Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in the face of growing opposition and the rise of the far right? These victories for sexual and reproductive rights and health are the result of relentless grassroots work and advocacy by our Member Associations, in partnership with community organizations, allied politicians, and the mobilization of public opinion.
Most Popular This Week

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in t
Kazakhstan
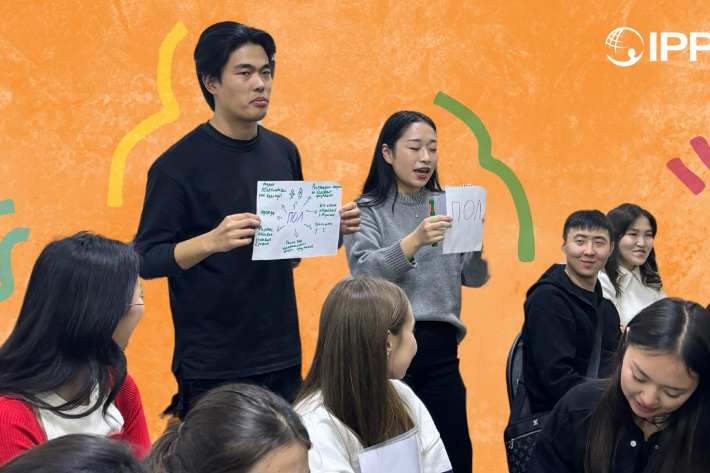

Kazakhstan's Rising HIV Crisis: A Call for Action
On World AIDS Day, we commemorate the remarkable achievements of IPPF Member Associations in their unwavering commitment to combating the HIV epidemic.

Ensuring SRHR in Humanitarian Crises: What You Need to Know
Over the past two decades, global forced displacement has consistently increased, affecting an estimated 114 million people as of mid-2023.
Estonia, Nepal, Namibia, Japan, Thailand

The Rainbow Wave for Marriage Equality
Love wins! The fight for marriage equality has seen incredible progress worldwide, with a recent surge in legalizations.
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
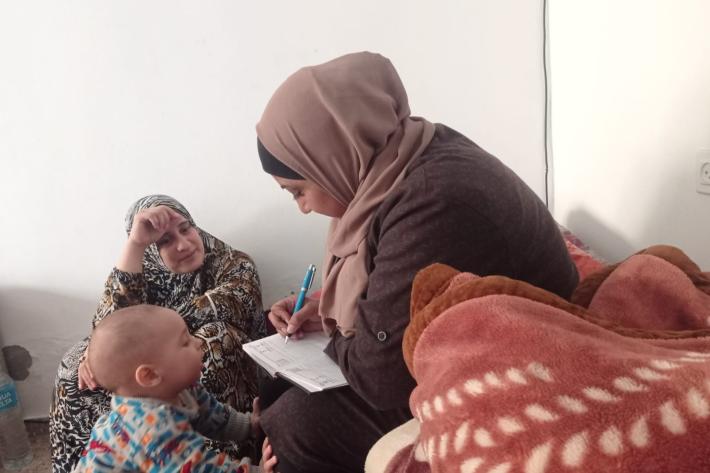

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Filter our stories by:
- Afghan Family Guidance Association
- Albanian Center for Population and Development
- Asociación Pro-Bienestar de la Familia Colombiana
- Associação Moçambicana para Desenvolvimento da Família
- Association Béninoise pour la Promotion de la Famille
- Association Burundaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial
- (-) Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille
- Association pour le Bien-Etre Familial/Naissances Désirables
- Association Sénégalaise pour le Bien-Étre Familial
- Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial
- Association Tunisienne de la Santé de la Reproduction
- Botswana Family Welfare Association
- Cameroon National Association for Family Welfare
- Cook Islands Family Welfare Association
- Eesti Seksuaaltervise Liit / Estonian Sexual Health Association
- Family Guidance Association of Ethiopia
- (-) Family Planning Association of India
- Family Planning Association of Malawi
- Family Planning Association of Nepal
- Family Planning Association of Sri Lanka
- Family Planning Association of Trinidad and Tobago
- Foundation for the Promotion of Responsible Parenthood - Aruba
- Indonesian Planned Parenthood Association
- Jamaica Family Planning Association
- Kazakhstan Association on Sexual and Reproductive Health (KMPA)
- Kiribati Family Health Association
- Lesotho Planned Parenthood Association
- Mouvement Français pour le Planning Familial
- Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA)
- Planned Parenthood Association of Ghana
- Planned Parenthood Association of Thailand
- Planned Parenthood Association of Zambia
- Planned Parenthood Federation of America
- Planned Parenthood Federation of Nigeria
- Pro Familia - Germany
- Rahnuma-Family Planning Association of Pakistan
- Reproductive & Family Health Association of Fiji
- Reproductive Health Association of Cambodia (RHAC)
- Reproductive Health Uganda
- Somaliland Family Health Association
- Sudan Family Planning Association
- Tonga Family Health Association
- Vanuatu Family Health Association
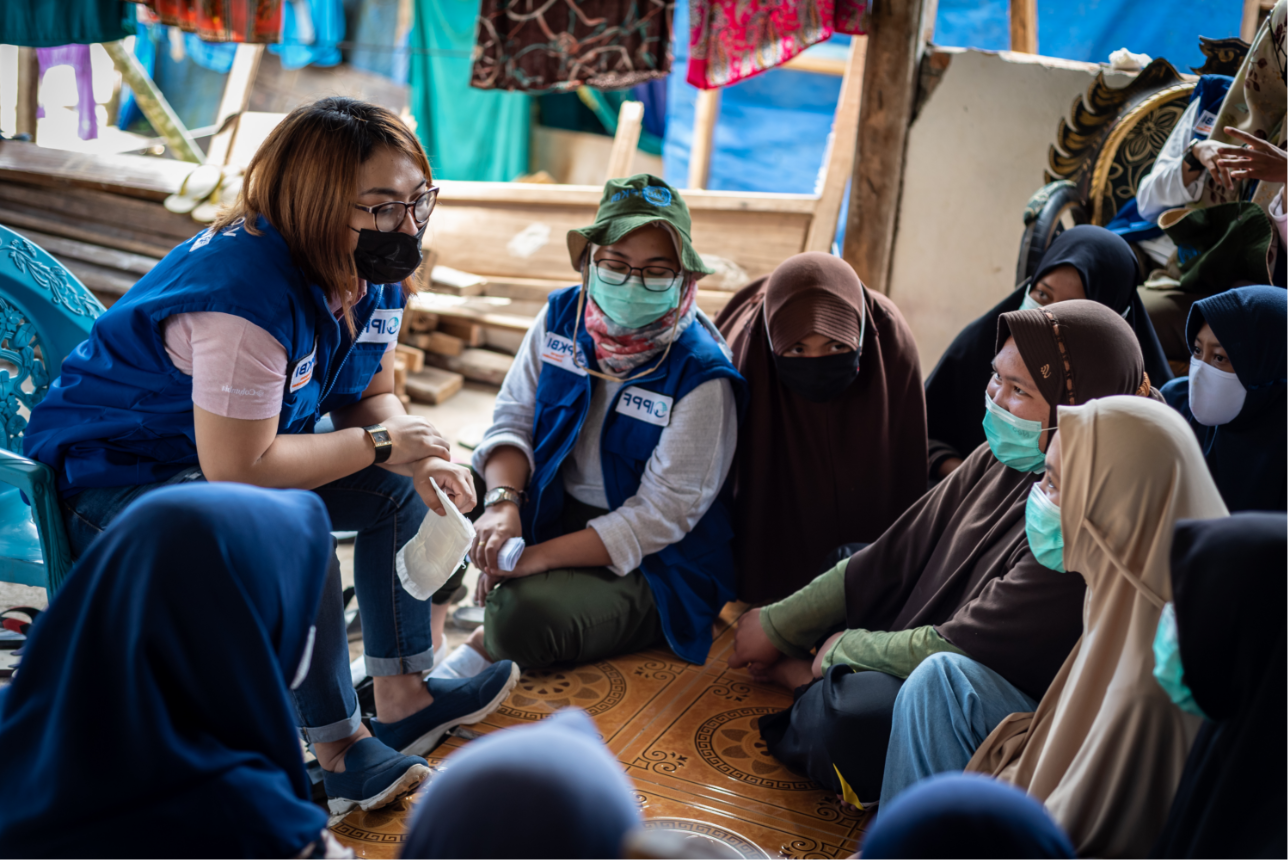


| 18 April 2024
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than 60 countries and territories have liberalized their abortion laws. Only four have regressed, including the United States. Abortion rights are increasingly becoming recognized as fundamental human rights for millions of people worldwide. The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.

| 18 April 2024
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than 60 countries and territories have liberalized their abortion laws. Only four have regressed, including the United States. Abortion rights are increasingly becoming recognized as fundamental human rights for millions of people worldwide. The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.

| 08 January 2021
"Girls have to know their rights"
Aminata Sonogo listened intently to the group of young volunteers as they explained different types of contraception, and raised her hand with questions. Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Aminata is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. Aminata is studying in Bamako, the capital of Mali. Just a quarter of Malian girls complete secondary school, according to UNICEF. But even if she will graduate later than most, Aminata is conscious of how far she has come. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said. At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Aminata got pregnant. She is far from alone: 38% of Malian girls will be pregnant or a mother by the age of 18. Abortion is illegal in Mali except in cases of rape, incest or danger to the mother’s life, and even then it is difficult to obtain, according to medical professionals. Determined to take control of her life “I felt a lot of stigma from my classmates and even my teachers. I tried to ignore them and carry on going to school and studying. But I gave birth to my daughter just before my exams, so I couldn’t take them.” Aminata went through her pregnancy with little support, as the father of her daughter, Fatoumata, distanced himself from her after arguments about their situation. “I have had some problems with the father of the baby. We fought a lot and I didn’t see him for most of the pregnancy, right until the birth,” she recalled. The first year of her daughter’s life was a blur of doctors’ appointments, as Fatoumata was often ill. It seemed Aminata’s chances of finishing school were slipping away. But gradually her family began to take a more active role in caring for her daughter, and she began demanding more help from Fatoumata’s father too. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. She no longer had time to hang out with friends after school, but attended classes, took care of her daughter and then studied more. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Aminata said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. "Family planning protects girls" Aminata’s next goal is her high school diploma, and obtaining it while trying to navigate the difficult world of relationships and sex. “It’s something you can talk about with your close friends. I would be too ashamed to talk about this with my parents,” she said. She is guided by visits from the young volunteers of the Association Malienne pour la Protection et Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk. “The guys come up to you and tell you that you are beautiful, but if you don’t want to sleep with them they will rape you. That’s the choice. You can accept or you can refuse and they will rape you anyway,” she said. “Girls have to know their rights”. After listening to the volunteers talk about all the different options for contraception, she is reviewing her own choices. “Family planning protects girls,” Aminata said. “It means we can protect ourselves from pregnancies that we don’t want”.

