker and activist, I tell people to fight climate change: to grow more mangroves, to clean up the beach, because we love our Kiribati.”©IPPF/Hannah Maule-Ffinch/Kiribati Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 22 January 2018
"I am a living example of having a good life..."
At a local bar, we meet nine women from Kirundo. They’re all sex workers who became friends through Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial's (ABUBEF) peer educator project. Yvonne is 40 and has known that she’s HIV-positive for 22 years. After her diagnosis she was isolated from her friends and stigmatized both in public and at home, where she was even given separate plates to eat from. “I started to get drunk every day,” she says. “I hoped death would take me in my sleep. I didn’t believe in tomorrow. I was lost and lonely. Until I got to the ABUBEF clinic.” ABUBEF has supported her treatment for the past six years. “I take my pill every day and I am living example of having a good life even with a previous death sentence,” Yvonne explains. “But I see that the awareness of HIV, protection and testing provided by ABUBEF is still very small.” Yvonne became a peer educator, speaking in public about HIV awareness, wearing an ABUBEF T-shirt. The project spread to the wider region, and volunteers were given travel expenses, materials and training, along with condoms for distribution. But funding cuts mean those expenses are no longer available. Yvonne says she’ll carry on in Kirundo even if she can’t travel more widely like she used to. Her friend, 29-year-old Perusi, shares her experience of ABUBEF as a safe space where her privacy will be respected. It often happens, she says, that her clients rape her, and run away, failing to pay. Since sex work is illegal, she says, and there’s no protection from the authorities, and sex workers like her often feel rejected by society. But at ABUBEF’s clinics, they are welcomed.

| 16 May 2025
"I am a living example of having a good life..."
At a local bar, we meet nine women from Kirundo. They’re all sex workers who became friends through Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial's (ABUBEF) peer educator project. Yvonne is 40 and has known that she’s HIV-positive for 22 years. After her diagnosis she was isolated from her friends and stigmatized both in public and at home, where she was even given separate plates to eat from. “I started to get drunk every day,” she says. “I hoped death would take me in my sleep. I didn’t believe in tomorrow. I was lost and lonely. Until I got to the ABUBEF clinic.” ABUBEF has supported her treatment for the past six years. “I take my pill every day and I am living example of having a good life even with a previous death sentence,” Yvonne explains. “But I see that the awareness of HIV, protection and testing provided by ABUBEF is still very small.” Yvonne became a peer educator, speaking in public about HIV awareness, wearing an ABUBEF T-shirt. The project spread to the wider region, and volunteers were given travel expenses, materials and training, along with condoms for distribution. But funding cuts mean those expenses are no longer available. Yvonne says she’ll carry on in Kirundo even if she can’t travel more widely like she used to. Her friend, 29-year-old Perusi, shares her experience of ABUBEF as a safe space where her privacy will be respected. It often happens, she says, that her clients rape her, and run away, failing to pay. Since sex work is illegal, she says, and there’s no protection from the authorities, and sex workers like her often feel rejected by society. But at ABUBEF’s clinics, they are welcomed.

| 22 January 2018
“They saved the life of me and my child”
Monica has never told anyone about the attack. She was pregnant at the time, already had two teenage sons, and rape is a taboo subject in her community in Burundi. Knowing that her attacker was HIV-positive, and fearing that her husband would accuse her of provocation - or worse still, leave her - she turned to a place she knew would help. ABUBEF is the Association Burundaise Pour Le Bien-Etre Familial. Their clinic in Kirundo offered Monica HIV counselling and treatment for the duration of her pregnancy. Above all, ABUBEF offered privacy. Neither Monica nor her daughter has tested positive for HIV. “They saved the life of me and my child,” Monica says. “I hope they get an award for their psychological and health support for women.” Three years on from the attack, Monica, now 45, raises her children and tends the family farm where she grows beans, cassava, potatoes and rice. She’s proud of her eldest son who’s due to start university this year. She educates her boys against violence, and spreads the word about ABUBEF. Monica speaks to other women to make sure they know where to seek help if they need it. Her attacker still lives in the neighbourhood, and she worries that he’s transmitting HIV. But the ABUBEF clinic that helped Monica is under threat from funding cuts. The possibility that it could close prompted her to tell her story. “This is a disaster for our community,” she says. “I know how much the clinic needs support from donors, how much they need new equipment and money for new staff. I want people to know that this facility is one of a kind - and without it many people will be lost.”

