Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in the face of growing opposition and the rise of the far right? These victories for sexual and reproductive rights and health are the result of relentless grassroots work and advocacy by our Member Associations, in partnership with community organizations, allied politicians, and the mobilization of public opinion.
Most Popular This Week

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in t
Kazakhstan
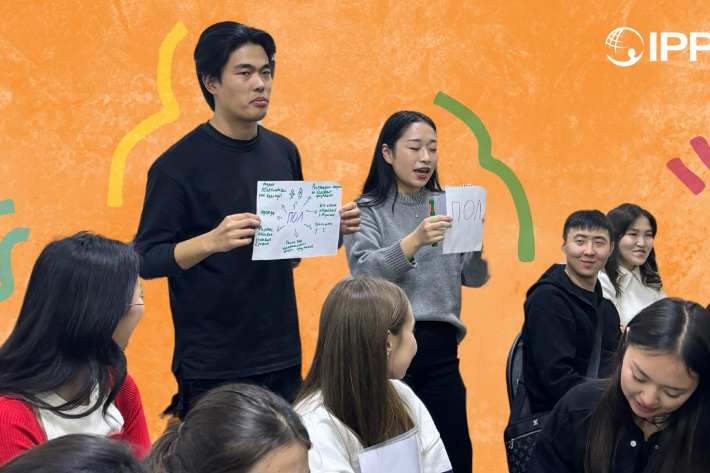

Kazakhstan's Rising HIV Crisis: A Call for Action
On World AIDS Day, we commemorate the remarkable achievements of IPPF Member Associations in their unwavering commitment to combating the HIV epidemic.

Ensuring SRHR in Humanitarian Crises: What You Need to Know
Over the past two decades, global forced displacement has consistently increased, affecting an estimated 114 million people as of mid-2023.
Estonia, Nepal, Namibia, Japan, Thailand

The Rainbow Wave for Marriage Equality
Love wins! The fight for marriage equality has seen incredible progress worldwide, with a recent surge in legalizations.
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
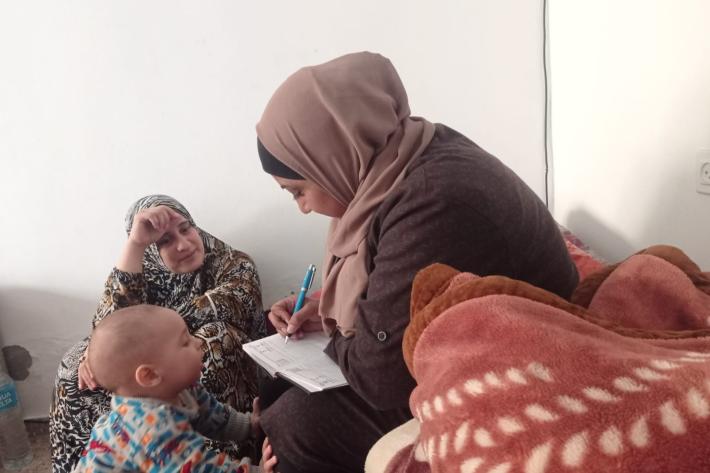

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
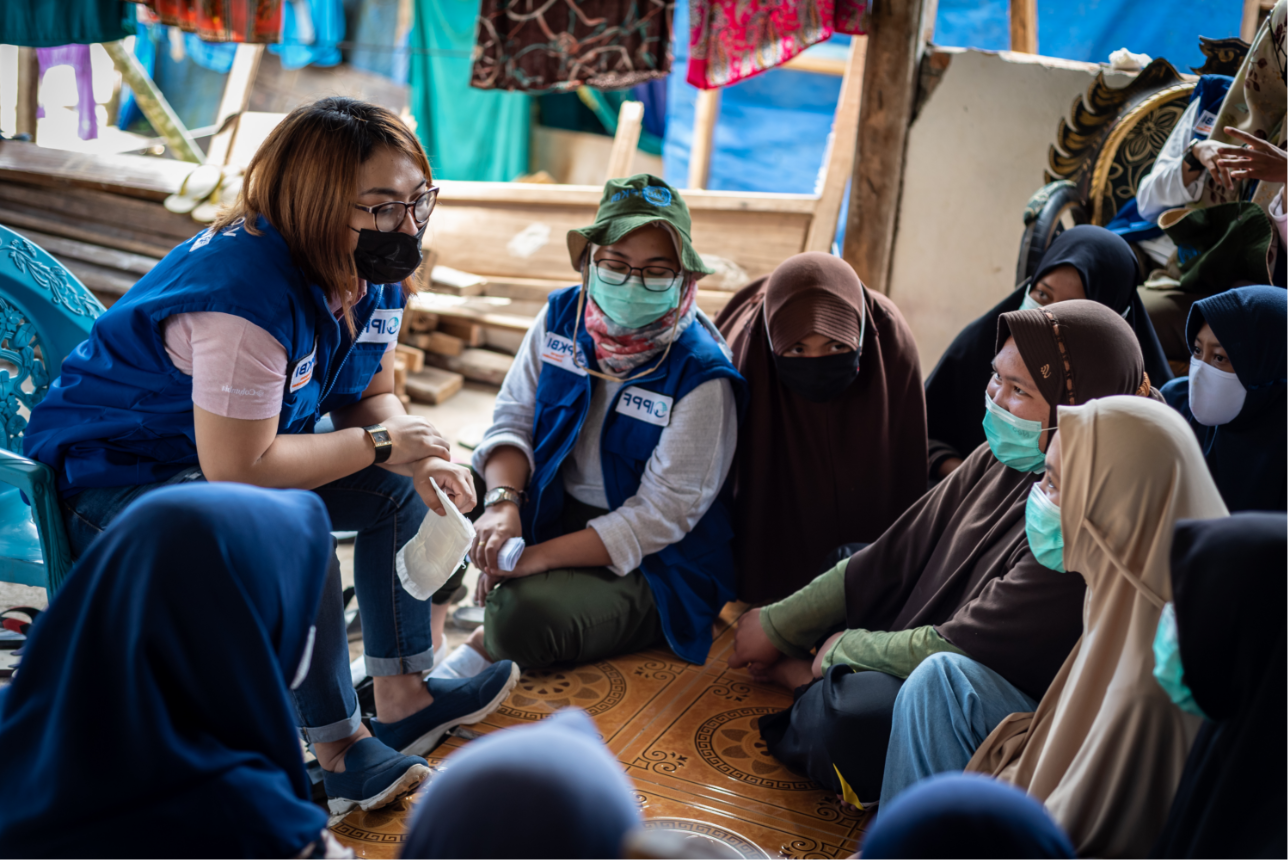
Vanuatu

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Filter our stories by:
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Aruba
- Bangladesh
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Colombia
- Congo, Dem. Rep.
- Cook Islands
- El Salvador
- Estonia
- Ethiopia
- Fiji
- France
- Germany
- Ghana
- Guinea-Conakry
- India
- Ireland
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Kiribati
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Palestine
- Poland
- Senegal
- Somaliland
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Thailand
- (-) Togo
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- (-) Uganda
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vanuatu
- Zambia

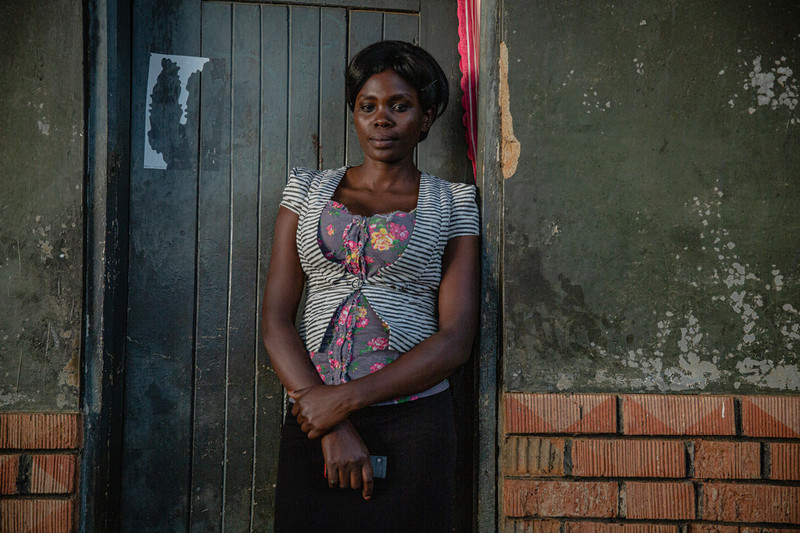
| 05 January 2022
In pictures: The changemaker keeping her community healthy and happy
The Get Up, Speak Out! initiative works with and for young people to overcome barriers such as unequal gender norms, negative attitudes towards sexuality, taboos about sex, menstruation, and abortion. Empowering youth communities - especially girls and young women - with information and knowledge about sexual and reproductive health, and the provision of access to health and contraceptive care, is at the heart of the initiative. Get Up, Speak Out! is an international initiative developed by a consortium of partners including IPPF, Rutgers, CHOICE for Youth & Sexuality, Dance4Life, Simavi, and Aidsfonds, with support from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
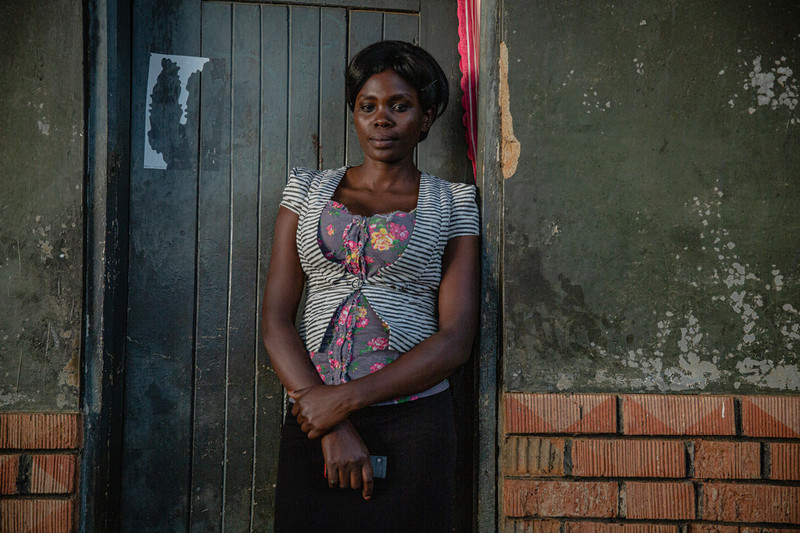
| 16 May 2025
In pictures: The changemaker keeping her community healthy and happy
The Get Up, Speak Out! initiative works with and for young people to overcome barriers such as unequal gender norms, negative attitudes towards sexuality, taboos about sex, menstruation, and abortion. Empowering youth communities - especially girls and young women - with information and knowledge about sexual and reproductive health, and the provision of access to health and contraceptive care, is at the heart of the initiative. Get Up, Speak Out! is an international initiative developed by a consortium of partners including IPPF, Rutgers, CHOICE for Youth & Sexuality, Dance4Life, Simavi, and Aidsfonds, with support from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.