| 15 May 2025
"Girls have to know their rights"
Aminata Sonogo listened intently to the group of young volunteers as they explained different types of contraception, and raised her hand with questions. Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Aminata is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. Aminata is studying in Bamako, the capital of Mali. Just a quarter of Malian girls complete secondary school, according to UNICEF. But even if she will graduate later than most, Aminata is conscious of how far she has come. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said. At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Aminata got pregnant. She is far from alone: 38% of Malian girls will be pregnant or a mother by the age of 18. Abortion is illegal in Mali except in cases of rape, incest or danger to the mother’s life, and even then it is difficult to obtain, according to medical professionals. Determined to take control of her life “I felt a lot of stigma from my classmates and even my teachers. I tried to ignore them and carry on going to school and studying. But I gave birth to my daughter just before my exams, so I couldn’t take them.” Aminata went through her pregnancy with little support, as the father of her daughter, Fatoumata, distanced himself from her after arguments about their situation. “I have had some problems with the father of the baby. We fought a lot and I didn’t see him for most of the pregnancy, right until the birth,” she recalled. The first year of her daughter’s life was a blur of doctors’ appointments, as Fatoumata was often ill. It seemed Aminata’s chances of finishing school were slipping away. But gradually her family began to take a more active role in caring for her daughter, and she began demanding more help from Fatoumata’s father too. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. She no longer had time to hang out with friends after school, but attended classes, took care of her daughter and then studied more. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Aminata said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. "Family planning protects girls" Aminata’s next goal is her high school diploma, and obtaining it while trying to navigate the difficult world of relationships and sex. “It’s something you can talk about with your close friends. I would be too ashamed to talk about this with my parents,” she said. She is guided by visits from the young volunteers of the Association Malienne pour la Protection et Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk. “The guys come up to you and tell you that you are beautiful, but if you don’t want to sleep with them they will rape you. That’s the choice. You can accept or you can refuse and they will rape you anyway,” she said. “Girls have to know their rights”. After listening to the volunteers talk about all the different options for contraception, she is reviewing her own choices. “Family planning protects girls,” Aminata said. “It means we can protect ourselves from pregnancies that we don’t want”.
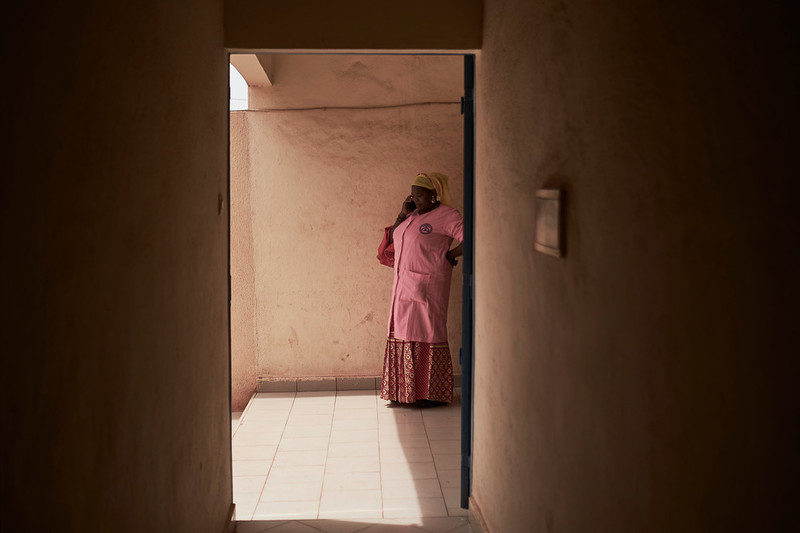

| 08 January 2021
"We see cases of early pregnancy from 14 years old – occasionally they are younger"
My name is Mariame Doumbia, I am a midwife with the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), providing family planning and sexual health services to Malians in and around the capital, Bamako. I have worked with AMPPF for almost six years in total, but there was a break two years ago when American funding stopped due to the Global Gag Rule. I was able to come back to work with Canadian funding for the project SheDecides, and they have paid my salary for the last two years. I work at fixed and mobile clinics in Bamako. In the neighbourhood of Kalabancoro, which is on the outskirts of the capital, I receive clients at the clinic who would not be able to afford travel to somewhere farther away. It’s a poor neighbourhood. Providing the correct information The women come with their ideas about sex, sometimes with lots of rumours, but we go through it all with them to explain what sexual health is and how to maintain it. We clarify things for them. More and more they come with their mothers, or their boyfriends or husbands. The youngest ones come to ask about their periods and how they can count their menstrual cycle. Then they start to ask about sex. These days the price of sanitary pads is going down, so they are using bits of fabric less often, which is what I used to see. Seeing the impact of our work We see cases of early pregnancy here in Kalabancoro, but the numbers are definitely going down. Most are from 14 years old upwards, though occasionally they are younger. SheDecides has brought so much to this clinic, starting with the fact that before the project’s arrival there was no one here at all for a prolonged period of time. Now the community has the right to information and I try my best to answer all their questions.

| 15 May 2025
"We see cases of early pregnancy from 14 years old – occasionally they are younger"
My name is Mariame Doumbia, I am a midwife with the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), providing family planning and sexual health services to Malians in and around the capital, Bamako. I have worked with AMPPF for almost six years in total, but there was a break two years ago when American funding stopped due to the Global Gag Rule. I was able to come back to work with Canadian funding for the project SheDecides, and they have paid my salary for the last two years. I work at fixed and mobile clinics in Bamako. In the neighbourhood of Kalabancoro, which is on the outskirts of the capital, I receive clients at the clinic who would not be able to afford travel to somewhere farther away. It’s a poor neighbourhood. Providing the correct information The women come with their ideas about sex, sometimes with lots of rumours, but we go through it all with them to explain what sexual health is and how to maintain it. We clarify things for them. More and more they come with their mothers, or their boyfriends or husbands. The youngest ones come to ask about their periods and how they can count their menstrual cycle. Then they start to ask about sex. These days the price of sanitary pads is going down, so they are using bits of fabric less often, which is what I used to see. Seeing the impact of our work We see cases of early pregnancy here in Kalabancoro, but the numbers are definitely going down. Most are from 14 years old upwards, though occasionally they are younger. SheDecides has brought so much to this clinic, starting with the fact that before the project’s arrival there was no one here at all for a prolonged period of time. Now the community has the right to information and I try my best to answer all their questions.
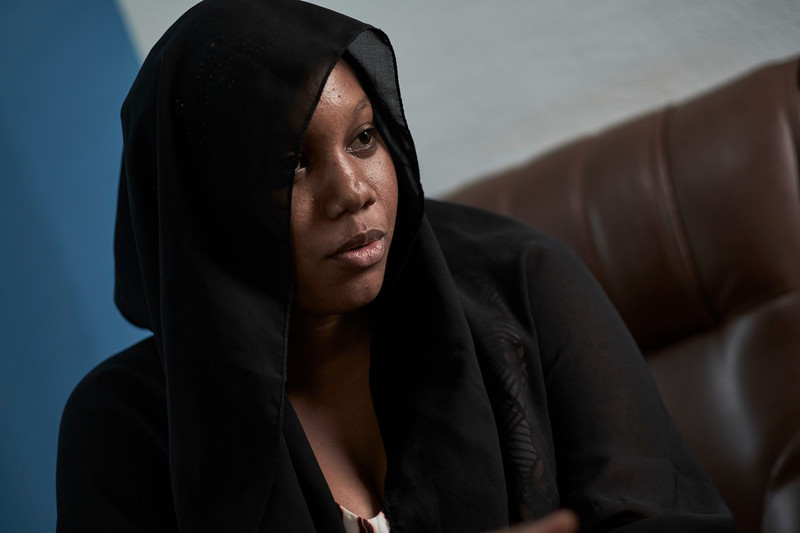

| 08 January 2021
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.