| 16 May 2025
“They saved the life of me and my child”
Monica has never told anyone about the attack. She was pregnant at the time, already had two teenage sons, and rape is a taboo subject in her community in Burundi. Knowing that her attacker was HIV-positive, and fearing that her husband would accuse her of provocation - or worse still, leave her - she turned to a place she knew would help. ABUBEF is the Association Burundaise Pour Le Bien-Etre Familial. Their clinic in Kirundo offered Monica HIV counselling and treatment for the duration of her pregnancy. Above all, ABUBEF offered privacy. Neither Monica nor her daughter has tested positive for HIV. “They saved the life of me and my child,” Monica says. “I hope they get an award for their psychological and health support for women.” Three years on from the attack, Monica, now 45, raises her children and tends the family farm where she grows beans, cassava, potatoes and rice. She’s proud of her eldest son who’s due to start university this year. She educates her boys against violence, and spreads the word about ABUBEF. Monica speaks to other women to make sure they know where to seek help if they need it. Her attacker still lives in the neighbourhood, and she worries that he’s transmitting HIV. But the ABUBEF clinic that helped Monica is under threat from funding cuts. The possibility that it could close prompted her to tell her story. “This is a disaster for our community,” she says. “I know how much the clinic needs support from donors, how much they need new equipment and money for new staff. I want people to know that this facility is one of a kind - and without it many people will be lost.”

| 19 January 2018
“I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one"
On Friday afternoon in Municipal Lycee of Nyakabiga, Burundi, headmistress Chantal Keza is introducing her students to the medical staff from Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ABUBEF). Peer educators at the school, trained by ABUBEF, will perform a short drama based around sexual health and will answer questions about contraception methods from students. One of the actresses is peer educator Ammande Berlyne Dushime. Ammande, who is 17 years old is one of three peer educators at the school. Ammande, together with her friends, perform their short drama on the stage based on a young girls quest for information on contraception. It ends on a positive note, with the girl receiving useful and correct information from a peer educator at her school. A story that could be a very real life scenario at her school. Peer programmes that trained Ammande, are under threat of closure due to the Global Gag rule. Ammande says, “I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one. I am ready to go on with work as peer educator, but if there are not going to be regular visits by the medical stuff from the clinic, then we will have no one to seek information and advice from. I am just a teenager, I know so little. Not only I will lose my support, but also I will not be taken serious by my schoolmates. With such important topic like sexual education and contraception, I am not the authority. I can only show the right way to go. And this road leads to ABUBEF.” She says “As peer educator I am responsible for Saturday morning meetings at the clinic. We sing songs, play games, have fun and learn new things about sex education, contraception, HIV protection and others. Visiting the clinic is then very easy, and no student has to be afraid, that showing up at the clinic that treats HIV positive people, will ruin their reputation. Now they know that we can meet there openly, and undercover of these meetings seek for help, information, professional advice and contraception methods” Peer educator classes are a safe and open place for students to openly talk about their sexual health. The Global Gage Rule will force peer educator programmes like this to close due to lack of funding. Help us bridge the funding gap Learn more about the Global Gag Rule

| 16 May 2025
“I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one"
On Friday afternoon in Municipal Lycee of Nyakabiga, Burundi, headmistress Chantal Keza is introducing her students to the medical staff from Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ABUBEF). Peer educators at the school, trained by ABUBEF, will perform a short drama based around sexual health and will answer questions about contraception methods from students. One of the actresses is peer educator Ammande Berlyne Dushime. Ammande, who is 17 years old is one of three peer educators at the school. Ammande, together with her friends, perform their short drama on the stage based on a young girls quest for information on contraception. It ends on a positive note, with the girl receiving useful and correct information from a peer educator at her school. A story that could be a very real life scenario at her school. Peer programmes that trained Ammande, are under threat of closure due to the Global Gag rule. Ammande says, “I am afraid what will happen when there will be no more projects like this one. I am ready to go on with work as peer educator, but if there are not going to be regular visits by the medical stuff from the clinic, then we will have no one to seek information and advice from. I am just a teenager, I know so little. Not only I will lose my support, but also I will not be taken serious by my schoolmates. With such important topic like sexual education and contraception, I am not the authority. I can only show the right way to go. And this road leads to ABUBEF.” She says “As peer educator I am responsible for Saturday morning meetings at the clinic. We sing songs, play games, have fun and learn new things about sex education, contraception, HIV protection and others. Visiting the clinic is then very easy, and no student has to be afraid, that showing up at the clinic that treats HIV positive people, will ruin their reputation. Now they know that we can meet there openly, and undercover of these meetings seek for help, information, professional advice and contraception methods” Peer educator classes are a safe and open place for students to openly talk about their sexual health. The Global Gage Rule will force peer educator programmes like this to close due to lack of funding. Help us bridge the funding gap Learn more about the Global Gag Rule