| 23 September 2020
In pictures: Innovating during COVID-19
Women around the world have faced multiple barriers to accessing safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic including the de-prioritization of sexual and reproductive healthcare, overwhelmed health systems and restrictions on movement. The COVID-19 crisis has sparked innovation among IPPF Member Associations who responded swiftly by developing new approaches to reach women with safe abortion care including telemedicine and home-based provision of medical abortion. Strong evidence generated from this work supports the continuation and strengthening of these approaches beyond the end of the pandemic. Cameroon Cameroon National Planning Association for Family Welfare (CAMNAFAW) To ensure that quality abortion care can be provided to women during travel restrictions, CAMNAFAW’s service providers travel to partner clinics in underserved areas and to clients’ homes to provide medical and surgical abortion care. This model of taking safe abortion care closer to women will continue even with easing of travel restrictions, as this has been found to be an effective and acceptable approach to increasing access.Photo: IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Cameroon Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Guinea Association Guinéenne pour le Bien-Etre Familial (AGBEF) Building on lessons learned during the Ebola crisis in Guinea, AGBEF quickly took measures to prevent infection in its clinics to continue providing sexual and reproductive healthcare, including surgical and medical abortion, in a safe environment. AGBEF donated protective materials to communities, including hand-washing stations, face masks and antibacterial gel, alongside messaging on infection prevention. This community visibility reassures clients they can safely attend AGBEF clinics for abortion and contraceptive care.Photo: AGBEF/Guinea Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email India Family Planning Association of India (FPA India) FPA India and partners advocated to have sexual and reproductive healthcare, including abortion, recognized as essential by the government, which meant FPA India could continue healthcare delivery during the national lockdown. To reduce in-person clinic visits, FPA India established teleconsultation and counselling for abortion care, and is continuing to provide in-clinic care for both medical and surgical abortion. Photo: IPPF/Alison Joyce/India Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nepal Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN) FPAN and partners advocated for interim approval of home provision of medical abortion and telemedicine for abortion counselling during COVID-19. FPAN is now implementing these approaches, ensuring continued access to abortion care in Nepal, where many people live in remote locations with limited mobility, which has been further restricted by COVID-19 lockdowns. Photo: FPAN/Nepal Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Pakistan Rahnuma – Family Planning Association of Pakistan (Rahnuma-FPAP) Rahnuma-FPAP and partners successfully advocated for the government to class sexual and reproductive healthcare as ‘essential’, which enabled the team to continue providing post-abortion care during the pandemic. Rahnuma-FPAP expanded its telemedicine and home-based provision for menstrual regulation counselling and post-abortion care. These new approaches have ensured continued access to services for clients unable to reach clinics.Photo: Rahnuma-FPAP/Pakistan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Palestine Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA) In response to the government-mandated closure of its clinics, PFPPA quickly established a toll-free call centre which provides consultations, counselling, referrals and follow-up, including consultation for abortion care through a harm reduction approach, ensuring that women are provided with accurate information. Due to its success, PFPPA is exploring options for continuing this healthcare delivery model beyond the pandemic, with the aim of keeping it free of charge for users.Photo: SAAF/Samar Hazboun/Palestine Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sudan Sudan Family Planning Association (SFPA) Following a nation-wide shutdown in April, SFPA established a call centre to increase access to healthcare, including abortion and contraceptive counselling and referrals. An unexpected outcome of the new call centre is that it has reached an increased number of young women who regularly call to discuss their reproductive health and rights. SFPA is working towards institutionalizing this model for continuation beyond the pandemic.Photo: SFPA/Sudan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Togo Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ATBEF) ATBEF adapted its mobile application ‘Infos Ado Jeunes’, adding a toll-free teleconsultation service for young clients to use to access abortion consultations and pre- and post-abortion counselling. This app has given young clients ongoing access to care when they face challenges travelling to clinics. It has also eased overall client flow in clinics at a time when social distancing is being implemented.Photo: ATBEF/Togo Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Innovating during COVID-19
Women around the world have faced multiple barriers to accessing safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic including the de-prioritization of sexual and reproductive healthcare, overwhelmed health systems and restrictions on movement. The COVID-19 crisis has sparked innovation among IPPF Member Associations who responded swiftly by developing new approaches to reach women with safe abortion care including telemedicine and home-based provision of medical abortion. Strong evidence generated from this work supports the continuation and strengthening of these approaches beyond the end of the pandemic. Cameroon Cameroon National Planning Association for Family Welfare (CAMNAFAW) To ensure that quality abortion care can be provided to women during travel restrictions, CAMNAFAW’s service providers travel to partner clinics in underserved areas and to clients’ homes to provide medical and surgical abortion care. This model of taking safe abortion care closer to women will continue even with easing of travel restrictions, as this has been found to be an effective and acceptable approach to increasing access.Photo: IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Cameroon Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Guinea Association Guinéenne pour le Bien-Etre Familial (AGBEF) Building on lessons learned during the Ebola crisis in Guinea, AGBEF quickly took measures to prevent infection in its clinics to continue providing sexual and reproductive healthcare, including surgical and medical abortion, in a safe environment. AGBEF donated protective materials to communities, including hand-washing stations, face masks and antibacterial gel, alongside messaging on infection prevention. This community visibility reassures clients they can safely attend AGBEF clinics for abortion and contraceptive care.Photo: AGBEF/Guinea Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email India Family Planning Association of India (FPA India) FPA India and partners advocated to have sexual and reproductive healthcare, including abortion, recognized as essential by the government, which meant FPA India could continue healthcare delivery during the national lockdown. To reduce in-person clinic visits, FPA India established teleconsultation and counselling for abortion care, and is continuing to provide in-clinic care for both medical and surgical abortion. Photo: IPPF/Alison Joyce/India Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nepal Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN) FPAN and partners advocated for interim approval of home provision of medical abortion and telemedicine for abortion counselling during COVID-19. FPAN is now implementing these approaches, ensuring continued access to abortion care in Nepal, where many people live in remote locations with limited mobility, which has been further restricted by COVID-19 lockdowns. Photo: FPAN/Nepal Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Pakistan Rahnuma – Family Planning Association of Pakistan (Rahnuma-FPAP) Rahnuma-FPAP and partners successfully advocated for the government to class sexual and reproductive healthcare as ‘essential’, which enabled the team to continue providing post-abortion care during the pandemic. Rahnuma-FPAP expanded its telemedicine and home-based provision for menstrual regulation counselling and post-abortion care. These new approaches have ensured continued access to services for clients unable to reach clinics.Photo: Rahnuma-FPAP/Pakistan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Palestine Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA) In response to the government-mandated closure of its clinics, PFPPA quickly established a toll-free call centre which provides consultations, counselling, referrals and follow-up, including consultation for abortion care through a harm reduction approach, ensuring that women are provided with accurate information. Due to its success, PFPPA is exploring options for continuing this healthcare delivery model beyond the pandemic, with the aim of keeping it free of charge for users.Photo: SAAF/Samar Hazboun/Palestine Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sudan Sudan Family Planning Association (SFPA) Following a nation-wide shutdown in April, SFPA established a call centre to increase access to healthcare, including abortion and contraceptive counselling and referrals. An unexpected outcome of the new call centre is that it has reached an increased number of young women who regularly call to discuss their reproductive health and rights. SFPA is working towards institutionalizing this model for continuation beyond the pandemic.Photo: SFPA/Sudan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Togo Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ATBEF) ATBEF adapted its mobile application ‘Infos Ado Jeunes’, adding a toll-free teleconsultation service for young clients to use to access abortion consultations and pre- and post-abortion counselling. This app has given young clients ongoing access to care when they face challenges travelling to clinics. It has also eased overall client flow in clinics at a time when social distancing is being implemented.Photo: ATBEF/Togo Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email
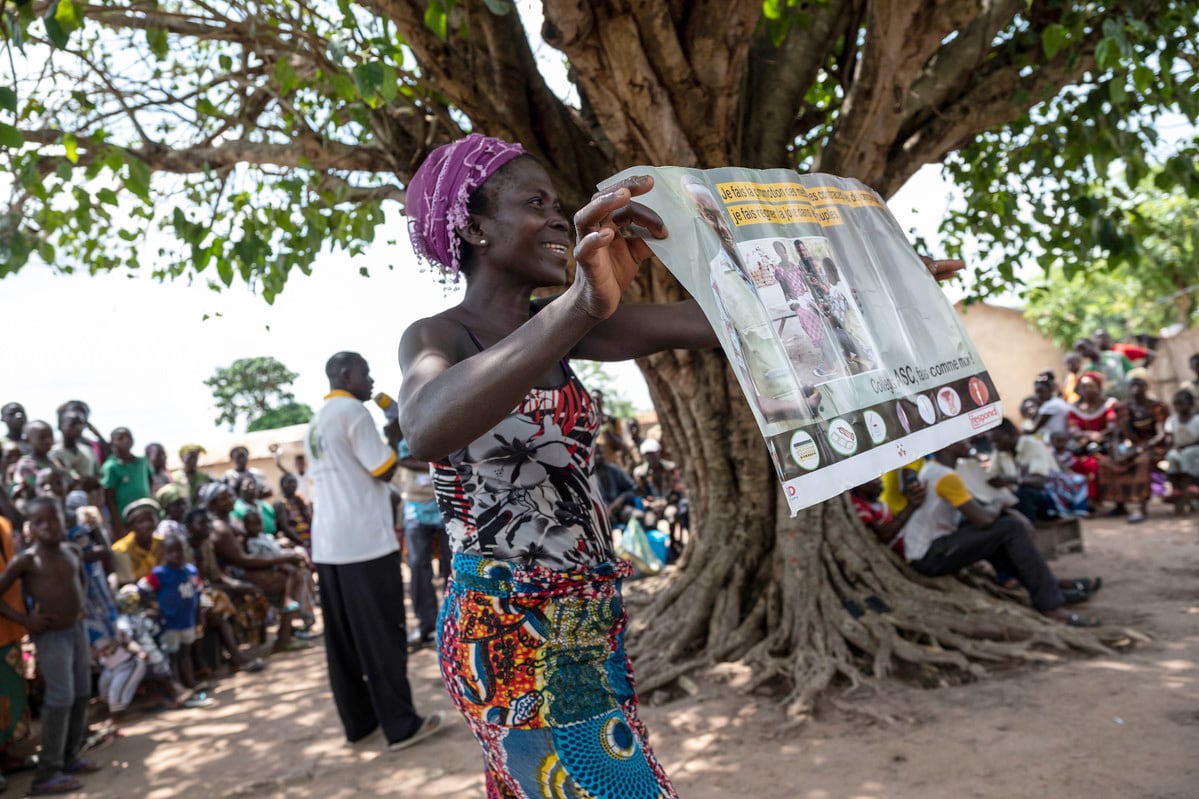

| 25 February 2019
In pictures: Togo and the rise in contraception use
Félicité Sonhaye ATBEF Regional Coordinator The Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), has led a pioneering programme training community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. “The injection is used more than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. “Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies”, Sonhaye added. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sossou Sagna Ilama village chief Men like Sossou Sagna, have great influence and respect within Togo’s rural communities. As Ilama’s village chief his approval was required for the ATBEF community project to take root. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied. Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty. Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abla Abassa Community health worker Abla is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets visiting households that have signed up to an innovative programme providing contraception in hard-to-reach places. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project the community is now able to space their births. I have seen the number of children per family going down. That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that everyone wants to send their children to school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Essivi Koutchona Client Facing prohibitive costs of school fees and food prices for six children, Essivi Koutchona, began using the contraceptive injection after deciding with her husband they did not want another child. She has received the injection every three months and has not experienced any side effects. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects. We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Edem Badagbo Client 33-year-old Edem is a widowed father of three children. Edem hopes to have a vasectomy within the next month or so. His wife died following the birth of their third child but he is adamant he wants to follow through with a procedure they agreed upon before her death. “My wife agreed with the idea. I was scared when I first heard of it, but that’s because there was so little information available. When I came to the ATBEF clinic I received a lot more detail and that’s when I decided to do it. I have three children. That’s enough.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Yaori Ajossou Vasectomy client Yaori Ajossou, a retired soldier, heard about vasectomy while listening to an ABTEF awareness raising campaign on the radio. It prompted him to take on the responsibility for family planning in his marriage. “Before I had the idea that maybe I'd want to have more children, but after the campaign, and after my wife had talked a little bit about her health problems, I thought, well, maybe it's better to put the brakes on. I was about to retire. Why carry on having children? Six children is already a lot. It's already maybe too many.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Dede Koussawo Client 34-year-old Dede visits the ATBEF clinic in Lomé, Togo with her husband, Edem. “We do this together if his schedule permits it. I asked and he accepted. It's not typical (for men to come). Before the pregnancy, I was taking the pill. Before the first I was taking the pill and I used an IUD after my son's birth and after my daughter's birth as well. We've been really happy with the family planning we've got here so we decided to come here for Prescillia’s birth as well.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mensah Awity Teacher and ABTEF youth club coordinator in Tohoun Mensah Awity is a teacher at a local school in Tohoun. He also coordinates the ABTEF youth club where they provide information and opportunities for the students to talk about sexual health, pregnancy, contraception. “At the beginning it was difficult for the club. Now teachers have started accepting the ideas and some pupils behave much better so it’s hard for them to keep condemning it. There are three girls who gave birth and who came back to school afterwards. At the beginning it was tough for them but we explained to the students that they shouldn’t be treated differently. The rate of pregnancy has definitely gone down at school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Emefa Charita Ankouy Youth activist and student “I'm studying for a degree in English and I'm a young activist volunteer with the IPPF youth movement. We promote, we try to help young girls who are in education to have more information about sexual health and reproduction to help them to adopt a method to avoid a pregnancy. They don't have enough information about sexual health and reproduction. I think it's because of that that they've become pregnant. They want to have sex quite early. There is pressure and there's a lack of communication between the students and their parents. Here in Togo sex is taboo for everyone, above all for parents.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Evedoh Worou Community Health Worker, Ilama “The ones who prefer the pill are young students or apprentices. Often, they take it to reduce PMS, and it regulates their period. Sometimes women will forget to take the pill, which means the injection is preferred as it’s just once for three months. The women here have more autonomy and they now have the space to earn money themselves for the household as a result of the programme. At the beginning, there were some reservations among the men in the community but after our awareness campaigns, more and more of them accompany women for family planning.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 16 May 2025
In pictures: Togo and the rise in contraception use
Félicité Sonhaye ATBEF Regional Coordinator The Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), has led a pioneering programme training community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. “The injection is used more than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. “Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies”, Sonhaye added. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sossou Sagna Ilama village chief Men like Sossou Sagna, have great influence and respect within Togo’s rural communities. As Ilama’s village chief his approval was required for the ATBEF community project to take root. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied. Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty. Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abla Abassa Community health worker Abla is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets visiting households that have signed up to an innovative programme providing contraception in hard-to-reach places. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project the community is now able to space their births. I have seen the number of children per family going down. That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that everyone wants to send their children to school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Essivi Koutchona Client Facing prohibitive costs of school fees and food prices for six children, Essivi Koutchona, began using the contraceptive injection after deciding with her husband they did not want another child. She has received the injection every three months and has not experienced any side effects. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects. We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Edem Badagbo Client 33-year-old Edem is a widowed father of three children. Edem hopes to have a vasectomy within the next month or so. His wife died following the birth of their third child but he is adamant he wants to follow through with a procedure they agreed upon before her death. “My wife agreed with the idea. I was scared when I first heard of it, but that’s because there was so little information available. When I came to the ATBEF clinic I received a lot more detail and that’s when I decided to do it. I have three children. That’s enough.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Yaori Ajossou Vasectomy client Yaori Ajossou, a retired soldier, heard about vasectomy while listening to an ABTEF awareness raising campaign on the radio. It prompted him to take on the responsibility for family planning in his marriage. “Before I had the idea that maybe I'd want to have more children, but after the campaign, and after my wife had talked a little bit about her health problems, I thought, well, maybe it's better to put the brakes on. I was about to retire. Why carry on having children? Six children is already a lot. It's already maybe too many.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Dede Koussawo Client 34-year-old Dede visits the ATBEF clinic in Lomé, Togo with her husband, Edem. “We do this together if his schedule permits it. I asked and he accepted. It's not typical (for men to come). Before the pregnancy, I was taking the pill. Before the first I was taking the pill and I used an IUD after my son's birth and after my daughter's birth as well. We've been really happy with the family planning we've got here so we decided to come here for Prescillia’s birth as well.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mensah Awity Teacher and ABTEF youth club coordinator in Tohoun Mensah Awity is a teacher at a local school in Tohoun. He also coordinates the ABTEF youth club where they provide information and opportunities for the students to talk about sexual health, pregnancy, contraception. “At the beginning it was difficult for the club. Now teachers have started accepting the ideas and some pupils behave much better so it’s hard for them to keep condemning it. There are three girls who gave birth and who came back to school afterwards. At the beginning it was tough for them but we explained to the students that they shouldn’t be treated differently. The rate of pregnancy has definitely gone down at school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Emefa Charita Ankouy Youth activist and student “I'm studying for a degree in English and I'm a young activist volunteer with the IPPF youth movement. We promote, we try to help young girls who are in education to have more information about sexual health and reproduction to help them to adopt a method to avoid a pregnancy. They don't have enough information about sexual health and reproduction. I think it's because of that that they've become pregnant. They want to have sex quite early. There is pressure and there's a lack of communication between the students and their parents. Here in Togo sex is taboo for everyone, above all for parents.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Evedoh Worou Community Health Worker, Ilama “The ones who prefer the pill are young students or apprentices. Often, they take it to reduce PMS, and it regulates their period. Sometimes women will forget to take the pill, which means the injection is preferred as it’s just once for three months. The women here have more autonomy and they now have the space to earn money themselves for the household as a result of the programme. At the beginning, there were some reservations among the men in the community but after our awareness campaigns, more and more of them accompany women for family planning.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF
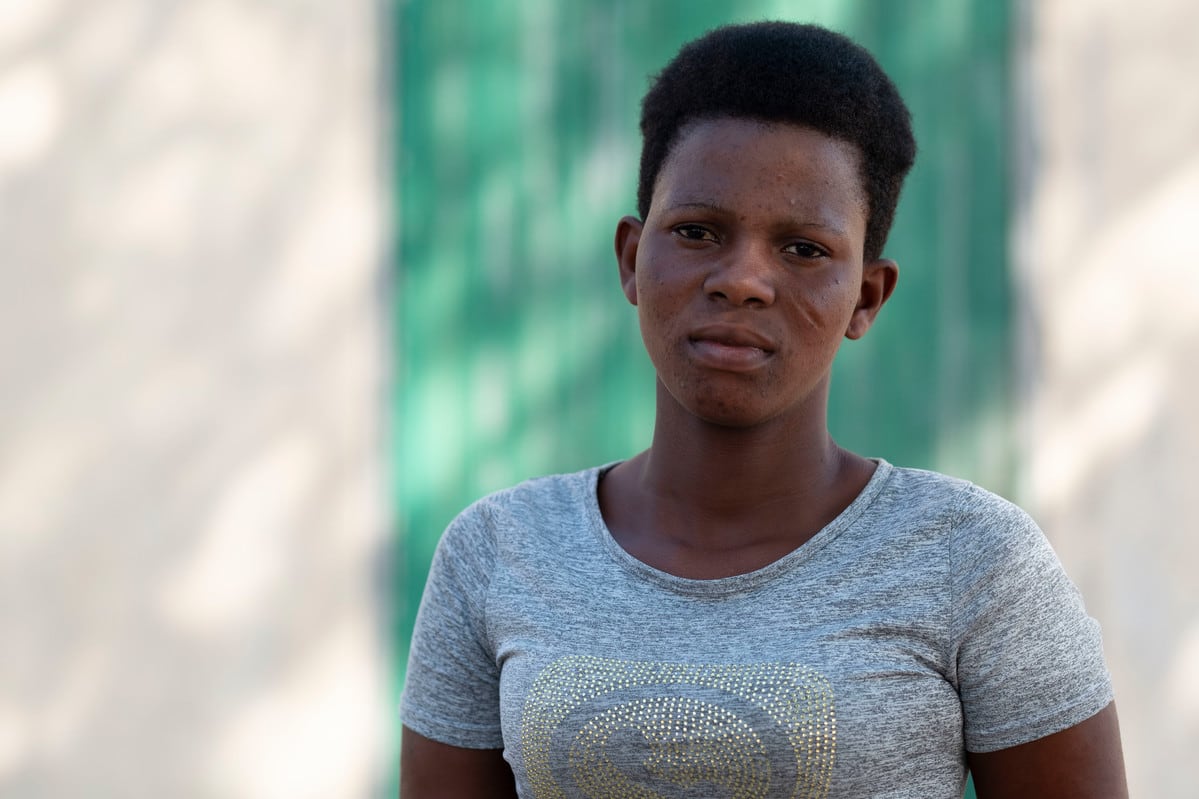