| 15 May 2025
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.
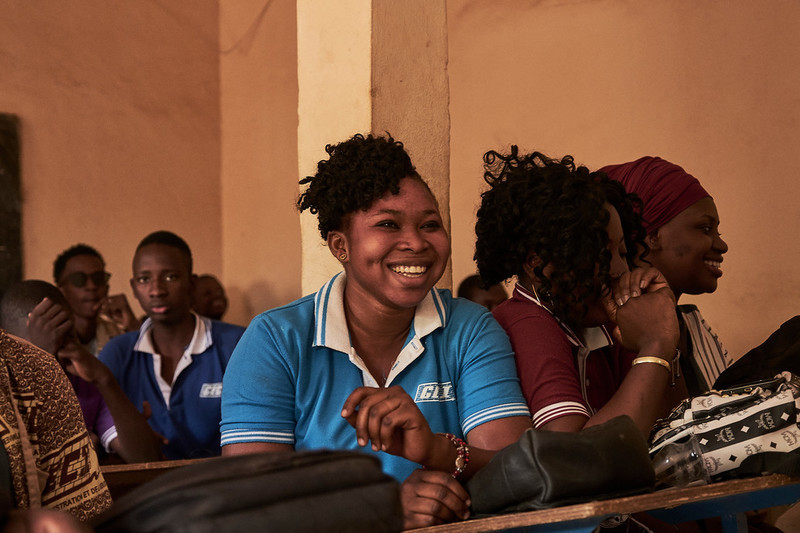
| 07 January 2021
In pictures: Overcoming the impact of the Global Gag Rule in Mali
In 2017, the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), was hit hard by the reinstatement of the Global Gag Rule (GGR). The impact was swift and devastating – depleted budgets meant that AMPPF had to cut back on key staff and suspend education activities and community healthcare provision. The situation turned around with funding from the Canadian Government supporting the SheDecides project, filling the gap left by GGR. AMPPF has been able to employ staff ensuring their team can reach the most vulnerable clients who would otherwise be left without access to sexual healthcare and increase their outreach to youth. Putting communities first Mama Keita Sy Diallo, midwife The SheDecides project has allowed AMPPF to maintain three mobile clinics, travelling to more remote areas where transportation costs and huge distances separate women from access to health and contraceptive care.“SheDecides has helped us a lot, above all in our work outside our own permanent clinics. When we go out in the community we have a lot of clients, and many women come to us who would otherwise not have the means to obtain advice or contraception,” explained Mama Keita Sy Diallo, a midwife and AMPPF board member. She runs consultations at community health centers in underserved areas of the Malian capital. “Everything is free for the women in these sessions.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email SheDecides projects ensures free access to healthcare and contraception Fatoumata Dramé, client By 9am at the Asaco Sekasi community health center in Bamako, its wooden benches are full of clients waiting their turn at a SheDecides outreach session. Fatoumata Dramé, 30, got here early and has already been fitted for a new implant. “I came here for family planning, and it’s my first time. I’ve just moved to the area so I came because it’s close to home,” she said. Bouncing two-month-old Tiemoko on her knee, Dramé said her main motivation was to space the births of her children. “I am a mum of three now. My first child is 7 years old. I try to leave three years between each child. It helps with my health,” she explained. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Targeting youth Mamadou Bah, Youth Action Movement “After the arrival of SheDecides, we intensified our targeting of vulnerable groups with activities in the evening, when domestic workers and those working during the day could attend,” said Mariam Modibo Tandina, who heads the national committee of the Youth Action Movement in Mali. “That means that young people in precarious situations could learn more about safer sex and family planning. Now they know how to protect themselves against sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Speaking out against FGM Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga, youth volunteer Fatoumata’s decision to join the Youth Action Movement was fueled by a personal loss. “My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Using dance and comedy to talk about sex Abdoulaye Camara, Head of AMPPF dance troupe Abdoulaye’s moves are not just for fun. He is head of the dance troupe of the AMPPF’s Youth Action Movement, which uses dance and comedy sketches to talk about sex. It’s a canny way to deliver messages about everything from using condoms to taking counterfeit antibiotics, to an audience who are often confused and ashamed about such topics. “We distract them with dance and humour and then we transmit those important messages about sex without offending them,” explained Abdoulaye. “We show them that it’s not to insult them or show them up, but just to explain how these things happen.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Determination to graduate Aminata Sonogo, student Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Sonogo is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said.At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Sonogo got pregnant. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Sonogo said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. She is guided by visits from the AMPPF youth volunteers and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk of an unwanted pregnancy. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email AMPPF’s mobile clinic offers a lifeline to remote communities Mariame Doumbia, midwife “I work at a mobile clinic. It’s important for accessibility, so that the women living in poorly serviced areas can access sexual and reproductive health services, and reliable information.I like what I do. I like helping people, especially the young ones. They know I am always on call to help them, and even if I don’t know the answer at that moment, I will find out. I like everything about my work. Actually, it’s not just work for me, and I became a midwife for that reason. I’ve always been an educator on these issues in my community.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Trust underpins the relationship between AMPPF’s mobile team and the village of Missala Adama Samaké, village elder and chief of the Missala Health Center Adama Samaké, chief of the Missala Health Center, oversees the proceedings as a village elder with deep trust from his community. When the mobile clinic isn’t around, his center offers maternity services and treats the many cases of malaria that are diagnosed in the community. “Given the distance between here and Bamako, most of the villagers around here rely on us for treatment,” he said. “But when we announce that the mobile clinic is coming, the women make sure they are here.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Contraceptive choice Kadidiatou Sogoba, client Kadidiatou Sogoba, a mother of seven, waited nervously for her turn. “I came today because I keep getting ill and I have felt very weak, just not myself, since I had a Caesarean section three years ago. I lost a lot of blood,” she said. “I have been very afraid since the birth of my last child. We have been using condoms and we were getting a bit tired of them, so I am looking for another longer-term type of contraception.”After emerging half an hour later, Sogoba clutched a packet of the contraceptive pill, and said next time she would go for a cervical screening.Photos ©IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Mali Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
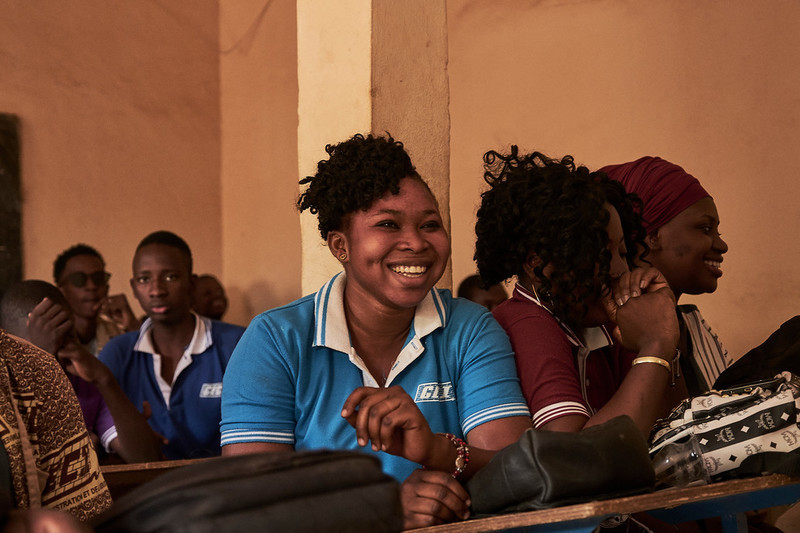
| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Overcoming the impact of the Global Gag Rule in Mali
In 2017, the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), was hit hard by the reinstatement of the Global Gag Rule (GGR). The impact was swift and devastating – depleted budgets meant that AMPPF had to cut back on key staff and suspend education activities and community healthcare provision. The situation turned around with funding from the Canadian Government supporting the SheDecides project, filling the gap left by GGR. AMPPF has been able to employ staff ensuring their team can reach the most vulnerable clients who would otherwise be left without access to sexual healthcare and increase their outreach to youth. Putting communities first Mama Keita Sy Diallo, midwife The SheDecides project has allowed AMPPF to maintain three mobile clinics, travelling to more remote areas where transportation costs and huge distances separate women from access to health and contraceptive care.“SheDecides has helped us a lot, above all in our work outside our own permanent clinics. When we go out in the community we have a lot of clients, and many women come to us who would otherwise not have the means to obtain advice or contraception,” explained Mama Keita Sy Diallo, a midwife and AMPPF board member. She runs consultations at community health centers in underserved areas of the Malian capital. “Everything is free for the women in these sessions.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email SheDecides projects ensures free access to healthcare and contraception Fatoumata Dramé, client By 9am at the Asaco Sekasi community health center in Bamako, its wooden benches are full of clients waiting their turn at a SheDecides outreach session. Fatoumata Dramé, 30, got here early and has already been fitted for a new implant. “I came here for family planning, and it’s my first time. I’ve just moved to the area so I came because it’s close to home,” she said. Bouncing two-month-old Tiemoko on her knee, Dramé said her main motivation was to space the births of her children. “I am a mum of three now. My first child is 7 years old. I try to leave three years between each child. It helps with my health,” she explained. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Targeting youth Mamadou Bah, Youth Action Movement “After the arrival of SheDecides, we intensified our targeting of vulnerable groups with activities in the evening, when domestic workers and those working during the day could attend,” said Mariam Modibo Tandina, who heads the national committee of the Youth Action Movement in Mali. “That means that young people in precarious situations could learn more about safer sex and family planning. Now they know how to protect themselves against sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Speaking out against FGM Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga, youth volunteer Fatoumata’s decision to join the Youth Action Movement was fueled by a personal loss. “My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Using dance and comedy to talk about sex Abdoulaye Camara, Head of AMPPF dance troupe Abdoulaye’s moves are not just for fun. He is head of the dance troupe of the AMPPF’s Youth Action Movement, which uses dance and comedy sketches to talk about sex. It’s a canny way to deliver messages about everything from using condoms to taking counterfeit antibiotics, to an audience who are often confused and ashamed about such topics. “We distract them with dance and humour and then we transmit those important messages about sex without offending them,” explained Abdoulaye. “We show them that it’s not to insult them or show them up, but just to explain how these things happen.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Determination to graduate Aminata Sonogo, student Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Sonogo is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said.At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Sonogo got pregnant. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Sonogo said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. She is guided by visits from the AMPPF youth volunteers and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk of an unwanted pregnancy. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email AMPPF’s mobile clinic offers a lifeline to remote communities Mariame Doumbia, midwife “I work at a mobile clinic. It’s important for accessibility, so that the women living in poorly serviced areas can access sexual and reproductive health services, and reliable information.I like what I do. I like helping people, especially the young ones. They know I am always on call to help them, and even if I don’t know the answer at that moment, I will find out. I like everything about my work. Actually, it’s not just work for me, and I became a midwife for that reason. I’ve always been an educator on these issues in my community.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Trust underpins the relationship between AMPPF’s mobile team and the village of Missala Adama Samaké, village elder and chief of the Missala Health Center Adama Samaké, chief of the Missala Health Center, oversees the proceedings as a village elder with deep trust from his community. When the mobile clinic isn’t around, his center offers maternity services and treats the many cases of malaria that are diagnosed in the community. “Given the distance between here and Bamako, most of the villagers around here rely on us for treatment,” he said. “But when we announce that the mobile clinic is coming, the women make sure they are here.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Contraceptive choice Kadidiatou Sogoba, client Kadidiatou Sogoba, a mother of seven, waited nervously for her turn. “I came today because I keep getting ill and I have felt very weak, just not myself, since I had a Caesarean section three years ago. I lost a lot of blood,” she said. “I have been very afraid since the birth of my last child. We have been using condoms and we were getting a bit tired of them, so I am looking for another longer-term type of contraception.”After emerging half an hour later, Sogoba clutched a packet of the contraceptive pill, and said next time she would go for a cervical screening.Photos ©IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Mali Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
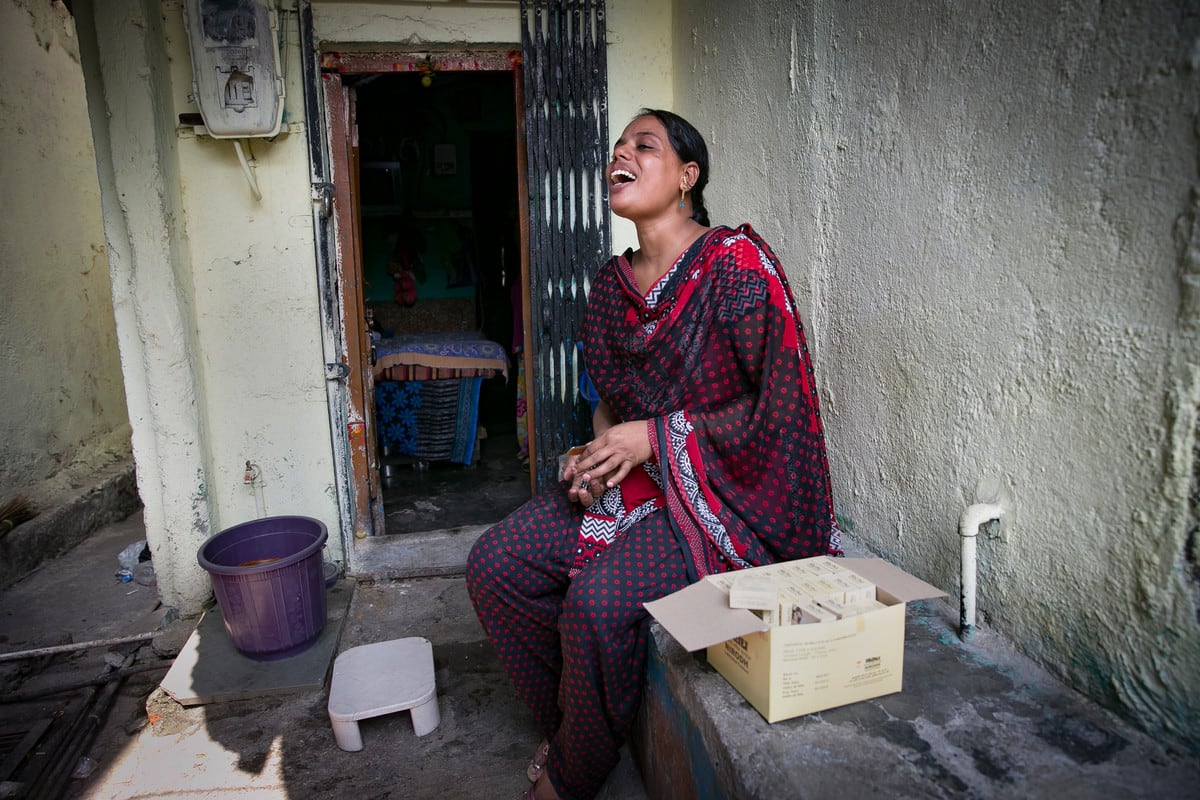