| 25 February 2019
“I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child”
Every three months, Mawoula Dahide meets a community health worker in her village in central Togo to receive a single contraceptive injection and then carries on with her busy day. Dahide, 20, has a two-and-a-half year old son and a husband living in the capital and juggles an apprenticeship in tailoring with caring for her child. After recovering from the birth, Dahide tried the injection and immediately felt relief, knowing she would decide when she got pregnant again. “I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child,” she said. Lack of access Until 2013, Dahide and the other women living in the village of Ilama had no access to regular contraception at all, and its use was sometimes regarded with suspicion, and even fear. In her community, the average age of a mother’s first pregnancy is around 16, and women might bear a total of six or seven children compared to the national average of 4.7, according to local health workers. That trend is changing with a pioneering programme run by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), which has trained community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. ATBEF has focused their distribution of contraceptives within poor and rural communities, and with mobile outreach clinics that go to villages with no trained health workers. The unmet need for contraception in Togo stands at 34% of the population, and in rural communities, this is even higher. The association contributes a fifth of overall contraception cover to couples in Togo, a West Africa nation of 7.8 million people. There is a clear favourite among the methods offered, which include male and female condoms, the pill, and the contraceptive injection. “The injection is more used than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, Sonhaye added, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies. From client to advocate Dahide has become an advocate for the method among her peers within her community. “My friends are getting the injection as well. I was the first to start using it and it was great, so I told them about it,” she said. Another convert to the injection is Ilama’s village chief, Sossou Sagna. The father of seven agreed with his wife they didn’t want anymore children. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied,” Sagna noted in the cool of the shade. “My wife chose the three-month injection,” he added. Sagna had not anticipated some of the wider effects of increasing contraceptive use within the community, which have become prevalent over the last couple of years. “Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty,” he said. Families have more money to spend feeding and educating their children in an economy where the cost of living keeps rising. Villagers who see Sagna attending family planning sessions are also convinced that rumours about contraception making them ill are untrue. “Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family,” he added. The gains of the ATBEF rural programme will now go even further with the imminent introduction of Sayana Press, a contraceptive injection that women can self-administer. Learn more about some of the most popular contraception methods available and if they are right for you Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 15 May 2025
“I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child”
Every three months, Mawoula Dahide meets a community health worker in her village in central Togo to receive a single contraceptive injection and then carries on with her busy day. Dahide, 20, has a two-and-a-half year old son and a husband living in the capital and juggles an apprenticeship in tailoring with caring for her child. After recovering from the birth, Dahide tried the injection and immediately felt relief, knowing she would decide when she got pregnant again. “I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child,” she said. Lack of access Until 2013, Dahide and the other women living in the village of Ilama had no access to regular contraception at all, and its use was sometimes regarded with suspicion, and even fear. In her community, the average age of a mother’s first pregnancy is around 16, and women might bear a total of six or seven children compared to the national average of 4.7, according to local health workers. That trend is changing with a pioneering programme run by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), which has trained community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. ATBEF has focused their distribution of contraceptives within poor and rural communities, and with mobile outreach clinics that go to villages with no trained health workers. The unmet need for contraception in Togo stands at 34% of the population, and in rural communities, this is even higher. The association contributes a fifth of overall contraception cover to couples in Togo, a West Africa nation of 7.8 million people. There is a clear favourite among the methods offered, which include male and female condoms, the pill, and the contraceptive injection. “The injection is more used than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, Sonhaye added, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies. From client to advocate Dahide has become an advocate for the method among her peers within her community. “My friends are getting the injection as well. I was the first to start using it and it was great, so I told them about it,” she said. Another convert to the injection is Ilama’s village chief, Sossou Sagna. The father of seven agreed with his wife they didn’t want anymore children. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied,” Sagna noted in the cool of the shade. “My wife chose the three-month injection,” he added. Sagna had not anticipated some of the wider effects of increasing contraceptive use within the community, which have become prevalent over the last couple of years. “Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty,” he said. Families have more money to spend feeding and educating their children in an economy where the cost of living keeps rising. Villagers who see Sagna attending family planning sessions are also convinced that rumours about contraception making them ill are untrue. “Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family,” he added. The gains of the ATBEF rural programme will now go even further with the imminent introduction of Sayana Press, a contraceptive injection that women can self-administer. Learn more about some of the most popular contraception methods available and if they are right for you Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF
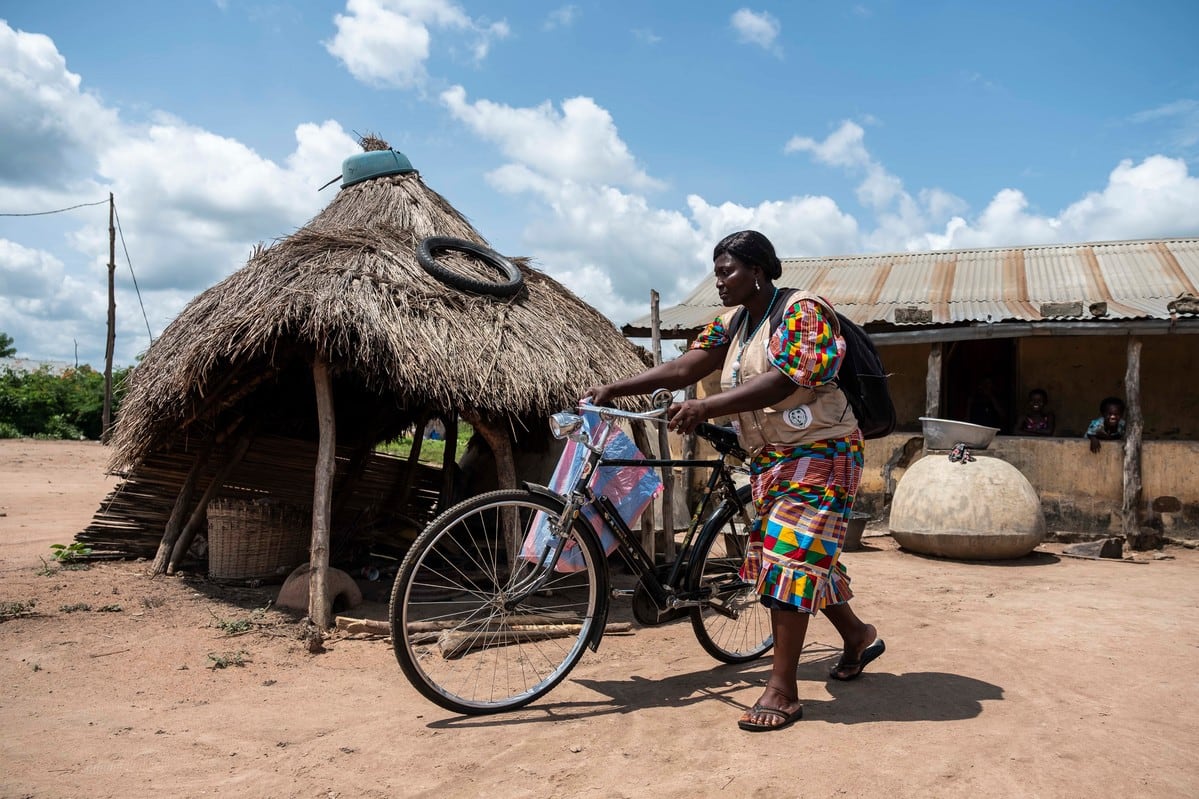

| 20 February 2019
“Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves”
Abla Abassa lives in the village of Ilama, population 2,000, in rural central Togo. After waking up early each morning to prepare for the day ahead, she sits down to map out her route. Abassa is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets to visit households who have signed up to an innovative programme that provides contraception in hard-to-reach places. The village is an hour by bumpy dirt track from the regional capital of Atakpamé, and few residents have the time or money to travel into town on a regular basis to refill prescriptions. For years, that meant the women of the community had just one form of protection against pregnancy: avoiding sex altogether. In 2013, Abassa became one of 279 community health workers in the Plateaux region funded by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), working in two districts where the unmet need for contraception was greatest. Today, Abassa has three different clients, but can deal with as many as five a day. The health worker meets women on their own or with their husbands, and conversation flows about village life before she administers a contraceptive injection, or leaves behind a small pile of condoms. Reaching those in need She begins the day a few doors down at the home of Essivi Koutchona, a mother of six who has used the contraceptive injection for the last two-and-a-half years. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects,” Koutchona said. “We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection”. Koutchona’s husband, Konou Aboudou, credits Abassa and the ATBEF with improving his marriage, which he said was strained by the rhythm [calendar] method and supporting many young children at once. “Now we can better understand and support our wives. We avoid adultery and pregnancies are planned,” he explained. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project we have undertaken with ATBEF since 2013, the community is now able to space their births,” Abassa said, adding the couple had told her they wished the programmed has started years ago. Togo currently has a fertility rate of 4.7 children per woman, according to the United Nations Statistics Division, but is trying to bring that number down. Battling misinformation The government faces entrenched attitudes about the value of a large family, and misinformation spread about contraception. A community health worker has two roles: safely providing contraception, but also reassuring women that many of the rumours they have heard that the injection or pill will make them sick are false. “I tell them that side effects come from the product, so if they have an irregular period it’s not because they are ill,” Abassa said, adding it had taken much persuasion over the last five years to reach the point where she was now trusted. Abassa’s next client preferred to meet at the health worker’s home for some privacy. At 45, Adjo Amagna is still having periods and wants to avoid any chance of another pregnancy. “I think I want to go for the injection. I have never used contraception before so I think I will do it for three months to see how it goes,” she said. After the death of her fifth child, the only baby she had with her second husband, Amagna wants to focus on caring of the four children she has left. She sat down with the health worker and was passed condoms, femidoms and the pill, while Abassa explained how the injection works. After a half hour chat, Amagna agreed to begin the injection on her next visit. Changes within the community On the way to see Mawoula Dahide, a 20-year-old with one child, her last client of the day, Abassa reflected on the changes she has seen in the community since her job began. “I have seen the number of children per family going down,” she said. “That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that these days everyone wants to send their children to school.” The prevalence of contraceptive use was at 17% before the programme began, but with the focus on rural communities this has risen to 23% nationwide, even though not all areas of Togo are covered by dedicated health workers yet. We met Dahide in a quiet corner as she took a short break from an apprenticeship in tailoring. “It’s pretty tough balancing my son and my apprenticeship. If I had waited to have a kid before starting it would have been a lot easier,” she admitted. “My husband is studying at the university in Lomé so I only see him during the holidays and maybe a few weekends during term time.” Younger women like Dahide are sometimes harder to reach, said Abassa, and have a greater unmet need for contraception in a community where many have their first child around the age of 16. “Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves,” the health worker explained, adding her focus was always on recruiting more teenagers to her cause. As she heads home for the day, Abassa waved to clients and neighbours, while wondering who might be on her doorstep looking for advice when she gets there. Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 16 May 2025
“Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves”
Abla Abassa lives in the village of Ilama, population 2,000, in rural central Togo. After waking up early each morning to prepare for the day ahead, she sits down to map out her route. Abassa is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets to visit households who have signed up to an innovative programme that provides contraception in hard-to-reach places. The village is an hour by bumpy dirt track from the regional capital of Atakpamé, and few residents have the time or money to travel into town on a regular basis to refill prescriptions. For years, that meant the women of the community had just one form of protection against pregnancy: avoiding sex altogether. In 2013, Abassa became one of 279 community health workers in the Plateaux region funded by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), working in two districts where the unmet need for contraception was greatest. Today, Abassa has three different clients, but can deal with as many as five a day. The health worker meets women on their own or with their husbands, and conversation flows about village life before she administers a contraceptive injection, or leaves behind a small pile of condoms. Reaching those in need She begins the day a few doors down at the home of Essivi Koutchona, a mother of six who has used the contraceptive injection for the last two-and-a-half years. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects,” Koutchona said. “We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection”. Koutchona’s husband, Konou Aboudou, credits Abassa and the ATBEF with improving his marriage, which he said was strained by the rhythm [calendar] method and supporting many young children at once. “Now we can better understand and support our wives. We avoid adultery and pregnancies are planned,” he explained. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project we have undertaken with ATBEF since 2013, the community is now able to space their births,” Abassa said, adding the couple had told her they wished the programmed has started years ago. Togo currently has a fertility rate of 4.7 children per woman, according to the United Nations Statistics Division, but is trying to bring that number down. Battling misinformation The government faces entrenched attitudes about the value of a large family, and misinformation spread about contraception. A community health worker has two roles: safely providing contraception, but also reassuring women that many of the rumours they have heard that the injection or pill will make them sick are false. “I tell them that side effects come from the product, so if they have an irregular period it’s not because they are ill,” Abassa said, adding it had taken much persuasion over the last five years to reach the point where she was now trusted. Abassa’s next client preferred to meet at the health worker’s home for some privacy. At 45, Adjo Amagna is still having periods and wants to avoid any chance of another pregnancy. “I think I want to go for the injection. I have never used contraception before so I think I will do it for three months to see how it goes,” she said. After the death of her fifth child, the only baby she had with her second husband, Amagna wants to focus on caring of the four children she has left. She sat down with the health worker and was passed condoms, femidoms and the pill, while Abassa explained how the injection works. After a half hour chat, Amagna agreed to begin the injection on her next visit. Changes within the community On the way to see Mawoula Dahide, a 20-year-old with one child, her last client of the day, Abassa reflected on the changes she has seen in the community since her job began. “I have seen the number of children per family going down,” she said. “That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that these days everyone wants to send their children to school.” The prevalence of contraceptive use was at 17% before the programme began, but with the focus on rural communities this has risen to 23% nationwide, even though not all areas of Togo are covered by dedicated health workers yet. We met Dahide in a quiet corner as she took a short break from an apprenticeship in tailoring. “It’s pretty tough balancing my son and my apprenticeship. If I had waited to have a kid before starting it would have been a lot easier,” she admitted. “My husband is studying at the university in Lomé so I only see him during the holidays and maybe a few weekends during term time.” Younger women like Dahide are sometimes harder to reach, said Abassa, and have a greater unmet need for contraception in a community where many have their first child around the age of 16. “Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves,” the health worker explained, adding her focus was always on recruiting more teenagers to her cause. As she heads home for the day, Abassa waved to clients and neighbours, while wondering who might be on her doorstep looking for advice when she gets there. Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 22 August 2018
“A radio announcement saved my life” – Gertrude’s story
Gertrude Mugala is a teacher in Fort Portal, a town in Western Uganda. While Gertrude considered herself fairly knowledgeable about cancer, she had never considered taking a screening test or imagined herself ever having the disease. Then one day, she heard an announcement on the radio urging women to go for cervical cancer screenings at a Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) clinic. “The radio presenter was talking about cervical cancer, and in her message she encouraged all women to get screened. I decided to go and try it out,” she said. Gertrude made her way to RHU's Fort Portal Branch clinic for the free cervical cancer screening. There, she met Ms. Irene Kugonza, an RHU service provider. Ms. Kugonza educated Gertrude and a group of other women about cervical cancer and the importance of routine screening. Gertrude received a type of cervical cancer screening called VIA (visual inspection with acetic acid). "I did not know what was happening" But Gertrude's results were not what she expected; she received a positive result. The good news, however, is that precancerous lesions can be treated if detected early. “I was so shaken when I was told I had pre-cancerous lesions. I did not know what was happening and I didn't believe what I was hearing. I had no idea of my health status. I thought I was healthy, but I was actually harbouring a potential killer disease in me. What would have happened if I didn't go for the screening? If I hadn't heard the radio announcement?” Gertrude was then referred for cryotherapy. “Following cryotherapy, I am now in the process of healing, and I am supposed to go back for review after three months,” said Gertrude. Community screenings Today, Gertrude advocates for cervical cancer screening in her community. She talks to women about cancer, especially cervical cancer, at her workplace, at the market, in meetings, and any other opportunity she gets. “I decided to let women know that cervical cancer is real and it is here with us, and that it kills. At the moment, those are the platforms I have, and I will continue educating women about cancer and encourage them to go for routine testing. I am also happy that I was near my radio that day, where I heard that announcement encouraging all women to get tested for cervical cancer. It might be because of that radio announcement that I am here today,” she said.

| 16 May 2025
“A radio announcement saved my life” – Gertrude’s story
Gertrude Mugala is a teacher in Fort Portal, a town in Western Uganda. While Gertrude considered herself fairly knowledgeable about cancer, she had never considered taking a screening test or imagined herself ever having the disease. Then one day, she heard an announcement on the radio urging women to go for cervical cancer screenings at a Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) clinic. “The radio presenter was talking about cervical cancer, and in her message she encouraged all women to get screened. I decided to go and try it out,” she said. Gertrude made her way to RHU's Fort Portal Branch clinic for the free cervical cancer screening. There, she met Ms. Irene Kugonza, an RHU service provider. Ms. Kugonza educated Gertrude and a group of other women about cervical cancer and the importance of routine screening. Gertrude received a type of cervical cancer screening called VIA (visual inspection with acetic acid). "I did not know what was happening" But Gertrude's results were not what she expected; she received a positive result. The good news, however, is that precancerous lesions can be treated if detected early. “I was so shaken when I was told I had pre-cancerous lesions. I did not know what was happening and I didn't believe what I was hearing. I had no idea of my health status. I thought I was healthy, but I was actually harbouring a potential killer disease in me. What would have happened if I didn't go for the screening? If I hadn't heard the radio announcement?” Gertrude was then referred for cryotherapy. “Following cryotherapy, I am now in the process of healing, and I am supposed to go back for review after three months,” said Gertrude. Community screenings Today, Gertrude advocates for cervical cancer screening in her community. She talks to women about cancer, especially cervical cancer, at her workplace, at the market, in meetings, and any other opportunity she gets. “I decided to let women know that cervical cancer is real and it is here with us, and that it kills. At the moment, those are the platforms I have, and I will continue educating women about cancer and encourage them to go for routine testing. I am also happy that I was near my radio that day, where I heard that announcement encouraging all women to get tested for cervical cancer. It might be because of that radio announcement that I am here today,” she said.

| 21 May 2017
A graduate in need turns to sex work
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. I am Pretty Lynn, aged 25. I am a sex worker but I went to university. I graduated with a Bachelor's Degree in Tourism in 2013. But now, during the day I’m sleeping and during the night I’m working. That is how my day goes every day. I got into sex work through friends. Okay it is not good but I am earning. I tried to get a job when I graduated. I have been applying since I graduated in 2013. I’m still applying but I’m not getting anywhere. You know to get jobs in Uganda; you have to know someone there and no one knows me there. To be a sex worker is like a curse. People look at you like, I don’t know, as someone that has no use in society. People look at you in a bad way. They even don’t consider why you are selling. They just see you as the worst thing that can happen in the society. So it is not comfortable, it is really hard but we try and survive. The fact sex working is illegal means you have to hide yourself when you are selling so that police cannot take you. And then you get diseases, men don’t want to pay. When the police come and take us, sometimes they even use us and don’t pay. So it is really hard. They want a free service. Like if they come and take you and pay that would be fair. But they say it is illegal to sell yourself. But they still use you yet they are saying it is illegal. You can’t report the police because there is no evidence. Abortion and unwanted pregnancies are really common because men don’t want to use condoms and female condoms are really rare and they are expensive. Though at times we get female condoms from Lady Marmaid’s Bureau (LMB) because there are so many of us they can’t keep on giving you them all the time. At times when we get pregnant we use local methods. You can go and use local herbs but it is not safe. One time I used local herbs and I was successful. Then the other time I used Omo washing powder and tea leaves but it was really hard for me. I almost died. I had a friend who died last year from this. But the good thing is that LMB taught us about safe abortion. I have had a safe abortion too. There are some tabs they are called Miso (misoprostol). It costs about fifty thousand shillings (£10 pounds or $20.) It is a lot of money. But if I’m working and I know I’m pregnant, I can say, "this week I’m working for my safe abortion". So if I’m working for twenty thousand, by the end of the week I will have the money. It is expensive compared to Omo at five hundred shillings but that is risky. So if I say I will work this whole week for Miso (misoprostol) it is better. But I'm working and I'm not eating. A project like this one from Lady Mermaid's can help young girls and women. But to take us from sex work, it would really be hard. They would not have enough money to cater for all of us. So what they have to do is to teach us how to protect ourselves, how to defend ourselves. Safe abortion yes. They will just have to sensitise us more about our lives, protection, female condoms and all that. I don't have a boyfriend but maybe when I get money and leave this job I will. But for now, no man would like a woman who sells. No man will bear the wife selling herself. And that will happen only if I get funds, settle somewhere else and become responsible woman. I don’t want this job. I don’t want to be in this business of sex work all the time. I want be married, with my children happily, not selling myself. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 15 May 2025
A graduate in need turns to sex work
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. I am Pretty Lynn, aged 25. I am a sex worker but I went to university. I graduated with a Bachelor's Degree in Tourism in 2013. But now, during the day I’m sleeping and during the night I’m working. That is how my day goes every day. I got into sex work through friends. Okay it is not good but I am earning. I tried to get a job when I graduated. I have been applying since I graduated in 2013. I’m still applying but I’m not getting anywhere. You know to get jobs in Uganda; you have to know someone there and no one knows me there. To be a sex worker is like a curse. People look at you like, I don’t know, as someone that has no use in society. People look at you in a bad way. They even don’t consider why you are selling. They just see you as the worst thing that can happen in the society. So it is not comfortable, it is really hard but we try and survive. The fact sex working is illegal means you have to hide yourself when you are selling so that police cannot take you. And then you get diseases, men don’t want to pay. When the police come and take us, sometimes they even use us and don’t pay. So it is really hard. They want a free service. Like if they come and take you and pay that would be fair. But they say it is illegal to sell yourself. But they still use you yet they are saying it is illegal. You can’t report the police because there is no evidence. Abortion and unwanted pregnancies are really common because men don’t want to use condoms and female condoms are really rare and they are expensive. Though at times we get female condoms from Lady Marmaid’s Bureau (LMB) because there are so many of us they can’t keep on giving you them all the time. At times when we get pregnant we use local methods. You can go and use local herbs but it is not safe. One time I used local herbs and I was successful. Then the other time I used Omo washing powder and tea leaves but it was really hard for me. I almost died. I had a friend who died last year from this. But the good thing is that LMB taught us about safe abortion. I have had a safe abortion too. There are some tabs they are called Miso (misoprostol). It costs about fifty thousand shillings (£10 pounds or $20.) It is a lot of money. But if I’m working and I know I’m pregnant, I can say, "this week I’m working for my safe abortion". So if I’m working for twenty thousand, by the end of the week I will have the money. It is expensive compared to Omo at five hundred shillings but that is risky. So if I say I will work this whole week for Miso (misoprostol) it is better. But I'm working and I'm not eating. A project like this one from Lady Mermaid's can help young girls and women. But to take us from sex work, it would really be hard. They would not have enough money to cater for all of us. So what they have to do is to teach us how to protect ourselves, how to defend ourselves. Safe abortion yes. They will just have to sensitise us more about our lives, protection, female condoms and all that. I don't have a boyfriend but maybe when I get money and leave this job I will. But for now, no man would like a woman who sells. No man will bear the wife selling herself. And that will happen only if I get funds, settle somewhere else and become responsible woman. I don’t want this job. I don’t want to be in this business of sex work all the time. I want be married, with my children happily, not selling myself. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
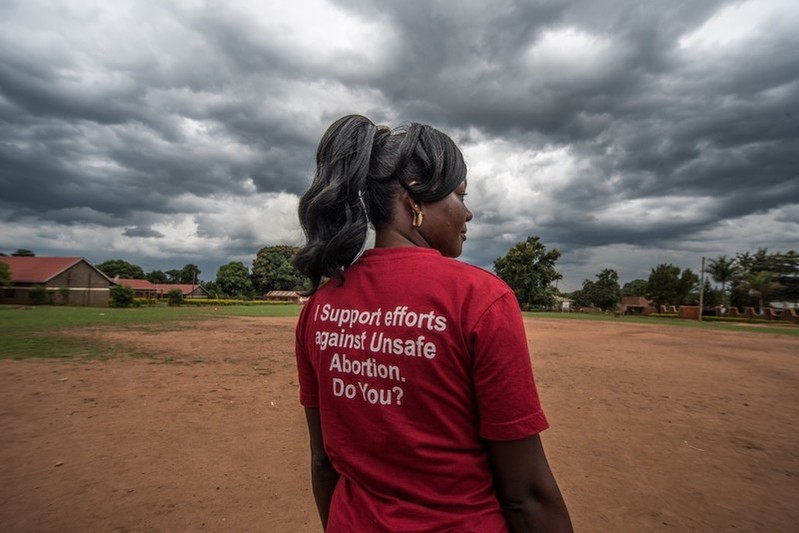