| 22 November 2018
"Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person"
“Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person, but working as a peer educator has helped enabled me to help many like me.” Hasina is one of the estimated 1,500 sex workers living in Haunman Tekri, a red-light area in Bhiwandi, a town near Mumbai. When her husband passed away six years ago leaving behind a three-year-old daughter, Hasina turned to sex work as her only option to earn money. She admits that it came with a feeling of powerlessness. "You don't choose this trade; it is the result of life circumstances.” She works as a peer educator with PSK, one of the Family Planning Association of India's (FPAI) clinics. "Working with Parivar Swasthya Kedra (PSK), has made me feel less helpless; it's given me some control over my body; the ability to choose whether or not to bring another life into this world.” Building trust through education Hasina has been a peer educator for three years, working within the district to educate other women on safe sex, contraception, and abortion. Hasina admits she was once wary of PSK workers. "I used to think that these workers who insist we use condoms, would only sabotage my clientele. But soon I realized they were only looking out for us." When talking with local women, Hasina advocates the use of contraception but says in the case of an unintended pregnancy, abortion is a viable option. "It's easy to judge us, but many of us have no choice; we simply cannot feed another on just Rs. 400 a day." Hasina is now the go-to woman in the district when it comes to sexual health. "Since I am one of them, the women trust me." This is the secret behind PSK success; a model where sex workers educate their peers, understanding the complexities and prejudices of their daily lives. "I hope one day I am able to put all of this behind me. But I hope that through PSK I am able to make another woman's life just a little bit safer, a little bit better." Do you want to show your support for women and girls to be free to decide what happens to their body? Pledge your voice to our I Decide campaign,IPPF’s movement for safe abortion access for all. You'll be provided with toolkits on how to talk about abortion and you'll have access to a range of content from personal testimonies to videos explaining the different types of abortion available.

| 15 May 2025
"Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person"
“Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person, but working as a peer educator has helped enabled me to help many like me.” Hasina is one of the estimated 1,500 sex workers living in Haunman Tekri, a red-light area in Bhiwandi, a town near Mumbai. When her husband passed away six years ago leaving behind a three-year-old daughter, Hasina turned to sex work as her only option to earn money. She admits that it came with a feeling of powerlessness. "You don't choose this trade; it is the result of life circumstances.” She works as a peer educator with PSK, one of the Family Planning Association of India's (FPAI) clinics. "Working with Parivar Swasthya Kedra (PSK), has made me feel less helpless; it's given me some control over my body; the ability to choose whether or not to bring another life into this world.” Building trust through education Hasina has been a peer educator for three years, working within the district to educate other women on safe sex, contraception, and abortion. Hasina admits she was once wary of PSK workers. "I used to think that these workers who insist we use condoms, would only sabotage my clientele. But soon I realized they were only looking out for us." When talking with local women, Hasina advocates the use of contraception but says in the case of an unintended pregnancy, abortion is a viable option. "It's easy to judge us, but many of us have no choice; we simply cannot feed another on just Rs. 400 a day." Hasina is now the go-to woman in the district when it comes to sexual health. "Since I am one of them, the women trust me." This is the secret behind PSK success; a model where sex workers educate their peers, understanding the complexities and prejudices of their daily lives. "I hope one day I am able to put all of this behind me. But I hope that through PSK I am able to make another woman's life just a little bit safer, a little bit better." Do you want to show your support for women and girls to be free to decide what happens to their body? Pledge your voice to our I Decide campaign,IPPF’s movement for safe abortion access for all. You'll be provided with toolkits on how to talk about abortion and you'll have access to a range of content from personal testimonies to videos explaining the different types of abortion available.
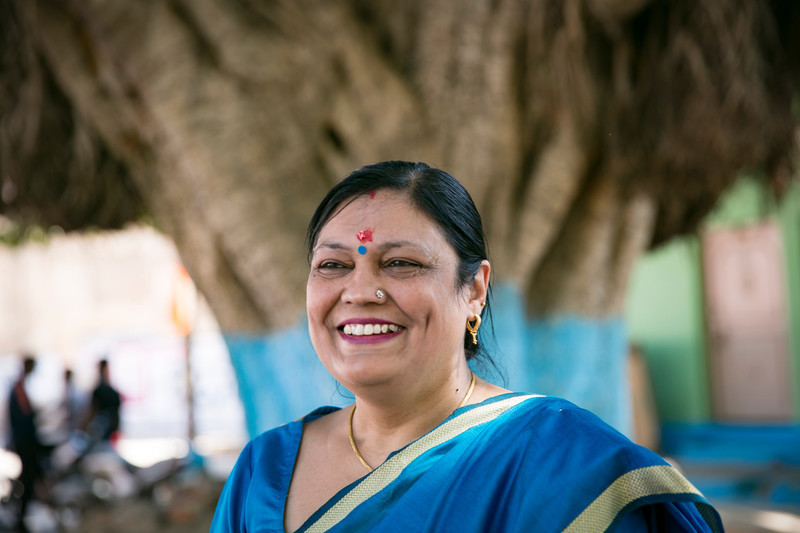

| 22 November 2018
"Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions"
In the district of Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh, the summer season has started and the heat in town is already extreme. Here, the Family Planning Association of India GCACI clinic serves many people living in poverty. In the ten years since the GCACI project started there, the clinic has provided 16,301 women with comprehensive abortion care and 202,758 women with contraceptive services. The two-storey clinic is situated in a residential area and, inside, women queue up to see the counsellors and medical staff. Many are accompanied by link workers who have travelled with them from outlying districts. Neelam Dixit is in charge of the branch. “Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions. By the time they visit our clinic, the woman is already a couple of months pregnant”. FPA India’s work is making an impact and Dixit is seeing views change on abortion. “There is a shift in attitude among women since FPAI started providing services. Presently, there is little stigma attached to abortion. Our aim is to provide quality health services at low cost. We create awareness about the consequences of unsafe abortion and train volunteers to be sure women in villages are aware of our clinic.” The clinic has served around 300,000 people from rural and semi-urban populations with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services, and provides both first- and second-trimester abortion services.

| 15 May 2025
"Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions"
In the district of Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh, the summer season has started and the heat in town is already extreme. Here, the Family Planning Association of India GCACI clinic serves many people living in poverty. In the ten years since the GCACI project started there, the clinic has provided 16,301 women with comprehensive abortion care and 202,758 women with contraceptive services. The two-storey clinic is situated in a residential area and, inside, women queue up to see the counsellors and medical staff. Many are accompanied by link workers who have travelled with them from outlying districts. Neelam Dixit is in charge of the branch. “Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions. By the time they visit our clinic, the woman is already a couple of months pregnant”. FPA India’s work is making an impact and Dixit is seeing views change on abortion. “There is a shift in attitude among women since FPAI started providing services. Presently, there is little stigma attached to abortion. Our aim is to provide quality health services at low cost. We create awareness about the consequences of unsafe abortion and train volunteers to be sure women in villages are aware of our clinic.” The clinic has served around 300,000 people from rural and semi-urban populations with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services, and provides both first- and second-trimester abortion services.