| 20 May 2017
Working to stop unsafe abortion for school girls
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Unsafe abortion is a huge problem in Uganda with an estimated 400,000 women having an unsafe abortion per year. The law is confusing and unclear, with abortion permitted only under certain circumstances. Post-abortion care is permitted to treat women who have undergone an unsafe abortion, however lack of awareness of the law and stigma surrounding abortion mean that service providers are not always willing to treat patients who arrive seeking care. The VODA project aims to ensure that young women in Uganda are able to lead healthier lives free from unsafe abortion related deaths or complications through reducing abortion stigma in the community, increasing access to abortion-related services and ensuring the providers are trained to provide quality post-abortion care services. I am Helen. I have been a midwife at this small clinic for seven years and I have worked with VODA for four years. Unsafe abortion continues and some schoolgirls are raped. They then go to local herbalists and some of them tell me that they are given emilandira [roots] which they insert inside themselves to rupture the membranes. Some of them even try to induce an abortion by using Omo [douching with detergent or bleach]. At the end of the day they get complications then they land here, so we help them. Unsafe abortion is very common. In one month you can get more than five cases. It is a big problem. We help them, they need to go back to school, and we counsel them. If it is less than 12 weeks, we handle them from here. If they are more than 12 weeks along we refer them to the hospital. Most referrals from VODA are related to unwanted pregnancies, HIV testing, family planning, and youth friendly services. A few parents come for services for their children who are at school. So we counsel them that contraception, other than condoms, will only prevent pregnancy, but you can still get HIV and STIs, so take care. I am Josephine and I work as a midwife at a rural health centre. I deal with pregnant mothers, postnatal mothers, and there are girls who come with problems like unwanted pregnancy. I used to have a negative attitude towards abortion. But then VODA helped us understand the importance of helping someone with the problem because many people were dying in the villages because of unsafe abortion. According to my religion, helping someone to have an abortion was not allowed. But again when you look into it, it’s not good to leave someone to die. So I decided to change my attitude to help people. Post-abortion care has helped many people because these days we don’t have many people in the villages dying because of unsafe abortion. These days I’m proud of what we are doing because before I didn’t know the importance of helping someone with a problem. But these days, since people no longer die, people no longer get problems and I’m proud and happy because we help so many people. My name is Jonathan. I am married with three children. I have a Bachelor of Social Work and Social Administration. I have worked with VODA as a project officer since 2008. Due to the training that we have done about abortion many people have changed their attitudes and we have helped people to talk about the issue. Most people were against abortion before but they are now realising that if it’s done safely it is important because otherwise many people die from unsafe abortion. I have talked to religious leaders, I have talked to local leaders; I have talked to people of different categories. At first when you approach them, they have a different perception. The health workers were difficult to work with at first. However they knew people were approaching them with the problems of unsafe abortion. Due to religion, communities can be hard against this issue. But after some time we have seen that they have changed their perception toward the issue of safe and unsafe abortion. And now many of them know that in some instances, abortion is inevitable but it should be done in a safe way. I’m Stevens and I am nurse. We have some clients who come when they have already attempted an unsafe abortion. You find that it is often inevitable. The only solution you have to help those clients is to provide treatment of incomplete abortion as part of post-abortion care. Because of the VODA project there is a very remarkable change in the community. Now, those people who used to have unsafe abortions locally, know where to go for post-abortion care - unlike in the past. I remember a schoolgirl, she was in a very sorry state because she had tried some local remedies to abort. I attended to her and things went well. She went back to school. I feel so proud because that was a big life rescue. A girl like that could have died but now she is alive and I see her carrying on with her studies, I feel so proud. I praise VODA for that encouragement. This service should be legalised because whether they restrict it or not, there is abortion and it is going on. And if it’s not out in the open, so that our people know where to go for such services, it leads to more deaths. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
Working to stop unsafe abortion for school girls
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Unsafe abortion is a huge problem in Uganda with an estimated 400,000 women having an unsafe abortion per year. The law is confusing and unclear, with abortion permitted only under certain circumstances. Post-abortion care is permitted to treat women who have undergone an unsafe abortion, however lack of awareness of the law and stigma surrounding abortion mean that service providers are not always willing to treat patients who arrive seeking care. The VODA project aims to ensure that young women in Uganda are able to lead healthier lives free from unsafe abortion related deaths or complications through reducing abortion stigma in the community, increasing access to abortion-related services and ensuring the providers are trained to provide quality post-abortion care services. I am Helen. I have been a midwife at this small clinic for seven years and I have worked with VODA for four years. Unsafe abortion continues and some schoolgirls are raped. They then go to local herbalists and some of them tell me that they are given emilandira [roots] which they insert inside themselves to rupture the membranes. Some of them even try to induce an abortion by using Omo [douching with detergent or bleach]. At the end of the day they get complications then they land here, so we help them. Unsafe abortion is very common. In one month you can get more than five cases. It is a big problem. We help them, they need to go back to school, and we counsel them. If it is less than 12 weeks, we handle them from here. If they are more than 12 weeks along we refer them to the hospital. Most referrals from VODA are related to unwanted pregnancies, HIV testing, family planning, and youth friendly services. A few parents come for services for their children who are at school. So we counsel them that contraception, other than condoms, will only prevent pregnancy, but you can still get HIV and STIs, so take care. I am Josephine and I work as a midwife at a rural health centre. I deal with pregnant mothers, postnatal mothers, and there are girls who come with problems like unwanted pregnancy. I used to have a negative attitude towards abortion. But then VODA helped us understand the importance of helping someone with the problem because many people were dying in the villages because of unsafe abortion. According to my religion, helping someone to have an abortion was not allowed. But again when you look into it, it’s not good to leave someone to die. So I decided to change my attitude to help people. Post-abortion care has helped many people because these days we don’t have many people in the villages dying because of unsafe abortion. These days I’m proud of what we are doing because before I didn’t know the importance of helping someone with a problem. But these days, since people no longer die, people no longer get problems and I’m proud and happy because we help so many people. My name is Jonathan. I am married with three children. I have a Bachelor of Social Work and Social Administration. I have worked with VODA as a project officer since 2008. Due to the training that we have done about abortion many people have changed their attitudes and we have helped people to talk about the issue. Most people were against abortion before but they are now realising that if it’s done safely it is important because otherwise many people die from unsafe abortion. I have talked to religious leaders, I have talked to local leaders; I have talked to people of different categories. At first when you approach them, they have a different perception. The health workers were difficult to work with at first. However they knew people were approaching them with the problems of unsafe abortion. Due to religion, communities can be hard against this issue. But after some time we have seen that they have changed their perception toward the issue of safe and unsafe abortion. And now many of them know that in some instances, abortion is inevitable but it should be done in a safe way. I’m Stevens and I am nurse. We have some clients who come when they have already attempted an unsafe abortion. You find that it is often inevitable. The only solution you have to help those clients is to provide treatment of incomplete abortion as part of post-abortion care. Because of the VODA project there is a very remarkable change in the community. Now, those people who used to have unsafe abortions locally, know where to go for post-abortion care - unlike in the past. I remember a schoolgirl, she was in a very sorry state because she had tried some local remedies to abort. I attended to her and things went well. She went back to school. I feel so proud because that was a big life rescue. A girl like that could have died but now she is alive and I see her carrying on with her studies, I feel so proud. I praise VODA for that encouragement. This service should be legalised because whether they restrict it or not, there is abortion and it is going on. And if it’s not out in the open, so that our people know where to go for such services, it leads to more deaths. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
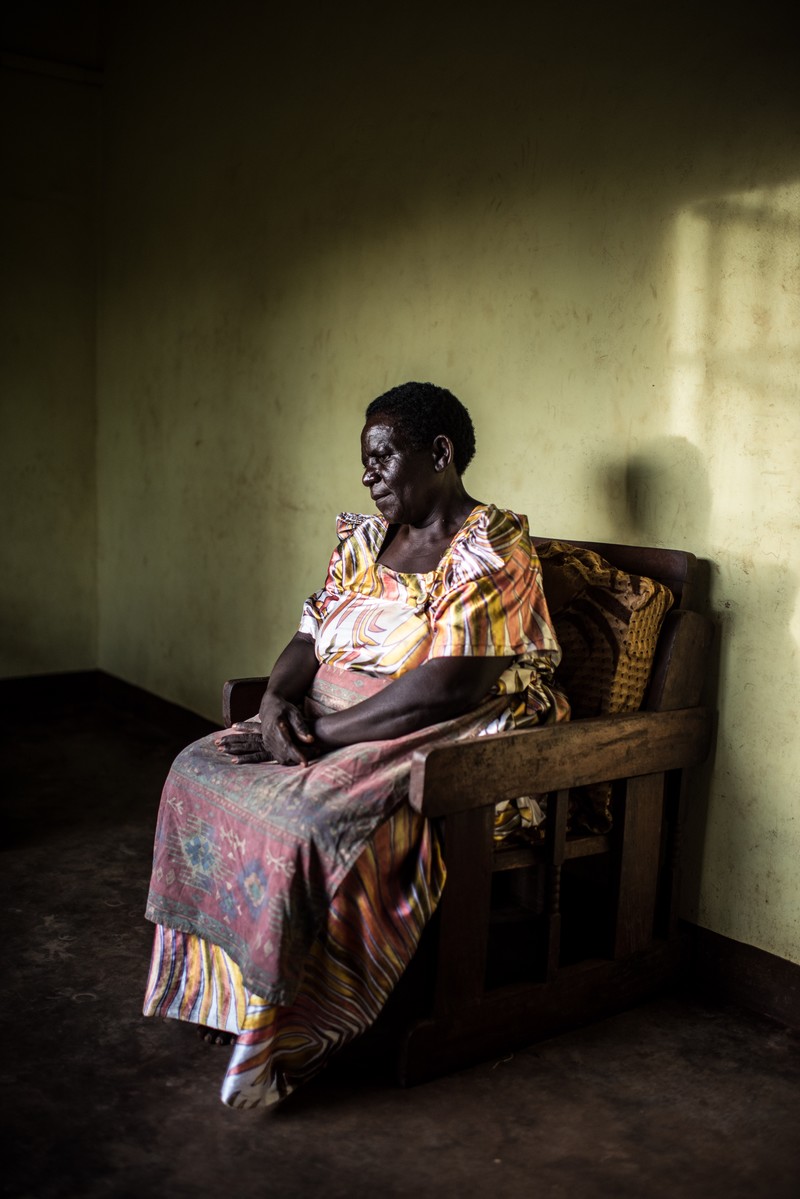

| 20 May 2017
A mother's heart break after losing teen daughter to unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Margaret's daughter, Gladys, was raped by a relative as a teenager and became pregnant. She did not tell her mother what had happened and not wanting to have a child at such a young age conceived through incest, Gladys tried to terminate the pregnancy herself using local herbs but got an infection and died. "My name is Margaret and I am a widow." "I lost my daughter in 2011. She was called Gladys and she was 16. I didn’t know that she was pregnant. She tried to use local herbs to abort. I only found out about it three days later when she was bleeding very heavily. I tried to take her to the hospital but unfortunately she died on the way." Despite being the cause of many deaths in the region, the stigma surrounding abortion means that most people do not mention the cause of death publically. However at Gladys' funeral one of her school friends spoke out and said that she had died due to unsafe abortion. This prompted VODA to start working on the issue and when the project started they included Margaret in their training on how to prevent unsafe abortion. "The training made me stronger to talk about it. Now, I continue to tell my remaining two girls about the dangers of unsafe abortion, sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies. VODA has really helped us. I think my girl wouldn’t have died if VODA was active then like it is now." "I have used VODA's information to carry on with my parental work. That information has been helpful because we are noticing change. I keep on reminding them, 'didn’t you see what happened to your friend here?'. So they have really changed especially with the ongoing help of the people from VODA." "Unsafe abortion was rampant in the past. We had tried to speak to the students, as parents, but it seemed that our information was not enough. But now we have another helping hand from VODA, especially with those seminars targeting the girls." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
A mother's heart break after losing teen daughter to unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Margaret's daughter, Gladys, was raped by a relative as a teenager and became pregnant. She did not tell her mother what had happened and not wanting to have a child at such a young age conceived through incest, Gladys tried to terminate the pregnancy herself using local herbs but got an infection and died. "My name is Margaret and I am a widow." "I lost my daughter in 2011. She was called Gladys and she was 16. I didn’t know that she was pregnant. She tried to use local herbs to abort. I only found out about it three days later when she was bleeding very heavily. I tried to take her to the hospital but unfortunately she died on the way." Despite being the cause of many deaths in the region, the stigma surrounding abortion means that most people do not mention the cause of death publically. However at Gladys' funeral one of her school friends spoke out and said that she had died due to unsafe abortion. This prompted VODA to start working on the issue and when the project started they included Margaret in their training on how to prevent unsafe abortion. "The training made me stronger to talk about it. Now, I continue to tell my remaining two girls about the dangers of unsafe abortion, sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies. VODA has really helped us. I think my girl wouldn’t have died if VODA was active then like it is now." "I have used VODA's information to carry on with my parental work. That information has been helpful because we are noticing change. I keep on reminding them, 'didn’t you see what happened to your friend here?'. So they have really changed especially with the ongoing help of the people from VODA." "Unsafe abortion was rampant in the past. We had tried to speak to the students, as parents, but it seemed that our information was not enough. But now we have another helping hand from VODA, especially with those seminars targeting the girls." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 20 May 2017
Educating their peers about unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grassroots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Peer educators in schools provide counselling and advice to other students, who otherwise would have no one to turn to in times of crisis. Today, we have the largest generation of young people ever, each one with their own unique needs. Peer educators are critical in gaining the trust and confidence of hundreds of young girls each term, and together they help each other gain more knowledge about their sexual and reproductive health. Peer educators themselves also gain a great deal from the training and experience and VODA has been successful in empowering many of these young girls to feel confident and be able to talk out in public, something that they were not able to do before. Poverty, gender inequality, lack of knowledge about sex and relationships and lack of access to sanitary protection mean that girls in rural Uganda are at high risk of sexual exploitation and abuse. All of this coupled with very little access to contraception means that Uganda has high rates of unintended pregnancies among young girls. Despite abortion being legal in Uganda in cases of rape and incest, most girls are not aware of the law and resort to unsafe abortion often using local herbs or washing liquid. The peer educators trained by VODA are able to listen to other young people's issues and provide support and information a range of issues including safe abortion as well as how to access contraception. My name is Mabel. I am in my final year of O'Levels and I am a peer counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I was selected with two others by VODA and my head teacher, and then trained to be a peer counsellor. We were trained to help our colleagues at school to handle various problems. Girls used to get pregnant and some were dropping out of school. So we counselled many of our colleagues about unwanted pregnancies. We have seen a change because we get free condoms from VODA. We could preach abstinence from sex. For those that could not manage abstinence, we could give them male condoms. Unsafe abortion has been a big problem. Girls were using local herbs and sharp instruments like metallic hangers for abortion. Many would get injured and some would die. I remember last year there was a girl who aborted using those local methods but she died and was buried in Seeta. If VODA wasn't here I think things would be very bad because as students, we did not have access to most of the information that we needed. We would have seen a big number of girls out of school because of unwanted pregnancies or unsafe abortion. I have benefited a lot. I have acquired information which I have used to keep myself safe in terms of unwanted pregnancies. I don’t think I could ever be lured to perform unsafe abortion because I know the risks. In the past, I wasn't able to speak in public but now I can stand and talk freely. I’m Sharon and I’m a student counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I counsel fellow students, young people in communities and even adults. Before I was selected for VODA training I thought it was just an organisation to promote abortion. But then I realised they were addressing a big problem that was happening at our school and our villages. I have learnt that when someone gets pregnant I don’t have to force her to abort and I don’t encourage her to go for unsafe abortion. If we hear that a certain girl has a boyfriend, we approach her and counsel her on issues like unwanted pregnancy. Many young girls have been lured into early sex because they need money, which is why we end up with unwanted pregnancies. In a bid to fulfil those needs, they get boyfriends or other guys who use them for money, impregnate them and then leave. The girls know about contraceptives like the pill and we have given some of them referral cards for them to access the contraceptives from the health centres. But there has been debate against giving young girls contraceptives. There are restrictions that the government puts in place but that does not mean that girls are not getting pregnant. I remember the girls who died after aborting through unsafe abortion methods and I think about the lives that would have been saved if they had knowledge about contraceptives. I’m Rita and I’m 15-years-old. I was twelve when I was selected to be a VODA counsellor in my primary school. I was lucky because many people wanted to be counsellors but I was chosen. My parents were very happy and they got interested. When I joined this school, I introduced myself to other students because I wanted to continue with my work as a counsellor. I told my colleagues to feel free to share with me their issues. We are lucky here because there are many counsellors. Girls are having unwanted pregnancies because they are lured by men who give them presents and things such as money for sanitary pads that they cannot get from their parents. Before I joined this school, there were many cases of girls terminating pregnancies with unsafe abortions. It was common to hear of or see someone who had aborted. Many would abort so that they would return to school. When I joined this school last year and we intensified the counselling sessions, many came and shared their problems with us. We have learnt that two girls at school gave birth and have since returned to school but we have not had cases of unsafe abortions here since I joined. I wasn’t as serious with studies before I became a counsellor but because I want to maintain my status, I have improved in my studies because I don’t want to feel ashamed in front of my fellow students. VODA gave us T-shirts for identification purposes which has made people in the community respect me as well. In terms of preventing unwanted pregnancies in schools, most of what we see here originates from the girls' homes. Many parents don’t provide for the girls’ necessities (like sanitary towels) so that makes them vulnerable to be lured by men. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
Educating their peers about unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grassroots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Peer educators in schools provide counselling and advice to other students, who otherwise would have no one to turn to in times of crisis. Today, we have the largest generation of young people ever, each one with their own unique needs. Peer educators are critical in gaining the trust and confidence of hundreds of young girls each term, and together they help each other gain more knowledge about their sexual and reproductive health. Peer educators themselves also gain a great deal from the training and experience and VODA has been successful in empowering many of these young girls to feel confident and be able to talk out in public, something that they were not able to do before. Poverty, gender inequality, lack of knowledge about sex and relationships and lack of access to sanitary protection mean that girls in rural Uganda are at high risk of sexual exploitation and abuse. All of this coupled with very little access to contraception means that Uganda has high rates of unintended pregnancies among young girls. Despite abortion being legal in Uganda in cases of rape and incest, most girls are not aware of the law and resort to unsafe abortion often using local herbs or washing liquid. The peer educators trained by VODA are able to listen to other young people's issues and provide support and information a range of issues including safe abortion as well as how to access contraception. My name is Mabel. I am in my final year of O'Levels and I am a peer counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I was selected with two others by VODA and my head teacher, and then trained to be a peer counsellor. We were trained to help our colleagues at school to handle various problems. Girls used to get pregnant and some were dropping out of school. So we counselled many of our colleagues about unwanted pregnancies. We have seen a change because we get free condoms from VODA. We could preach abstinence from sex. For those that could not manage abstinence, we could give them male condoms. Unsafe abortion has been a big problem. Girls were using local herbs and sharp instruments like metallic hangers for abortion. Many would get injured and some would die. I remember last year there was a girl who aborted using those local methods but she died and was buried in Seeta. If VODA wasn't here I think things would be very bad because as students, we did not have access to most of the information that we needed. We would have seen a big number of girls out of school because of unwanted pregnancies or unsafe abortion. I have benefited a lot. I have acquired information which I have used to keep myself safe in terms of unwanted pregnancies. I don’t think I could ever be lured to perform unsafe abortion because I know the risks. In the past, I wasn't able to speak in public but now I can stand and talk freely. I’m Sharon and I’m a student counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I counsel fellow students, young people in communities and even adults. Before I was selected for VODA training I thought it was just an organisation to promote abortion. But then I realised they were addressing a big problem that was happening at our school and our villages. I have learnt that when someone gets pregnant I don’t have to force her to abort and I don’t encourage her to go for unsafe abortion. If we hear that a certain girl has a boyfriend, we approach her and counsel her on issues like unwanted pregnancy. Many young girls have been lured into early sex because they need money, which is why we end up with unwanted pregnancies. In a bid to fulfil those needs, they get boyfriends or other guys who use them for money, impregnate them and then leave. The girls know about contraceptives like the pill and we have given some of them referral cards for them to access the contraceptives from the health centres. But there has been debate against giving young girls contraceptives. There are restrictions that the government puts in place but that does not mean that girls are not getting pregnant. I remember the girls who died after aborting through unsafe abortion methods and I think about the lives that would have been saved if they had knowledge about contraceptives. I’m Rita and I’m 15-years-old. I was twelve when I was selected to be a VODA counsellor in my primary school. I was lucky because many people wanted to be counsellors but I was chosen. My parents were very happy and they got interested. When I joined this school, I introduced myself to other students because I wanted to continue with my work as a counsellor. I told my colleagues to feel free to share with me their issues. We are lucky here because there are many counsellors. Girls are having unwanted pregnancies because they are lured by men who give them presents and things such as money for sanitary pads that they cannot get from their parents. Before I joined this school, there were many cases of girls terminating pregnancies with unsafe abortions. It was common to hear of or see someone who had aborted. Many would abort so that they would return to school. When I joined this school last year and we intensified the counselling sessions, many came and shared their problems with us. We have learnt that two girls at school gave birth and have since returned to school but we have not had cases of unsafe abortions here since I joined. I wasn’t as serious with studies before I became a counsellor but because I want to maintain my status, I have improved in my studies because I don’t want to feel ashamed in front of my fellow students. VODA gave us T-shirts for identification purposes which has made people in the community respect me as well. In terms of preventing unwanted pregnancies in schools, most of what we see here originates from the girls' homes. Many parents don’t provide for the girls’ necessities (like sanitary towels) so that makes them vulnerable to be lured by men. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda
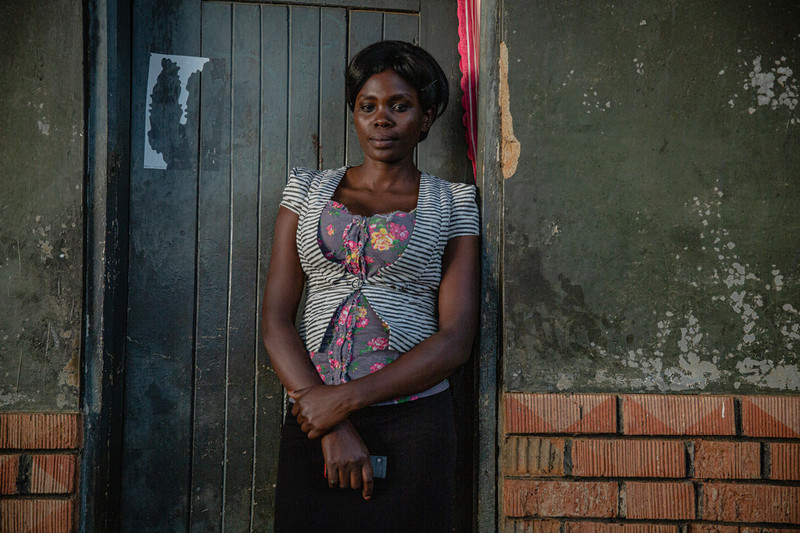
| 05 January 2022
In pictures: The changemaker keeping her community healthy and happy
The Get Up, Speak Out! initiative works with and for young people to overcome barriers such as unequal gender norms, negative attitudes towards sexuality, taboos about sex, menstruation, and abortion. Empowering youth communities - especially girls and young women - with information and knowledge about sexual and reproductive health, and the provision of access to health and contraceptive care, is at the heart of the initiative. Get Up, Speak Out! is an international initiative developed by a consortium of partners including IPPF, Rutgers, CHOICE for Youth & Sexuality, Dance4Life, Simavi, and Aidsfonds, with support from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
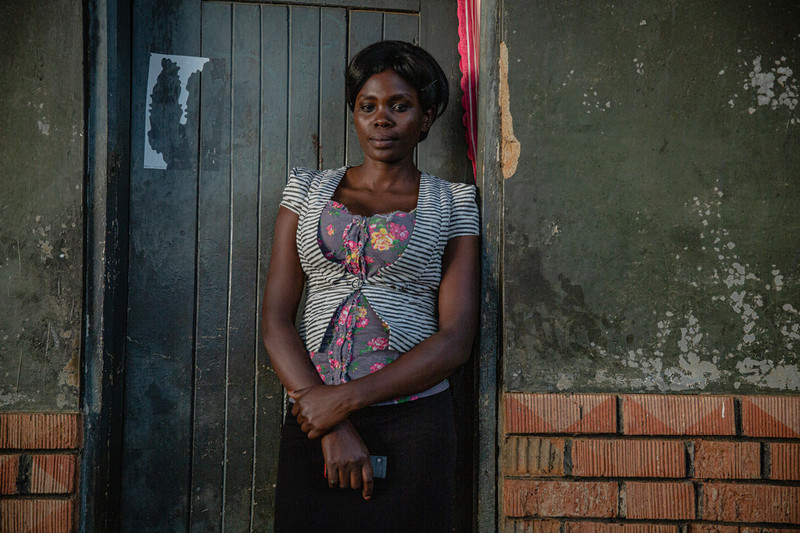
| 16 May 2025
In pictures: The changemaker keeping her community healthy and happy
The Get Up, Speak Out! initiative works with and for young people to overcome barriers such as unequal gender norms, negative attitudes towards sexuality, taboos about sex, menstruation, and abortion. Empowering youth communities - especially girls and young women - with information and knowledge about sexual and reproductive health, and the provision of access to health and contraceptive care, is at the heart of the initiative. Get Up, Speak Out! is an international initiative developed by a consortium of partners including IPPF, Rutgers, CHOICE for Youth & Sexuality, Dance4Life, Simavi, and Aidsfonds, with support from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.

| 23 September 2020
In pictures: Innovating during COVID-19
Women around the world have faced multiple barriers to accessing safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic including the de-prioritization of sexual and reproductive healthcare, overwhelmed health systems and restrictions on movement. The COVID-19 crisis has sparked innovation among IPPF Member Associations who responded swiftly by developing new approaches to reach women with safe abortion care including telemedicine and home-based provision of medical abortion. Strong evidence generated from this work supports the continuation and strengthening of these approaches beyond the end of the pandemic. Cameroon Cameroon National Planning Association for Family Welfare (CAMNAFAW) To ensure that quality abortion care can be provided to women during travel restrictions, CAMNAFAW’s service providers travel to partner clinics in underserved areas and to clients’ homes to provide medical and surgical abortion care. This model of taking safe abortion care closer to women will continue even with easing of travel restrictions, as this has been found to be an effective and acceptable approach to increasing access.Photo: IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Cameroon Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Guinea Association Guinéenne pour le Bien-Etre Familial (AGBEF) Building on lessons learned during the Ebola crisis in Guinea, AGBEF quickly took measures to prevent infection in its clinics to continue providing sexual and reproductive healthcare, including surgical and medical abortion, in a safe environment. AGBEF donated protective materials to communities, including hand-washing stations, face masks and antibacterial gel, alongside messaging on infection prevention. This community visibility reassures clients they can safely attend AGBEF clinics for abortion and contraceptive care.Photo: AGBEF/Guinea Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email India Family Planning Association of India (FPA India) FPA India and partners advocated to have sexual and reproductive healthcare, including abortion, recognized as essential by the government, which meant FPA India could continue healthcare delivery during the national lockdown. To reduce in-person clinic visits, FPA India established teleconsultation and counselling for abortion care, and is continuing to provide in-clinic care for both medical and surgical abortion. Photo: IPPF/Alison Joyce/India Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nepal Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN) FPAN and partners advocated for interim approval of home provision of medical abortion and telemedicine for abortion counselling during COVID-19. FPAN is now implementing these approaches, ensuring continued access to abortion care in Nepal, where many people live in remote locations with limited mobility, which has been further restricted by COVID-19 lockdowns. Photo: FPAN/Nepal Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Pakistan Rahnuma – Family Planning Association of Pakistan (Rahnuma-FPAP) Rahnuma-FPAP and partners successfully advocated for the government to class sexual and reproductive healthcare as ‘essential’, which enabled the team to continue providing post-abortion care during the pandemic. Rahnuma-FPAP expanded its telemedicine and home-based provision for menstrual regulation counselling and post-abortion care. These new approaches have ensured continued access to services for clients unable to reach clinics.Photo: Rahnuma-FPAP/Pakistan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Palestine Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA) In response to the government-mandated closure of its clinics, PFPPA quickly established a toll-free call centre which provides consultations, counselling, referrals and follow-up, including consultation for abortion care through a harm reduction approach, ensuring that women are provided with accurate information. Due to its success, PFPPA is exploring options for continuing this healthcare delivery model beyond the pandemic, with the aim of keeping it free of charge for users.Photo: SAAF/Samar Hazboun/Palestine Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sudan Sudan Family Planning Association (SFPA) Following a nation-wide shutdown in April, SFPA established a call centre to increase access to healthcare, including abortion and contraceptive counselling and referrals. An unexpected outcome of the new call centre is that it has reached an increased number of young women who regularly call to discuss their reproductive health and rights. SFPA is working towards institutionalizing this model for continuation beyond the pandemic.Photo: SFPA/Sudan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Togo Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ATBEF) ATBEF adapted its mobile application ‘Infos Ado Jeunes’, adding a toll-free teleconsultation service for young clients to use to access abortion consultations and pre- and post-abortion counselling. This app has given young clients ongoing access to care when they face challenges travelling to clinics. It has also eased overall client flow in clinics at a time when social distancing is being implemented.Photo: ATBEF/Togo Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 15 May 2025
In pictures: Innovating during COVID-19
Women around the world have faced multiple barriers to accessing safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic including the de-prioritization of sexual and reproductive healthcare, overwhelmed health systems and restrictions on movement. The COVID-19 crisis has sparked innovation among IPPF Member Associations who responded swiftly by developing new approaches to reach women with safe abortion care including telemedicine and home-based provision of medical abortion. Strong evidence generated from this work supports the continuation and strengthening of these approaches beyond the end of the pandemic. Cameroon Cameroon National Planning Association for Family Welfare (CAMNAFAW) To ensure that quality abortion care can be provided to women during travel restrictions, CAMNAFAW’s service providers travel to partner clinics in underserved areas and to clients’ homes to provide medical and surgical abortion care. This model of taking safe abortion care closer to women will continue even with easing of travel restrictions, as this has been found to be an effective and acceptable approach to increasing access.Photo: IPPF/Xaume Olleros/Cameroon Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Guinea Association Guinéenne pour le Bien-Etre Familial (AGBEF) Building on lessons learned during the Ebola crisis in Guinea, AGBEF quickly took measures to prevent infection in its clinics to continue providing sexual and reproductive healthcare, including surgical and medical abortion, in a safe environment. AGBEF donated protective materials to communities, including hand-washing stations, face masks and antibacterial gel, alongside messaging on infection prevention. This community visibility reassures clients they can safely attend AGBEF clinics for abortion and contraceptive care.Photo: AGBEF/Guinea Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email India Family Planning Association of India (FPA India) FPA India and partners advocated to have sexual and reproductive healthcare, including abortion, recognized as essential by the government, which meant FPA India could continue healthcare delivery during the national lockdown. To reduce in-person clinic visits, FPA India established teleconsultation and counselling for abortion care, and is continuing to provide in-clinic care for both medical and surgical abortion. Photo: IPPF/Alison Joyce/India Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Nepal Family Planning Association of Nepal (FPAN) FPAN and partners advocated for interim approval of home provision of medical abortion and telemedicine for abortion counselling during COVID-19. FPAN is now implementing these approaches, ensuring continued access to abortion care in Nepal, where many people live in remote locations with limited mobility, which has been further restricted by COVID-19 lockdowns. Photo: FPAN/Nepal Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Pakistan Rahnuma – Family Planning Association of Pakistan (Rahnuma-FPAP) Rahnuma-FPAP and partners successfully advocated for the government to class sexual and reproductive healthcare as ‘essential’, which enabled the team to continue providing post-abortion care during the pandemic. Rahnuma-FPAP expanded its telemedicine and home-based provision for menstrual regulation counselling and post-abortion care. These new approaches have ensured continued access to services for clients unable to reach clinics.Photo: Rahnuma-FPAP/Pakistan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Palestine Palestinian Family Planning and Protection Association (PFPPA) In response to the government-mandated closure of its clinics, PFPPA quickly established a toll-free call centre which provides consultations, counselling, referrals and follow-up, including consultation for abortion care through a harm reduction approach, ensuring that women are provided with accurate information. Due to its success, PFPPA is exploring options for continuing this healthcare delivery model beyond the pandemic, with the aim of keeping it free of charge for users.Photo: SAAF/Samar Hazboun/Palestine Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sudan Sudan Family Planning Association (SFPA) Following a nation-wide shutdown in April, SFPA established a call centre to increase access to healthcare, including abortion and contraceptive counselling and referrals. An unexpected outcome of the new call centre is that it has reached an increased number of young women who regularly call to discuss their reproductive health and rights. SFPA is working towards institutionalizing this model for continuation beyond the pandemic.Photo: SFPA/Sudan Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Togo Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Etre Familial (ATBEF) ATBEF adapted its mobile application ‘Infos Ado Jeunes’, adding a toll-free teleconsultation service for young clients to use to access abortion consultations and pre- and post-abortion counselling. This app has given young clients ongoing access to care when they face challenges travelling to clinics. It has also eased overall client flow in clinics at a time when social distancing is being implemented.Photo: ATBEF/Togo Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email