| 22 November 2018
In pictures: Expanding access to safe abortion in India
Konika* Mother of three, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Konika is 20 years old, and the mother of three girls. Like many local young women, she decided to have an abortion when she became pregnant for the fourth time within five years. Citing financial issues as the driving force behind her decision, despite her mother-in-laws desire for her to have another child, hoping this time it would be a boy. Through a neighbour, she approached the PSK clinic in Bhiwandi for an abortion. In Konika’s community, many young women are married and have kids by the time they are 20. Now with PSK, women like Konika have a choice to be pregnant or not. *Name has been changed Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Rehkha Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Family Planning Association of India, works with a network of volunteer link workers, who disseminate information about services available in the PSK clinic, make referrals, and often accompany women to the clinic for support. One of these link workers is Rehkha. Rekha says: "I have been involved with PSK for five years. And today I can proudly say that since the first awareness campaigns, there has been not a single death in the village due to an unsafe abortion." She adds: "These women are my flesh and blood. They know I only want the best for them… Within our communities we spread the message of safe sex and safe abortion through songs and skits which are easily understood. And I think the trick is to include mother-in-laws in our work. We have a high success rate in providing safe abortion care.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Shajahan Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Shajahan is a link worker in the nearby Muslim district, where women pack into a house in the narrow village lanes to wait to speak to her. She says: "I am a Muslim. In my community, abortion is frowned upon, and contraception is considered a sin. Initially, the women thought I was going against our customs, and the men thought I was a bad influence on their wives. Some of the men in our area even approached my husband and asked him to order me to stop these efforts." But her husband was supportive, telling other men that it was also their responsibility to be part of the process. It took several years, but eventually Shajahan won the trust of the women and men of her area. "Today, every woman in my area comes to me when it concerns matters of sexual health." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gauri Family Planning Association of India (FPAI) staff Gauri has worked for FPAI for years and remembers hearing about the experiences of women who’d had unsafe abortions. "I had heard first-hand accounts of [unsafe] abortions that left women reeling in pain, suffering permanent infertility. I had also seen the grief in the faces of men whose wives died. So today when I see women leaving us, after an abortion, in perfect health, I feel like I've done something right with my life." Gauri continues: "My work may have started with one area, but I want to reach every corner of the country with FPAI - so that no woman in India becomes a statistic." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nisha Mother of two At 23, Nisha Boudh is already a mother to two children and severely anaemic. She feels she is in no position to have a third child, but her in-laws are not supportive. Nisha chose to have an abortion at FPAI’s Gwalior clinic. “I have been weak since childhood and, honestly, motherhood has taken a toll on my health. Doctors in other clinics were not willing help me and I would have died had FPAI not come to my rescue. With their doctors’ advice I have now decided to undergo an operation [tubal ligation] as I do not want to conceive. My mother-in-law was upset with my decision but I want to live to see my other children grow,” said Boudh. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Diti* Sex worker Diti is a sex worker living in Kolkata. She says she, "owes her life to PSK". Diti was forced into an early marriage when she was just 12 years old. "Before my body could even develop, my husband was forcing himself upon me." By the age of 20, Diti had five children. Struggling to cope at such an early age, and married to an abusive husband, Diti ran away. "I don't enjoy having sex with strangers, but I need the money." She makes 300 rupees a day ($4 USD). When Diti became pregnant she didn’t want to continue with the pregnancy. "There's no way I can feed a child. Besides, this is no place to bring a child into the world. Another sex worker recommended the PSK clinic.” Diti was worried about visiting the clinic, fearing stigma and discrimination from staff for working as a sex worker. Her experience was vastly different, finding the clinic team to be welcoming, reassuring and supportive. "They treated me like a human being." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mala Medical officer “The big problem in this part of India is early marriage and pregnancy. Both of which need to be handled very delicately,” says medical officer Mala Tiwari. “Slowly, things are changing as women are becoming aware of their rights. Previously when GCACI did not exist there was very little interaction with the link workers, and they [and the community] feared it was illegal to get an abortion. They did not know they did not need the consent of their husbands and in-laws. They now know, women have a right over their body.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Manju Mother of two, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Manju Rana was forced to marry at fifteen. “I have had two children in eight years of marriage,” she says. “My mother-in-law wanted me to keep having children. She does not understand I would not be able to give them a good education if I had more children. My husband is a driver and we cannot afford to have any more. When I learnt I was pregnant, without taking anyone’s permission, I went with the link worker of my area to the clinic and had an abortion.” Manju adds: “In these affordable clinics we can choose about pregnancy. They also made sure I was counselled, as coming to a decision about abortion is not easy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Expanding access to safe abortion in India
Konika* Mother of three, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Konika is 20 years old, and the mother of three girls. Like many local young women, she decided to have an abortion when she became pregnant for the fourth time within five years. Citing financial issues as the driving force behind her decision, despite her mother-in-laws desire for her to have another child, hoping this time it would be a boy. Through a neighbour, she approached the PSK clinic in Bhiwandi for an abortion. In Konika’s community, many young women are married and have kids by the time they are 20. Now with PSK, women like Konika have a choice to be pregnant or not. *Name has been changed Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Rehkha Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Family Planning Association of India, works with a network of volunteer link workers, who disseminate information about services available in the PSK clinic, make referrals, and often accompany women to the clinic for support. One of these link workers is Rehkha. Rekha says: "I have been involved with PSK for five years. And today I can proudly say that since the first awareness campaigns, there has been not a single death in the village due to an unsafe abortion." She adds: "These women are my flesh and blood. They know I only want the best for them… Within our communities we spread the message of safe sex and safe abortion through songs and skits which are easily understood. And I think the trick is to include mother-in-laws in our work. We have a high success rate in providing safe abortion care.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Shajahan Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Shajahan is a link worker in the nearby Muslim district, where women pack into a house in the narrow village lanes to wait to speak to her. She says: "I am a Muslim. In my community, abortion is frowned upon, and contraception is considered a sin. Initially, the women thought I was going against our customs, and the men thought I was a bad influence on their wives. Some of the men in our area even approached my husband and asked him to order me to stop these efforts." But her husband was supportive, telling other men that it was also their responsibility to be part of the process. It took several years, but eventually Shajahan won the trust of the women and men of her area. "Today, every woman in my area comes to me when it concerns matters of sexual health." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gauri Family Planning Association of India (FPAI) staff Gauri has worked for FPAI for years and remembers hearing about the experiences of women who’d had unsafe abortions. "I had heard first-hand accounts of [unsafe] abortions that left women reeling in pain, suffering permanent infertility. I had also seen the grief in the faces of men whose wives died. So today when I see women leaving us, after an abortion, in perfect health, I feel like I've done something right with my life." Gauri continues: "My work may have started with one area, but I want to reach every corner of the country with FPAI - so that no woman in India becomes a statistic." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nisha Mother of two At 23, Nisha Boudh is already a mother to two children and severely anaemic. She feels she is in no position to have a third child, but her in-laws are not supportive. Nisha chose to have an abortion at FPAI’s Gwalior clinic. “I have been weak since childhood and, honestly, motherhood has taken a toll on my health. Doctors in other clinics were not willing help me and I would have died had FPAI not come to my rescue. With their doctors’ advice I have now decided to undergo an operation [tubal ligation] as I do not want to conceive. My mother-in-law was upset with my decision but I want to live to see my other children grow,” said Boudh. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Diti* Sex worker Diti is a sex worker living in Kolkata. She says she, "owes her life to PSK". Diti was forced into an early marriage when she was just 12 years old. "Before my body could even develop, my husband was forcing himself upon me." By the age of 20, Diti had five children. Struggling to cope at such an early age, and married to an abusive husband, Diti ran away. "I don't enjoy having sex with strangers, but I need the money." She makes 300 rupees a day ($4 USD). When Diti became pregnant she didn’t want to continue with the pregnancy. "There's no way I can feed a child. Besides, this is no place to bring a child into the world. Another sex worker recommended the PSK clinic.” Diti was worried about visiting the clinic, fearing stigma and discrimination from staff for working as a sex worker. Her experience was vastly different, finding the clinic team to be welcoming, reassuring and supportive. "They treated me like a human being." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mala Medical officer “The big problem in this part of India is early marriage and pregnancy. Both of which need to be handled very delicately,” says medical officer Mala Tiwari. “Slowly, things are changing as women are becoming aware of their rights. Previously when GCACI did not exist there was very little interaction with the link workers, and they [and the community] feared it was illegal to get an abortion. They did not know they did not need the consent of their husbands and in-laws. They now know, women have a right over their body.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Manju Mother of two, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Manju Rana was forced to marry at fifteen. “I have had two children in eight years of marriage,” she says. “My mother-in-law wanted me to keep having children. She does not understand I would not be able to give them a good education if I had more children. My husband is a driver and we cannot afford to have any more. When I learnt I was pregnant, without taking anyone’s permission, I went with the link worker of my area to the clinic and had an abortion.” Manju adds: “In these affordable clinics we can choose about pregnancy. They also made sure I was counselled, as coming to a decision about abortion is not easy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 18 April 2024
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than 60 countries and territories have liberalized their abortion laws. Only four have regressed, including the United States. Abortion rights are increasingly becoming recognized as fundamental human rights for millions of people worldwide. The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.

| 18 April 2024
Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than 60 countries and territories have liberalized their abortion laws. Only four have regressed, including the United States. Abortion rights are increasingly becoming recognized as fundamental human rights for millions of people worldwide. The global landscape of abortion rights continues to evolve in 2024, with new legislation and feminist movements fighting for better access. Let's take a trip around the world to see the latest developments.

| 08 January 2021
"Girls have to know their rights"
Aminata Sonogo listened intently to the group of young volunteers as they explained different types of contraception, and raised her hand with questions. Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Aminata is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. Aminata is studying in Bamako, the capital of Mali. Just a quarter of Malian girls complete secondary school, according to UNICEF. But even if she will graduate later than most, Aminata is conscious of how far she has come. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said. At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Aminata got pregnant. She is far from alone: 38% of Malian girls will be pregnant or a mother by the age of 18. Abortion is illegal in Mali except in cases of rape, incest or danger to the mother’s life, and even then it is difficult to obtain, according to medical professionals. Determined to take control of her life “I felt a lot of stigma from my classmates and even my teachers. I tried to ignore them and carry on going to school and studying. But I gave birth to my daughter just before my exams, so I couldn’t take them.” Aminata went through her pregnancy with little support, as the father of her daughter, Fatoumata, distanced himself from her after arguments about their situation. “I have had some problems with the father of the baby. We fought a lot and I didn’t see him for most of the pregnancy, right until the birth,” she recalled. The first year of her daughter’s life was a blur of doctors’ appointments, as Fatoumata was often ill. It seemed Aminata’s chances of finishing school were slipping away. But gradually her family began to take a more active role in caring for her daughter, and she began demanding more help from Fatoumata’s father too. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. She no longer had time to hang out with friends after school, but attended classes, took care of her daughter and then studied more. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Aminata said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. "Family planning protects girls" Aminata’s next goal is her high school diploma, and obtaining it while trying to navigate the difficult world of relationships and sex. “It’s something you can talk about with your close friends. I would be too ashamed to talk about this with my parents,” she said. She is guided by visits from the young volunteers of the Association Malienne pour la Protection et Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk. “The guys come up to you and tell you that you are beautiful, but if you don’t want to sleep with them they will rape you. That’s the choice. You can accept or you can refuse and they will rape you anyway,” she said. “Girls have to know their rights”. After listening to the volunteers talk about all the different options for contraception, she is reviewing her own choices. “Family planning protects girls,” Aminata said. “It means we can protect ourselves from pregnancies that we don’t want”.

| 15 May 2025
"Girls have to know their rights"
Aminata Sonogo listened intently to the group of young volunteers as they explained different types of contraception, and raised her hand with questions. Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Aminata is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. Aminata is studying in Bamako, the capital of Mali. Just a quarter of Malian girls complete secondary school, according to UNICEF. But even if she will graduate later than most, Aminata is conscious of how far she has come. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said. At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Aminata got pregnant. She is far from alone: 38% of Malian girls will be pregnant or a mother by the age of 18. Abortion is illegal in Mali except in cases of rape, incest or danger to the mother’s life, and even then it is difficult to obtain, according to medical professionals. Determined to take control of her life “I felt a lot of stigma from my classmates and even my teachers. I tried to ignore them and carry on going to school and studying. But I gave birth to my daughter just before my exams, so I couldn’t take them.” Aminata went through her pregnancy with little support, as the father of her daughter, Fatoumata, distanced himself from her after arguments about their situation. “I have had some problems with the father of the baby. We fought a lot and I didn’t see him for most of the pregnancy, right until the birth,” she recalled. The first year of her daughter’s life was a blur of doctors’ appointments, as Fatoumata was often ill. It seemed Aminata’s chances of finishing school were slipping away. But gradually her family began to take a more active role in caring for her daughter, and she began demanding more help from Fatoumata’s father too. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. She no longer had time to hang out with friends after school, but attended classes, took care of her daughter and then studied more. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Aminata said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. "Family planning protects girls" Aminata’s next goal is her high school diploma, and obtaining it while trying to navigate the difficult world of relationships and sex. “It’s something you can talk about with your close friends. I would be too ashamed to talk about this with my parents,” she said. She is guided by visits from the young volunteers of the Association Malienne pour la Protection et Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk. “The guys come up to you and tell you that you are beautiful, but if you don’t want to sleep with them they will rape you. That’s the choice. You can accept or you can refuse and they will rape you anyway,” she said. “Girls have to know their rights”. After listening to the volunteers talk about all the different options for contraception, she is reviewing her own choices. “Family planning protects girls,” Aminata said. “It means we can protect ourselves from pregnancies that we don’t want”.