| 25 February 2019
In pictures: Togo and the rise in contraception use
Félicité Sonhaye ATBEF Regional Coordinator The Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), has led a pioneering programme training community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. “The injection is used more than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. “Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies”, Sonhaye added. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sossou Sagna Ilama village chief Men like Sossou Sagna, have great influence and respect within Togo’s rural communities. As Ilama’s village chief his approval was required for the ATBEF community project to take root. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied. Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty. Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abla Abassa Community health worker Abla is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets visiting households that have signed up to an innovative programme providing contraception in hard-to-reach places. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project the community is now able to space their births. I have seen the number of children per family going down. That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that everyone wants to send their children to school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Essivi Koutchona Client Facing prohibitive costs of school fees and food prices for six children, Essivi Koutchona, began using the contraceptive injection after deciding with her husband they did not want another child. She has received the injection every three months and has not experienced any side effects. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects. We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Edem Badagbo Client 33-year-old Edem is a widowed father of three children. Edem hopes to have a vasectomy within the next month or so. His wife died following the birth of their third child but he is adamant he wants to follow through with a procedure they agreed upon before her death. “My wife agreed with the idea. I was scared when I first heard of it, but that’s because there was so little information available. When I came to the ATBEF clinic I received a lot more detail and that’s when I decided to do it. I have three children. That’s enough.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Yaori Ajossou Vasectomy client Yaori Ajossou, a retired soldier, heard about vasectomy while listening to an ABTEF awareness raising campaign on the radio. It prompted him to take on the responsibility for family planning in his marriage. “Before I had the idea that maybe I'd want to have more children, but after the campaign, and after my wife had talked a little bit about her health problems, I thought, well, maybe it's better to put the brakes on. I was about to retire. Why carry on having children? Six children is already a lot. It's already maybe too many.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Dede Koussawo Client 34-year-old Dede visits the ATBEF clinic in Lomé, Togo with her husband, Edem. “We do this together if his schedule permits it. I asked and he accepted. It's not typical (for men to come). Before the pregnancy, I was taking the pill. Before the first I was taking the pill and I used an IUD after my son's birth and after my daughter's birth as well. We've been really happy with the family planning we've got here so we decided to come here for Prescillia’s birth as well.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mensah Awity Teacher and ABTEF youth club coordinator in Tohoun Mensah Awity is a teacher at a local school in Tohoun. He also coordinates the ABTEF youth club where they provide information and opportunities for the students to talk about sexual health, pregnancy, contraception. “At the beginning it was difficult for the club. Now teachers have started accepting the ideas and some pupils behave much better so it’s hard for them to keep condemning it. There are three girls who gave birth and who came back to school afterwards. At the beginning it was tough for them but we explained to the students that they shouldn’t be treated differently. The rate of pregnancy has definitely gone down at school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Emefa Charita Ankouy Youth activist and student “I'm studying for a degree in English and I'm a young activist volunteer with the IPPF youth movement. We promote, we try to help young girls who are in education to have more information about sexual health and reproduction to help them to adopt a method to avoid a pregnancy. They don't have enough information about sexual health and reproduction. I think it's because of that that they've become pregnant. They want to have sex quite early. There is pressure and there's a lack of communication between the students and their parents. Here in Togo sex is taboo for everyone, above all for parents.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Evedoh Worou Community Health Worker, Ilama “The ones who prefer the pill are young students or apprentices. Often, they take it to reduce PMS, and it regulates their period. Sometimes women will forget to take the pill, which means the injection is preferred as it’s just once for three months. The women here have more autonomy and they now have the space to earn money themselves for the household as a result of the programme. At the beginning, there were some reservations among the men in the community but after our awareness campaigns, more and more of them accompany women for family planning.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 16 May 2025
In pictures: Togo and the rise in contraception use
Félicité Sonhaye ATBEF Regional Coordinator The Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), has led a pioneering programme training community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. “The injection is used more than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. “Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies”, Sonhaye added. Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Sossou Sagna Ilama village chief Men like Sossou Sagna, have great influence and respect within Togo’s rural communities. As Ilama’s village chief his approval was required for the ATBEF community project to take root. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied. Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty. Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Abla Abassa Community health worker Abla is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets visiting households that have signed up to an innovative programme providing contraception in hard-to-reach places. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project the community is now able to space their births. I have seen the number of children per family going down. That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that everyone wants to send their children to school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Essivi Koutchona Client Facing prohibitive costs of school fees and food prices for six children, Essivi Koutchona, began using the contraceptive injection after deciding with her husband they did not want another child. She has received the injection every three months and has not experienced any side effects. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects. We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Edem Badagbo Client 33-year-old Edem is a widowed father of three children. Edem hopes to have a vasectomy within the next month or so. His wife died following the birth of their third child but he is adamant he wants to follow through with a procedure they agreed upon before her death. “My wife agreed with the idea. I was scared when I first heard of it, but that’s because there was so little information available. When I came to the ATBEF clinic I received a lot more detail and that’s when I decided to do it. I have three children. That’s enough.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Yaori Ajossou Vasectomy client Yaori Ajossou, a retired soldier, heard about vasectomy while listening to an ABTEF awareness raising campaign on the radio. It prompted him to take on the responsibility for family planning in his marriage. “Before I had the idea that maybe I'd want to have more children, but after the campaign, and after my wife had talked a little bit about her health problems, I thought, well, maybe it's better to put the brakes on. I was about to retire. Why carry on having children? Six children is already a lot. It's already maybe too many.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Dede Koussawo Client 34-year-old Dede visits the ATBEF clinic in Lomé, Togo with her husband, Edem. “We do this together if his schedule permits it. I asked and he accepted. It's not typical (for men to come). Before the pregnancy, I was taking the pill. Before the first I was taking the pill and I used an IUD after my son's birth and after my daughter's birth as well. We've been really happy with the family planning we've got here so we decided to come here for Prescillia’s birth as well.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Mensah Awity Teacher and ABTEF youth club coordinator in Tohoun Mensah Awity is a teacher at a local school in Tohoun. He also coordinates the ABTEF youth club where they provide information and opportunities for the students to talk about sexual health, pregnancy, contraception. “At the beginning it was difficult for the club. Now teachers have started accepting the ideas and some pupils behave much better so it’s hard for them to keep condemning it. There are three girls who gave birth and who came back to school afterwards. At the beginning it was tough for them but we explained to the students that they shouldn’t be treated differently. The rate of pregnancy has definitely gone down at school.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Emefa Charita Ankouy Youth activist and student “I'm studying for a degree in English and I'm a young activist volunteer with the IPPF youth movement. We promote, we try to help young girls who are in education to have more information about sexual health and reproduction to help them to adopt a method to avoid a pregnancy. They don't have enough information about sexual health and reproduction. I think it's because of that that they've become pregnant. They want to have sex quite early. There is pressure and there's a lack of communication between the students and their parents. Here in Togo sex is taboo for everyone, above all for parents.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Evedoh Worou Community Health Worker, Ilama “The ones who prefer the pill are young students or apprentices. Often, they take it to reduce PMS, and it regulates their period. Sometimes women will forget to take the pill, which means the injection is preferred as it’s just once for three months. The women here have more autonomy and they now have the space to earn money themselves for the household as a result of the programme. At the beginning, there were some reservations among the men in the community but after our awareness campaigns, more and more of them accompany women for family planning.” Share on Twitter Share on Facebook Share via WhatsApp Share via Email Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 25 February 2019
“I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child”
Every three months, Mawoula Dahide meets a community health worker in her village in central Togo to receive a single contraceptive injection and then carries on with her busy day. Dahide, 20, has a two-and-a-half year old son and a husband living in the capital and juggles an apprenticeship in tailoring with caring for her child. After recovering from the birth, Dahide tried the injection and immediately felt relief, knowing she would decide when she got pregnant again. “I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child,” she said. Lack of access Until 2013, Dahide and the other women living in the village of Ilama had no access to regular contraception at all, and its use was sometimes regarded with suspicion, and even fear. In her community, the average age of a mother’s first pregnancy is around 16, and women might bear a total of six or seven children compared to the national average of 4.7, according to local health workers. That trend is changing with a pioneering programme run by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), which has trained community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. ATBEF has focused their distribution of contraceptives within poor and rural communities, and with mobile outreach clinics that go to villages with no trained health workers. The unmet need for contraception in Togo stands at 34% of the population, and in rural communities, this is even higher. The association contributes a fifth of overall contraception cover to couples in Togo, a West Africa nation of 7.8 million people. There is a clear favourite among the methods offered, which include male and female condoms, the pill, and the contraceptive injection. “The injection is more used than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, Sonhaye added, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies. From client to advocate Dahide has become an advocate for the method among her peers within her community. “My friends are getting the injection as well. I was the first to start using it and it was great, so I told them about it,” she said. Another convert to the injection is Ilama’s village chief, Sossou Sagna. The father of seven agreed with his wife they didn’t want anymore children. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied,” Sagna noted in the cool of the shade. “My wife chose the three-month injection,” he added. Sagna had not anticipated some of the wider effects of increasing contraceptive use within the community, which have become prevalent over the last couple of years. “Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty,” he said. Families have more money to spend feeding and educating their children in an economy where the cost of living keeps rising. Villagers who see Sagna attending family planning sessions are also convinced that rumours about contraception making them ill are untrue. “Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family,” he added. The gains of the ATBEF rural programme will now go even further with the imminent introduction of Sayana Press, a contraceptive injection that women can self-administer. Learn more about some of the most popular contraception methods available and if they are right for you Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 15 May 2025
“I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child”
Every three months, Mawoula Dahide meets a community health worker in her village in central Togo to receive a single contraceptive injection and then carries on with her busy day. Dahide, 20, has a two-and-a-half year old son and a husband living in the capital and juggles an apprenticeship in tailoring with caring for her child. After recovering from the birth, Dahide tried the injection and immediately felt relief, knowing she would decide when she got pregnant again. “I want to use it for a couple of years and then maybe we will think about having another child,” she said. Lack of access Until 2013, Dahide and the other women living in the village of Ilama had no access to regular contraception at all, and its use was sometimes regarded with suspicion, and even fear. In her community, the average age of a mother’s first pregnancy is around 16, and women might bear a total of six or seven children compared to the national average of 4.7, according to local health workers. That trend is changing with a pioneering programme run by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), which has trained community health workers to administer contraception in the rural areas where they live. ATBEF has focused their distribution of contraceptives within poor and rural communities, and with mobile outreach clinics that go to villages with no trained health workers. The unmet need for contraception in Togo stands at 34% of the population, and in rural communities, this is even higher. The association contributes a fifth of overall contraception cover to couples in Togo, a West Africa nation of 7.8 million people. There is a clear favourite among the methods offered, which include male and female condoms, the pill, and the contraceptive injection. “The injection is more used than any other method. Around 60% of women use it,” said Félicité Sonhaye, ATBEF Regional Coordinator for Togo’s Plateaux region, which covers Ilama. Women appreciate the reliability and long-lasting effects of the injection, Sonhaye added, which allow them to stop worrying about unexpected pregnancies. From client to advocate Dahide has become an advocate for the method among her peers within her community. “My friends are getting the injection as well. I was the first to start using it and it was great, so I told them about it,” she said. Another convert to the injection is Ilama’s village chief, Sossou Sagna. The father of seven agreed with his wife they didn’t want anymore children. “I sent my own wife to seek family planning. The lady helped us and it worked really well. I also went with my older brother’s wife and she was very satisfied,” Sagna noted in the cool of the shade. “My wife chose the three-month injection,” he added. Sagna had not anticipated some of the wider effects of increasing contraceptive use within the community, which have become prevalent over the last couple of years. “Every member of this community is now aware that having a large family drives them towards poverty,” he said. Families have more money to spend feeding and educating their children in an economy where the cost of living keeps rising. Villagers who see Sagna attending family planning sessions are also convinced that rumours about contraception making them ill are untrue. “Ignorance was the reason why we had so many children per family here before. Now with the family planning advice we have received, spacing births has become a reality and the reduction of the number of children per family,” he added. The gains of the ATBEF rural programme will now go even further with the imminent introduction of Sayana Press, a contraceptive injection that women can self-administer. Learn more about some of the most popular contraception methods available and if they are right for you Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 20 February 2019
“Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves”
Abla Abassa lives in the village of Ilama, population 2,000, in rural central Togo. After waking up early each morning to prepare for the day ahead, she sits down to map out her route. Abassa is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets to visit households who have signed up to an innovative programme that provides contraception in hard-to-reach places. The village is an hour by bumpy dirt track from the regional capital of Atakpamé, and few residents have the time or money to travel into town on a regular basis to refill prescriptions. For years, that meant the women of the community had just one form of protection against pregnancy: avoiding sex altogether. In 2013, Abassa became one of 279 community health workers in the Plateaux region funded by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), working in two districts where the unmet need for contraception was greatest. Today, Abassa has three different clients, but can deal with as many as five a day. The health worker meets women on their own or with their husbands, and conversation flows about village life before she administers a contraceptive injection, or leaves behind a small pile of condoms. Reaching those in need She begins the day a few doors down at the home of Essivi Koutchona, a mother of six who has used the contraceptive injection for the last two-and-a-half years. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects,” Koutchona said. “We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection”. Koutchona’s husband, Konou Aboudou, credits Abassa and the ATBEF with improving his marriage, which he said was strained by the rhythm [calendar] method and supporting many young children at once. “Now we can better understand and support our wives. We avoid adultery and pregnancies are planned,” he explained. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project we have undertaken with ATBEF since 2013, the community is now able to space their births,” Abassa said, adding the couple had told her they wished the programmed has started years ago. Togo currently has a fertility rate of 4.7 children per woman, according to the United Nations Statistics Division, but is trying to bring that number down. Battling misinformation The government faces entrenched attitudes about the value of a large family, and misinformation spread about contraception. A community health worker has two roles: safely providing contraception, but also reassuring women that many of the rumours they have heard that the injection or pill will make them sick are false. “I tell them that side effects come from the product, so if they have an irregular period it’s not because they are ill,” Abassa said, adding it had taken much persuasion over the last five years to reach the point where she was now trusted. Abassa’s next client preferred to meet at the health worker’s home for some privacy. At 45, Adjo Amagna is still having periods and wants to avoid any chance of another pregnancy. “I think I want to go for the injection. I have never used contraception before so I think I will do it for three months to see how it goes,” she said. After the death of her fifth child, the only baby she had with her second husband, Amagna wants to focus on caring of the four children she has left. She sat down with the health worker and was passed condoms, femidoms and the pill, while Abassa explained how the injection works. After a half hour chat, Amagna agreed to begin the injection on her next visit. Changes within the community On the way to see Mawoula Dahide, a 20-year-old with one child, her last client of the day, Abassa reflected on the changes she has seen in the community since her job began. “I have seen the number of children per family going down,” she said. “That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that these days everyone wants to send their children to school.” The prevalence of contraceptive use was at 17% before the programme began, but with the focus on rural communities this has risen to 23% nationwide, even though not all areas of Togo are covered by dedicated health workers yet. We met Dahide in a quiet corner as she took a short break from an apprenticeship in tailoring. “It’s pretty tough balancing my son and my apprenticeship. If I had waited to have a kid before starting it would have been a lot easier,” she admitted. “My husband is studying at the university in Lomé so I only see him during the holidays and maybe a few weekends during term time.” Younger women like Dahide are sometimes harder to reach, said Abassa, and have a greater unmet need for contraception in a community where many have their first child around the age of 16. “Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves,” the health worker explained, adding her focus was always on recruiting more teenagers to her cause. As she heads home for the day, Abassa waved to clients and neighbours, while wondering who might be on her doorstep looking for advice when she gets there. Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 16 May 2025
“Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves”
Abla Abassa lives in the village of Ilama, population 2,000, in rural central Togo. After waking up early each morning to prepare for the day ahead, she sits down to map out her route. Abassa is a community health worker, and spends her days cycling around Ilama’s dusty streets to visit households who have signed up to an innovative programme that provides contraception in hard-to-reach places. The village is an hour by bumpy dirt track from the regional capital of Atakpamé, and few residents have the time or money to travel into town on a regular basis to refill prescriptions. For years, that meant the women of the community had just one form of protection against pregnancy: avoiding sex altogether. In 2013, Abassa became one of 279 community health workers in the Plateaux region funded by the Association Togolaise pour le Bien-Être Familial (ATBEF), working in two districts where the unmet need for contraception was greatest. Today, Abassa has three different clients, but can deal with as many as five a day. The health worker meets women on their own or with their husbands, and conversation flows about village life before she administers a contraceptive injection, or leaves behind a small pile of condoms. Reaching those in need She begins the day a few doors down at the home of Essivi Koutchona, a mother of six who has used the contraceptive injection for the last two-and-a-half years. “The community health worker passed by our house one day and explained the method and a bit about the possible side effects,” Koutchona said. “We agreed as a couple that we wanted me to start using the injection”. Koutchona’s husband, Konou Aboudou, credits Abassa and the ATBEF with improving his marriage, which he said was strained by the rhythm [calendar] method and supporting many young children at once. “Now we can better understand and support our wives. We avoid adultery and pregnancies are planned,” he explained. “Before, people didn’t have a lot of information about contraception. With the project we have undertaken with ATBEF since 2013, the community is now able to space their births,” Abassa said, adding the couple had told her they wished the programmed has started years ago. Togo currently has a fertility rate of 4.7 children per woman, according to the United Nations Statistics Division, but is trying to bring that number down. Battling misinformation The government faces entrenched attitudes about the value of a large family, and misinformation spread about contraception. A community health worker has two roles: safely providing contraception, but also reassuring women that many of the rumours they have heard that the injection or pill will make them sick are false. “I tell them that side effects come from the product, so if they have an irregular period it’s not because they are ill,” Abassa said, adding it had taken much persuasion over the last five years to reach the point where she was now trusted. Abassa’s next client preferred to meet at the health worker’s home for some privacy. At 45, Adjo Amagna is still having periods and wants to avoid any chance of another pregnancy. “I think I want to go for the injection. I have never used contraception before so I think I will do it for three months to see how it goes,” she said. After the death of her fifth child, the only baby she had with her second husband, Amagna wants to focus on caring of the four children she has left. She sat down with the health worker and was passed condoms, femidoms and the pill, while Abassa explained how the injection works. After a half hour chat, Amagna agreed to begin the injection on her next visit. Changes within the community On the way to see Mawoula Dahide, a 20-year-old with one child, her last client of the day, Abassa reflected on the changes she has seen in the community since her job began. “I have seen the number of children per family going down,” she said. “That’s contraception but also the increasing cost of living, and the fact that these days everyone wants to send their children to school.” The prevalence of contraceptive use was at 17% before the programme began, but with the focus on rural communities this has risen to 23% nationwide, even though not all areas of Togo are covered by dedicated health workers yet. We met Dahide in a quiet corner as she took a short break from an apprenticeship in tailoring. “It’s pretty tough balancing my son and my apprenticeship. If I had waited to have a kid before starting it would have been a lot easier,” she admitted. “My husband is studying at the university in Lomé so I only see him during the holidays and maybe a few weekends during term time.” Younger women like Dahide are sometimes harder to reach, said Abassa, and have a greater unmet need for contraception in a community where many have their first child around the age of 16. “Some of the young women can’t educate their own children because they had to drop out of school themselves,” the health worker explained, adding her focus was always on recruiting more teenagers to her cause. As she heads home for the day, Abassa waved to clients and neighbours, while wondering who might be on her doorstep looking for advice when she gets there. Photography by Xaume Olleros for IPPF