| 08 January 2021
"We see cases of early pregnancy from 14 years old – occasionally they are younger"
My name is Mariame Doumbia, I am a midwife with the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), providing family planning and sexual health services to Malians in and around the capital, Bamako. I have worked with AMPPF for almost six years in total, but there was a break two years ago when American funding stopped due to the Global Gag Rule. I was able to come back to work with Canadian funding for the project SheDecides, and they have paid my salary for the last two years. I work at fixed and mobile clinics in Bamako. In the neighbourhood of Kalabancoro, which is on the outskirts of the capital, I receive clients at the clinic who would not be able to afford travel to somewhere farther away. It’s a poor neighbourhood. Providing the correct information The women come with their ideas about sex, sometimes with lots of rumours, but we go through it all with them to explain what sexual health is and how to maintain it. We clarify things for them. More and more they come with their mothers, or their boyfriends or husbands. The youngest ones come to ask about their periods and how they can count their menstrual cycle. Then they start to ask about sex. These days the price of sanitary pads is going down, so they are using bits of fabric less often, which is what I used to see. Seeing the impact of our work We see cases of early pregnancy here in Kalabancoro, but the numbers are definitely going down. Most are from 14 years old upwards, though occasionally they are younger. SheDecides has brought so much to this clinic, starting with the fact that before the project’s arrival there was no one here at all for a prolonged period of time. Now the community has the right to information and I try my best to answer all their questions.

| 15 May 2025
"We see cases of early pregnancy from 14 years old – occasionally they are younger"
My name is Mariame Doumbia, I am a midwife with the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), providing family planning and sexual health services to Malians in and around the capital, Bamako. I have worked with AMPPF for almost six years in total, but there was a break two years ago when American funding stopped due to the Global Gag Rule. I was able to come back to work with Canadian funding for the project SheDecides, and they have paid my salary for the last two years. I work at fixed and mobile clinics in Bamako. In the neighbourhood of Kalabancoro, which is on the outskirts of the capital, I receive clients at the clinic who would not be able to afford travel to somewhere farther away. It’s a poor neighbourhood. Providing the correct information The women come with their ideas about sex, sometimes with lots of rumours, but we go through it all with them to explain what sexual health is and how to maintain it. We clarify things for them. More and more they come with their mothers, or their boyfriends or husbands. The youngest ones come to ask about their periods and how they can count their menstrual cycle. Then they start to ask about sex. These days the price of sanitary pads is going down, so they are using bits of fabric less often, which is what I used to see. Seeing the impact of our work We see cases of early pregnancy here in Kalabancoro, but the numbers are definitely going down. Most are from 14 years old upwards, though occasionally they are younger. SheDecides has brought so much to this clinic, starting with the fact that before the project’s arrival there was no one here at all for a prolonged period of time. Now the community has the right to information and I try my best to answer all their questions.

| 08 January 2021
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.

| 15 May 2025
"The movement helps girls to know their rights and their bodies"
My name is Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga. I’m 23-years-old, and I’m an IT specialist. I joined the Youth Action Movement at the end of 2018. The head of the movement in Mali is a friend of mine, and I met her before I knew she was the president. She invited me to their events and over time persuaded me to join. I watched them raising awareness about sexual and reproductive health, using sketches and speeches. I learnt a lot. Overcoming taboos I went home and talked about what I had seen and learnt with my family. In Africa, and even more so in the village where I come from in Gao, northern Mali, people don’t talk about these things. I wanted to take my sisters to the events, but every time I spoke about them my relatives would just say it was to teach girls to have sex, and that it’s taboo. That’s not what I believe. I think the movement helps girls, most of all, to know their sexual rights, their bodies, what to do and what not to do to stay healthy and safe. They don’t understand this concept. My family would say it was just a smokescreen to convince girls to get involved in something dirty. I have had to tell my younger cousins about their periods, for example, when they came from the village to live in the city. One of my cousins was so scared, and told me she was bleeding from her vagina and didn’t know why. We talk about managing periods in the Youth Action Movement, as well as how to manage cramps and feel better. The devastating impact of FGM But there was a much more important reason for me to join the movement. My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Then, two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died. Normally, girls in Mali are cut when they are three or four years old, though for some it’s done at birth. When they are older and get pregnant, I know they face the same challenges as every woman does giving birth, but they also live with the dangerous consequences of this unhealthy practice. The importance of talking openly The problem lies with the families. I want us, as a movement, to talk with the parents and explain to them how they can contribute to their children’s sexual health. I wish it were no longer a taboo between parents and their girls. But if we talk in such direct terms, they only see disobedience, and say that we are encouraging promiscuity. We need to talk to teenagers because they are already parents in many cases. They are the ones who decide to go through with cutting their daughters, or not. A lot of Mali is hard to reach though. We need travelling groups to go to those isolated rural areas and talk to people about sexual health. Pregnancy is the girl’s decision, and girls have a right to be healthy, and to choose their future.
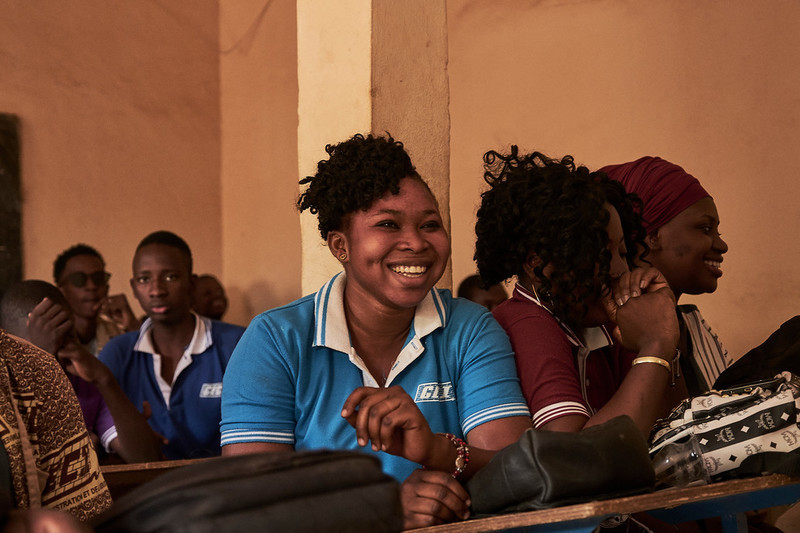
| 07 January 2021
In pictures: Overcoming the impact of the Global Gag Rule in Mali
In 2017, the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), was hit hard by the reinstatement of the Global Gag Rule (GGR). The impact was swift and devastating – depleted budgets meant that AMPPF had to cut back on key staff and suspend education activities and community healthcare provision. The situation turned around with funding from the Canadian Government supporting the SheDecides project, filling the gap left by GGR. AMPPF has been able to employ staff ensuring their team can reach the most vulnerable clients who would otherwise be left without access to sexual healthcare and increase their outreach to youth. Putting communities first Mama Keita Sy Diallo, midwife The SheDecides project has allowed AMPPF to maintain three mobile clinics, travelling to more remote areas where transportation costs and huge distances separate women from access to health and contraceptive care.“SheDecides has helped us a lot, above all in our work outside our own permanent clinics. When we go out in the community we have a lot of clients, and many women come to us who would otherwise not have the means to obtain advice or contraception,” explained Mama Keita Sy Diallo, a midwife and AMPPF board member. She runs consultations at community health centers in underserved areas of the Malian capital. “Everything is free for the women in these sessions.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email SheDecides projects ensures free access to healthcare and contraception Fatoumata Dramé, client By 9am at the Asaco Sekasi community health center in Bamako, its wooden benches are full of clients waiting their turn at a SheDecides outreach session. Fatoumata Dramé, 30, got here early and has already been fitted for a new implant. “I came here for family planning, and it’s my first time. I’ve just moved to the area so I came because it’s close to home,” she said. Bouncing two-month-old Tiemoko on her knee, Dramé said her main motivation was to space the births of her children. “I am a mum of three now. My first child is 7 years old. I try to leave three years between each child. It helps with my health,” she explained. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Targeting youth Mamadou Bah, Youth Action Movement “After the arrival of SheDecides, we intensified our targeting of vulnerable groups with activities in the evening, when domestic workers and those working during the day could attend,” said Mariam Modibo Tandina, who heads the national committee of the Youth Action Movement in Mali. “That means that young people in precarious situations could learn more about safer sex and family planning. Now they know how to protect themselves against sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Speaking out against FGM Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga, youth volunteer Fatoumata’s decision to join the Youth Action Movement was fueled by a personal loss. “My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Using dance and comedy to talk about sex Abdoulaye Camara, Head of AMPPF dance troupe Abdoulaye’s moves are not just for fun. He is head of the dance troupe of the AMPPF’s Youth Action Movement, which uses dance and comedy sketches to talk about sex. It’s a canny way to deliver messages about everything from using condoms to taking counterfeit antibiotics, to an audience who are often confused and ashamed about such topics. “We distract them with dance and humour and then we transmit those important messages about sex without offending them,” explained Abdoulaye. “We show them that it’s not to insult them or show them up, but just to explain how these things happen.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Determination to graduate Aminata Sonogo, student Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Sonogo is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said.At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Sonogo got pregnant. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Sonogo said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. She is guided by visits from the AMPPF youth volunteers and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk of an unwanted pregnancy. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email AMPPF’s mobile clinic offers a lifeline to remote communities Mariame Doumbia, midwife “I work at a mobile clinic. It’s important for accessibility, so that the women living in poorly serviced areas can access sexual and reproductive health services, and reliable information.I like what I do. I like helping people, especially the young ones. They know I am always on call to help them, and even if I don’t know the answer at that moment, I will find out. I like everything about my work. Actually, it’s not just work for me, and I became a midwife for that reason. I’ve always been an educator on these issues in my community.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Trust underpins the relationship between AMPPF’s mobile team and the village of Missala Adama Samaké, village elder and chief of the Missala Health Center Adama Samaké, chief of the Missala Health Center, oversees the proceedings as a village elder with deep trust from his community. When the mobile clinic isn’t around, his center offers maternity services and treats the many cases of malaria that are diagnosed in the community. “Given the distance between here and Bamako, most of the villagers around here rely on us for treatment,” he said. “But when we announce that the mobile clinic is coming, the women make sure they are here.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Contraceptive choice Kadidiatou Sogoba, client Kadidiatou Sogoba, a mother of seven, waited nervously for her turn. “I came today because I keep getting ill and I have felt very weak, just not myself, since I had a Caesarean section three years ago. I lost a lot of blood,” she said. “I have been very afraid since the birth of my last child. We have been using condoms and we were getting a bit tired of them, so I am looking for another longer-term type of contraception.”After emerging half an hour later, Sogoba clutched a packet of the contraceptive pill, and said next time she would go for a cervical screening.Photos ©IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Mali Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
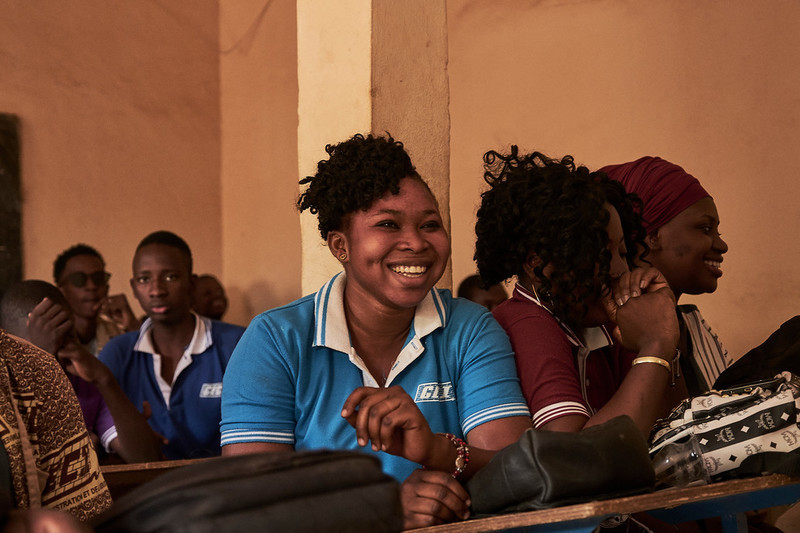
| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Overcoming the impact of the Global Gag Rule in Mali
In 2017, the Association Malienne pour la Protection et la Promotion de la Famille (AMPPF), was hit hard by the reinstatement of the Global Gag Rule (GGR). The impact was swift and devastating – depleted budgets meant that AMPPF had to cut back on key staff and suspend education activities and community healthcare provision. The situation turned around with funding from the Canadian Government supporting the SheDecides project, filling the gap left by GGR. AMPPF has been able to employ staff ensuring their team can reach the most vulnerable clients who would otherwise be left without access to sexual healthcare and increase their outreach to youth. Putting communities first Mama Keita Sy Diallo, midwife The SheDecides project has allowed AMPPF to maintain three mobile clinics, travelling to more remote areas where transportation costs and huge distances separate women from access to health and contraceptive care.“SheDecides has helped us a lot, above all in our work outside our own permanent clinics. When we go out in the community we have a lot of clients, and many women come to us who would otherwise not have the means to obtain advice or contraception,” explained Mama Keita Sy Diallo, a midwife and AMPPF board member. She runs consultations at community health centers in underserved areas of the Malian capital. “Everything is free for the women in these sessions.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email SheDecides projects ensures free access to healthcare and contraception Fatoumata Dramé, client By 9am at the Asaco Sekasi community health center in Bamako, its wooden benches are full of clients waiting their turn at a SheDecides outreach session. Fatoumata Dramé, 30, got here early and has already been fitted for a new implant. “I came here for family planning, and it’s my first time. I’ve just moved to the area so I came because it’s close to home,” she said. Bouncing two-month-old Tiemoko on her knee, Dramé said her main motivation was to space the births of her children. “I am a mum of three now. My first child is 7 years old. I try to leave three years between each child. It helps with my health,” she explained. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Targeting youth Mamadou Bah, Youth Action Movement “After the arrival of SheDecides, we intensified our targeting of vulnerable groups with activities in the evening, when domestic workers and those working during the day could attend,” said Mariam Modibo Tandina, who heads the national committee of the Youth Action Movement in Mali. “That means that young people in precarious situations could learn more about safer sex and family planning. Now they know how to protect themselves against sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Speaking out against FGM Fatoumata Yehiya Maiga, youth volunteer Fatoumata’s decision to join the Youth Action Movement was fueled by a personal loss. “My parents are educated, so me and my sisters were never cut. I learned about female genital mutilation at a conference I attended in 2016. I didn’t know that there were different types of severity and ways that girls could be cut. I hadn’t understood quite how dangerous this practice is. Two years ago, I lost my friend Aïssata. She got married young, at 17. She struggled to conceive until she was 23. The day she gave birth, there were complications and she died. The doctors said that the excision was botched and that’s what killed her. From that day on, I decided I needed to teach all the girls in my community about how harmful this practice is for their health. I was so horrified by the way she died.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Using dance and comedy to talk about sex Abdoulaye Camara, Head of AMPPF dance troupe Abdoulaye’s moves are not just for fun. He is head of the dance troupe of the AMPPF’s Youth Action Movement, which uses dance and comedy sketches to talk about sex. It’s a canny way to deliver messages about everything from using condoms to taking counterfeit antibiotics, to an audience who are often confused and ashamed about such topics. “We distract them with dance and humour and then we transmit those important messages about sex without offending them,” explained Abdoulaye. “We show them that it’s not to insult them or show them up, but just to explain how these things happen.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Determination to graduate Aminata Sonogo, student Sitting at a wooden school desk at 22, Sonogo is older than most of her classmates, but she shrugs off the looks and comments. She has fought hard to be here. “I wanted to go to high school but I needed to pass some exams to get here. In the end, it took me three years,” she said.At the start of her final year of collège, or middle school, Sonogo got pregnant. She went back to school in the autumn, 18 months after Fatoumata’s birth and with more determination than ever. At the end of the academic year, it paid off. “I did it. I passed my exams and now I am in high school,” Sonogo said, smiling and relaxing her shoulders. She is guided by visits from the AMPPF youth volunteers and shares her own story with classmates who she sees at risk of an unwanted pregnancy. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email AMPPF’s mobile clinic offers a lifeline to remote communities Mariame Doumbia, midwife “I work at a mobile clinic. It’s important for accessibility, so that the women living in poorly serviced areas can access sexual and reproductive health services, and reliable information.I like what I do. I like helping people, especially the young ones. They know I am always on call to help them, and even if I don’t know the answer at that moment, I will find out. I like everything about my work. Actually, it’s not just work for me, and I became a midwife for that reason. I’ve always been an educator on these issues in my community.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Trust underpins the relationship between AMPPF’s mobile team and the village of Missala Adama Samaké, village elder and chief of the Missala Health Center Adama Samaké, chief of the Missala Health Center, oversees the proceedings as a village elder with deep trust from his community. When the mobile clinic isn’t around, his center offers maternity services and treats the many cases of malaria that are diagnosed in the community. “Given the distance between here and Bamako, most of the villagers around here rely on us for treatment,” he said. “But when we announce that the mobile clinic is coming, the women make sure they are here.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Contraceptive choice Kadidiatou Sogoba, client Kadidiatou Sogoba, a mother of seven, waited nervously for her turn. “I came today because I keep getting ill and I have felt very weak, just not myself, since I had a Caesarean section three years ago. I lost a lot of blood,” she said. “I have been very afraid since the birth of my last child. We have been using condoms and we were getting a bit tired of them, so I am looking for another longer-term type of contraception.”After emerging half an hour later, Sogoba clutched a packet of the contraceptive pill, and said next time she would go for a cervical screening.Photos ©IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Mali Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 22 November 2018
"Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person"
“Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person, but working as a peer educator has helped enabled me to help many like me.” Hasina is one of the estimated 1,500 sex workers living in Haunman Tekri, a red-light area in Bhiwandi, a town near Mumbai. When her husband passed away six years ago leaving behind a three-year-old daughter, Hasina turned to sex work as her only option to earn money. She admits that it came with a feeling of powerlessness. "You don't choose this trade; it is the result of life circumstances.” She works as a peer educator with PSK, one of the Family Planning Association of India's (FPAI) clinics. "Working with Parivar Swasthya Kedra (PSK), has made me feel less helpless; it's given me some control over my body; the ability to choose whether or not to bring another life into this world.” Building trust through education Hasina has been a peer educator for three years, working within the district to educate other women on safe sex, contraception, and abortion. Hasina admits she was once wary of PSK workers. "I used to think that these workers who insist we use condoms, would only sabotage my clientele. But soon I realized they were only looking out for us." When talking with local women, Hasina advocates the use of contraception but says in the case of an unintended pregnancy, abortion is a viable option. "It's easy to judge us, but many of us have no choice; we simply cannot feed another on just Rs. 400 a day." Hasina is now the go-to woman in the district when it comes to sexual health. "Since I am one of them, the women trust me." This is the secret behind PSK success; a model where sex workers educate their peers, understanding the complexities and prejudices of their daily lives. "I hope one day I am able to put all of this behind me. But I hope that through PSK I am able to make another woman's life just a little bit safer, a little bit better." Do you want to show your support for women and girls to be free to decide what happens to their body? Pledge your voice to our I Decide campaign,IPPF’s movement for safe abortion access for all. You'll be provided with toolkits on how to talk about abortion and you'll have access to a range of content from personal testimonies to videos explaining the different types of abortion available.

| 15 May 2025
"Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person"
“Selling my body doesn’t make me a bad person, but working as a peer educator has helped enabled me to help many like me.” Hasina is one of the estimated 1,500 sex workers living in Haunman Tekri, a red-light area in Bhiwandi, a town near Mumbai. When her husband passed away six years ago leaving behind a three-year-old daughter, Hasina turned to sex work as her only option to earn money. She admits that it came with a feeling of powerlessness. "You don't choose this trade; it is the result of life circumstances.” She works as a peer educator with PSK, one of the Family Planning Association of India's (FPAI) clinics. "Working with Parivar Swasthya Kedra (PSK), has made me feel less helpless; it's given me some control over my body; the ability to choose whether or not to bring another life into this world.” Building trust through education Hasina has been a peer educator for three years, working within the district to educate other women on safe sex, contraception, and abortion. Hasina admits she was once wary of PSK workers. "I used to think that these workers who insist we use condoms, would only sabotage my clientele. But soon I realized they were only looking out for us." When talking with local women, Hasina advocates the use of contraception but says in the case of an unintended pregnancy, abortion is a viable option. "It's easy to judge us, but many of us have no choice; we simply cannot feed another on just Rs. 400 a day." Hasina is now the go-to woman in the district when it comes to sexual health. "Since I am one of them, the women trust me." This is the secret behind PSK success; a model where sex workers educate their peers, understanding the complexities and prejudices of their daily lives. "I hope one day I am able to put all of this behind me. But I hope that through PSK I am able to make another woman's life just a little bit safer, a little bit better." Do you want to show your support for women and girls to be free to decide what happens to their body? Pledge your voice to our I Decide campaign,IPPF’s movement for safe abortion access for all. You'll be provided with toolkits on how to talk about abortion and you'll have access to a range of content from personal testimonies to videos explaining the different types of abortion available.

| 22 November 2018
"Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions"
In the district of Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh, the summer season has started and the heat in town is already extreme. Here, the Family Planning Association of India GCACI clinic serves many people living in poverty. In the ten years since the GCACI project started there, the clinic has provided 16,301 women with comprehensive abortion care and 202,758 women with contraceptive services. The two-storey clinic is situated in a residential area and, inside, women queue up to see the counsellors and medical staff. Many are accompanied by link workers who have travelled with them from outlying districts. Neelam Dixit is in charge of the branch. “Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions. By the time they visit our clinic, the woman is already a couple of months pregnant”. FPA India’s work is making an impact and Dixit is seeing views change on abortion. “There is a shift in attitude among women since FPAI started providing services. Presently, there is little stigma attached to abortion. Our aim is to provide quality health services at low cost. We create awareness about the consequences of unsafe abortion and train volunteers to be sure women in villages are aware of our clinic.” The clinic has served around 300,000 people from rural and semi-urban populations with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services, and provides both first- and second-trimester abortion services.

| 15 May 2025
"Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions"
In the district of Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh, the summer season has started and the heat in town is already extreme. Here, the Family Planning Association of India GCACI clinic serves many people living in poverty. In the ten years since the GCACI project started there, the clinic has provided 16,301 women with comprehensive abortion care and 202,758 women with contraceptive services. The two-storey clinic is situated in a residential area and, inside, women queue up to see the counsellors and medical staff. Many are accompanied by link workers who have travelled with them from outlying districts. Neelam Dixit is in charge of the branch. “Most women are from marginalised sections of society and are denied the right to make their own decisions. By the time they visit our clinic, the woman is already a couple of months pregnant”. FPA India’s work is making an impact and Dixit is seeing views change on abortion. “There is a shift in attitude among women since FPAI started providing services. Presently, there is little stigma attached to abortion. Our aim is to provide quality health services at low cost. We create awareness about the consequences of unsafe abortion and train volunteers to be sure women in villages are aware of our clinic.” The clinic has served around 300,000 people from rural and semi-urban populations with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services, and provides both first- and second-trimester abortion services.

| 22 November 2018
In pictures: Expanding access to safe abortion in India
Konika* Mother of three, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Konika is 20 years old, and the mother of three girls. Like many local young women, she decided to have an abortion when she became pregnant for the fourth time within five years. Citing financial issues as the driving force behind her decision, despite her mother-in-laws desire for her to have another child, hoping this time it would be a boy. Through a neighbour, she approached the PSK clinic in Bhiwandi for an abortion. In Konika’s community, many young women are married and have kids by the time they are 20. Now with PSK, women like Konika have a choice to be pregnant or not. *Name has been changed Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Rehkha Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Family Planning Association of India, works with a network of volunteer link workers, who disseminate information about services available in the PSK clinic, make referrals, and often accompany women to the clinic for support. One of these link workers is Rehkha. Rekha says: "I have been involved with PSK for five years. And today I can proudly say that since the first awareness campaigns, there has been not a single death in the village due to an unsafe abortion." She adds: "These women are my flesh and blood. They know I only want the best for them… Within our communities we spread the message of safe sex and safe abortion through songs and skits which are easily understood. And I think the trick is to include mother-in-laws in our work. We have a high success rate in providing safe abortion care.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Shajahan Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Shajahan is a link worker in the nearby Muslim district, where women pack into a house in the narrow village lanes to wait to speak to her. She says: "I am a Muslim. In my community, abortion is frowned upon, and contraception is considered a sin. Initially, the women thought I was going against our customs, and the men thought I was a bad influence on their wives. Some of the men in our area even approached my husband and asked him to order me to stop these efforts." But her husband was supportive, telling other men that it was also their responsibility to be part of the process. It took several years, but eventually Shajahan won the trust of the women and men of her area. "Today, every woman in my area comes to me when it concerns matters of sexual health." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gauri Family Planning Association of India (FPAI) staff Gauri has worked for FPAI for years and remembers hearing about the experiences of women who’d had unsafe abortions. "I had heard first-hand accounts of [unsafe] abortions that left women reeling in pain, suffering permanent infertility. I had also seen the grief in the faces of men whose wives died. So today when I see women leaving us, after an abortion, in perfect health, I feel like I've done something right with my life." Gauri continues: "My work may have started with one area, but I want to reach every corner of the country with FPAI - so that no woman in India becomes a statistic." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nisha Mother of two At 23, Nisha Boudh is already a mother to two children and severely anaemic. She feels she is in no position to have a third child, but her in-laws are not supportive. Nisha chose to have an abortion at FPAI’s Gwalior clinic. “I have been weak since childhood and, honestly, motherhood has taken a toll on my health. Doctors in other clinics were not willing help me and I would have died had FPAI not come to my rescue. With their doctors’ advice I have now decided to undergo an operation [tubal ligation] as I do not want to conceive. My mother-in-law was upset with my decision but I want to live to see my other children grow,” said Boudh. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Diti* Sex worker Diti is a sex worker living in Kolkata. She says she, "owes her life to PSK". Diti was forced into an early marriage when she was just 12 years old. "Before my body could even develop, my husband was forcing himself upon me." By the age of 20, Diti had five children. Struggling to cope at such an early age, and married to an abusive husband, Diti ran away. "I don't enjoy having sex with strangers, but I need the money." She makes 300 rupees a day ($4 USD). When Diti became pregnant she didn’t want to continue with the pregnancy. "There's no way I can feed a child. Besides, this is no place to bring a child into the world. Another sex worker recommended the PSK clinic.” Diti was worried about visiting the clinic, fearing stigma and discrimination from staff for working as a sex worker. Her experience was vastly different, finding the clinic team to be welcoming, reassuring and supportive. "They treated me like a human being." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mala Medical officer “The big problem in this part of India is early marriage and pregnancy. Both of which need to be handled very delicately,” says medical officer Mala Tiwari. “Slowly, things are changing as women are becoming aware of their rights. Previously when GCACI did not exist there was very little interaction with the link workers, and they [and the community] feared it was illegal to get an abortion. They did not know they did not need the consent of their husbands and in-laws. They now know, women have a right over their body.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Manju Mother of two, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Manju Rana was forced to marry at fifteen. “I have had two children in eight years of marriage,” she says. “My mother-in-law wanted me to keep having children. She does not understand I would not be able to give them a good education if I had more children. My husband is a driver and we cannot afford to have any more. When I learnt I was pregnant, without taking anyone’s permission, I went with the link worker of my area to the clinic and had an abortion.” Manju adds: “In these affordable clinics we can choose about pregnancy. They also made sure I was counselled, as coming to a decision about abortion is not easy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Expanding access to safe abortion in India
Konika* Mother of three, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Konika is 20 years old, and the mother of three girls. Like many local young women, she decided to have an abortion when she became pregnant for the fourth time within five years. Citing financial issues as the driving force behind her decision, despite her mother-in-laws desire for her to have another child, hoping this time it would be a boy. Through a neighbour, she approached the PSK clinic in Bhiwandi for an abortion. In Konika’s community, many young women are married and have kids by the time they are 20. Now with PSK, women like Konika have a choice to be pregnant or not. *Name has been changed Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Rehkha Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Family Planning Association of India, works with a network of volunteer link workers, who disseminate information about services available in the PSK clinic, make referrals, and often accompany women to the clinic for support. One of these link workers is Rehkha. Rekha says: "I have been involved with PSK for five years. And today I can proudly say that since the first awareness campaigns, there has been not a single death in the village due to an unsafe abortion." She adds: "These women are my flesh and blood. They know I only want the best for them… Within our communities we spread the message of safe sex and safe abortion through songs and skits which are easily understood. And I think the trick is to include mother-in-laws in our work. We have a high success rate in providing safe abortion care.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Shajahan Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) link worker Shajahan is a link worker in the nearby Muslim district, where women pack into a house in the narrow village lanes to wait to speak to her. She says: "I am a Muslim. In my community, abortion is frowned upon, and contraception is considered a sin. Initially, the women thought I was going against our customs, and the men thought I was a bad influence on their wives. Some of the men in our area even approached my husband and asked him to order me to stop these efforts." But her husband was supportive, telling other men that it was also their responsibility to be part of the process. It took several years, but eventually Shajahan won the trust of the women and men of her area. "Today, every woman in my area comes to me when it concerns matters of sexual health." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Gauri Family Planning Association of India (FPAI) staff Gauri has worked for FPAI for years and remembers hearing about the experiences of women who’d had unsafe abortions. "I had heard first-hand accounts of [unsafe] abortions that left women reeling in pain, suffering permanent infertility. I had also seen the grief in the faces of men whose wives died. So today when I see women leaving us, after an abortion, in perfect health, I feel like I've done something right with my life." Gauri continues: "My work may have started with one area, but I want to reach every corner of the country with FPAI - so that no woman in India becomes a statistic." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nisha Mother of two At 23, Nisha Boudh is already a mother to two children and severely anaemic. She feels she is in no position to have a third child, but her in-laws are not supportive. Nisha chose to have an abortion at FPAI’s Gwalior clinic. “I have been weak since childhood and, honestly, motherhood has taken a toll on my health. Doctors in other clinics were not willing help me and I would have died had FPAI not come to my rescue. With their doctors’ advice I have now decided to undergo an operation [tubal ligation] as I do not want to conceive. My mother-in-law was upset with my decision but I want to live to see my other children grow,” said Boudh. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Diti* Sex worker Diti is a sex worker living in Kolkata. She says she, "owes her life to PSK". Diti was forced into an early marriage when she was just 12 years old. "Before my body could even develop, my husband was forcing himself upon me." By the age of 20, Diti had five children. Struggling to cope at such an early age, and married to an abusive husband, Diti ran away. "I don't enjoy having sex with strangers, but I need the money." She makes 300 rupees a day ($4 USD). When Diti became pregnant she didn’t want to continue with the pregnancy. "There's no way I can feed a child. Besides, this is no place to bring a child into the world. Another sex worker recommended the PSK clinic.” Diti was worried about visiting the clinic, fearing stigma and discrimination from staff for working as a sex worker. Her experience was vastly different, finding the clinic team to be welcoming, reassuring and supportive. "They treated me like a human being." Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mala Medical officer “The big problem in this part of India is early marriage and pregnancy. Both of which need to be handled very delicately,” says medical officer Mala Tiwari. “Slowly, things are changing as women are becoming aware of their rights. Previously when GCACI did not exist there was very little interaction with the link workers, and they [and the community] feared it was illegal to get an abortion. They did not know they did not need the consent of their husbands and in-laws. They now know, women have a right over their body.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Manju Mother of two, Parivar Swasthya Kendra (PSK) client Manju Rana was forced to marry at fifteen. “I have had two children in eight years of marriage,” she says. “My mother-in-law wanted me to keep having children. She does not understand I would not be able to give them a good education if I had more children. My husband is a driver and we cannot afford to have any more. When I learnt I was pregnant, without taking anyone’s permission, I went with the link worker of my area to the clinic and had an abortion.” Manju adds: “In these affordable clinics we can choose about pregnancy. They also made sure I was counselled, as coming to a decision about abortion is not easy.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email