| 22 August 2018
“A radio announcement saved my life” – Gertrude’s story
Gertrude Mugala is a teacher in Fort Portal, a town in Western Uganda. While Gertrude considered herself fairly knowledgeable about cancer, she had never considered taking a screening test or imagined herself ever having the disease. Then one day, she heard an announcement on the radio urging women to go for cervical cancer screenings at a Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) clinic. “The radio presenter was talking about cervical cancer, and in her message she encouraged all women to get screened. I decided to go and try it out,” she said. Gertrude made her way to RHU's Fort Portal Branch clinic for the free cervical cancer screening. There, she met Ms. Irene Kugonza, an RHU service provider. Ms. Kugonza educated Gertrude and a group of other women about cervical cancer and the importance of routine screening. Gertrude received a type of cervical cancer screening called VIA (visual inspection with acetic acid). "I did not know what was happening" But Gertrude's results were not what she expected; she received a positive result. The good news, however, is that precancerous lesions can be treated if detected early. “I was so shaken when I was told I had pre-cancerous lesions. I did not know what was happening and I didn't believe what I was hearing. I had no idea of my health status. I thought I was healthy, but I was actually harbouring a potential killer disease in me. What would have happened if I didn't go for the screening? If I hadn't heard the radio announcement?” Gertrude was then referred for cryotherapy. “Following cryotherapy, I am now in the process of healing, and I am supposed to go back for review after three months,” said Gertrude. Community screenings Today, Gertrude advocates for cervical cancer screening in her community. She talks to women about cancer, especially cervical cancer, at her workplace, at the market, in meetings, and any other opportunity she gets. “I decided to let women know that cervical cancer is real and it is here with us, and that it kills. At the moment, those are the platforms I have, and I will continue educating women about cancer and encourage them to go for routine testing. I am also happy that I was near my radio that day, where I heard that announcement encouraging all women to get tested for cervical cancer. It might be because of that radio announcement that I am here today,” she said.

| 16 May 2025
“A radio announcement saved my life” – Gertrude’s story
Gertrude Mugala is a teacher in Fort Portal, a town in Western Uganda. While Gertrude considered herself fairly knowledgeable about cancer, she had never considered taking a screening test or imagined herself ever having the disease. Then one day, she heard an announcement on the radio urging women to go for cervical cancer screenings at a Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) clinic. “The radio presenter was talking about cervical cancer, and in her message she encouraged all women to get screened. I decided to go and try it out,” she said. Gertrude made her way to RHU's Fort Portal Branch clinic for the free cervical cancer screening. There, she met Ms. Irene Kugonza, an RHU service provider. Ms. Kugonza educated Gertrude and a group of other women about cervical cancer and the importance of routine screening. Gertrude received a type of cervical cancer screening called VIA (visual inspection with acetic acid). "I did not know what was happening" But Gertrude's results were not what she expected; she received a positive result. The good news, however, is that precancerous lesions can be treated if detected early. “I was so shaken when I was told I had pre-cancerous lesions. I did not know what was happening and I didn't believe what I was hearing. I had no idea of my health status. I thought I was healthy, but I was actually harbouring a potential killer disease in me. What would have happened if I didn't go for the screening? If I hadn't heard the radio announcement?” Gertrude was then referred for cryotherapy. “Following cryotherapy, I am now in the process of healing, and I am supposed to go back for review after three months,” said Gertrude. Community screenings Today, Gertrude advocates for cervical cancer screening in her community. She talks to women about cancer, especially cervical cancer, at her workplace, at the market, in meetings, and any other opportunity she gets. “I decided to let women know that cervical cancer is real and it is here with us, and that it kills. At the moment, those are the platforms I have, and I will continue educating women about cancer and encourage them to go for routine testing. I am also happy that I was near my radio that day, where I heard that announcement encouraging all women to get tested for cervical cancer. It might be because of that radio announcement that I am here today,” she said.

| 21 May 2017
A graduate in need turns to sex work
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. I am Pretty Lynn, aged 25. I am a sex worker but I went to university. I graduated with a Bachelor's Degree in Tourism in 2013. But now, during the day I’m sleeping and during the night I’m working. That is how my day goes every day. I got into sex work through friends. Okay it is not good but I am earning. I tried to get a job when I graduated. I have been applying since I graduated in 2013. I’m still applying but I’m not getting anywhere. You know to get jobs in Uganda; you have to know someone there and no one knows me there. To be a sex worker is like a curse. People look at you like, I don’t know, as someone that has no use in society. People look at you in a bad way. They even don’t consider why you are selling. They just see you as the worst thing that can happen in the society. So it is not comfortable, it is really hard but we try and survive. The fact sex working is illegal means you have to hide yourself when you are selling so that police cannot take you. And then you get diseases, men don’t want to pay. When the police come and take us, sometimes they even use us and don’t pay. So it is really hard. They want a free service. Like if they come and take you and pay that would be fair. But they say it is illegal to sell yourself. But they still use you yet they are saying it is illegal. You can’t report the police because there is no evidence. Abortion and unwanted pregnancies are really common because men don’t want to use condoms and female condoms are really rare and they are expensive. Though at times we get female condoms from Lady Marmaid’s Bureau (LMB) because there are so many of us they can’t keep on giving you them all the time. At times when we get pregnant we use local methods. You can go and use local herbs but it is not safe. One time I used local herbs and I was successful. Then the other time I used Omo washing powder and tea leaves but it was really hard for me. I almost died. I had a friend who died last year from this. But the good thing is that LMB taught us about safe abortion. I have had a safe abortion too. There are some tabs they are called Miso (misoprostol). It costs about fifty thousand shillings (£10 pounds or $20.) It is a lot of money. But if I’m working and I know I’m pregnant, I can say, "this week I’m working for my safe abortion". So if I’m working for twenty thousand, by the end of the week I will have the money. It is expensive compared to Omo at five hundred shillings but that is risky. So if I say I will work this whole week for Miso (misoprostol) it is better. But I'm working and I'm not eating. A project like this one from Lady Mermaid's can help young girls and women. But to take us from sex work, it would really be hard. They would not have enough money to cater for all of us. So what they have to do is to teach us how to protect ourselves, how to defend ourselves. Safe abortion yes. They will just have to sensitise us more about our lives, protection, female condoms and all that. I don't have a boyfriend but maybe when I get money and leave this job I will. But for now, no man would like a woman who sells. No man will bear the wife selling herself. And that will happen only if I get funds, settle somewhere else and become responsible woman. I don’t want this job. I don’t want to be in this business of sex work all the time. I want be married, with my children happily, not selling myself. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 15 May 2025
A graduate in need turns to sex work
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Lady Mermaid's Bureau. I am Pretty Lynn, aged 25. I am a sex worker but I went to university. I graduated with a Bachelor's Degree in Tourism in 2013. But now, during the day I’m sleeping and during the night I’m working. That is how my day goes every day. I got into sex work through friends. Okay it is not good but I am earning. I tried to get a job when I graduated. I have been applying since I graduated in 2013. I’m still applying but I’m not getting anywhere. You know to get jobs in Uganda; you have to know someone there and no one knows me there. To be a sex worker is like a curse. People look at you like, I don’t know, as someone that has no use in society. People look at you in a bad way. They even don’t consider why you are selling. They just see you as the worst thing that can happen in the society. So it is not comfortable, it is really hard but we try and survive. The fact sex working is illegal means you have to hide yourself when you are selling so that police cannot take you. And then you get diseases, men don’t want to pay. When the police come and take us, sometimes they even use us and don’t pay. So it is really hard. They want a free service. Like if they come and take you and pay that would be fair. But they say it is illegal to sell yourself. But they still use you yet they are saying it is illegal. You can’t report the police because there is no evidence. Abortion and unwanted pregnancies are really common because men don’t want to use condoms and female condoms are really rare and they are expensive. Though at times we get female condoms from Lady Marmaid’s Bureau (LMB) because there are so many of us they can’t keep on giving you them all the time. At times when we get pregnant we use local methods. You can go and use local herbs but it is not safe. One time I used local herbs and I was successful. Then the other time I used Omo washing powder and tea leaves but it was really hard for me. I almost died. I had a friend who died last year from this. But the good thing is that LMB taught us about safe abortion. I have had a safe abortion too. There are some tabs they are called Miso (misoprostol). It costs about fifty thousand shillings (£10 pounds or $20.) It is a lot of money. But if I’m working and I know I’m pregnant, I can say, "this week I’m working for my safe abortion". So if I’m working for twenty thousand, by the end of the week I will have the money. It is expensive compared to Omo at five hundred shillings but that is risky. So if I say I will work this whole week for Miso (misoprostol) it is better. But I'm working and I'm not eating. A project like this one from Lady Mermaid's can help young girls and women. But to take us from sex work, it would really be hard. They would not have enough money to cater for all of us. So what they have to do is to teach us how to protect ourselves, how to defend ourselves. Safe abortion yes. They will just have to sensitise us more about our lives, protection, female condoms and all that. I don't have a boyfriend but maybe when I get money and leave this job I will. But for now, no man would like a woman who sells. No man will bear the wife selling herself. And that will happen only if I get funds, settle somewhere else and become responsible woman. I don’t want this job. I don’t want to be in this business of sex work all the time. I want be married, with my children happily, not selling myself. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 20 May 2017
Working to stop unsafe abortion for school girls
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Unsafe abortion is a huge problem in Uganda with an estimated 400,000 women having an unsafe abortion per year. The law is confusing and unclear, with abortion permitted only under certain circumstances. Post-abortion care is permitted to treat women who have undergone an unsafe abortion, however lack of awareness of the law and stigma surrounding abortion mean that service providers are not always willing to treat patients who arrive seeking care. The VODA project aims to ensure that young women in Uganda are able to lead healthier lives free from unsafe abortion related deaths or complications through reducing abortion stigma in the community, increasing access to abortion-related services and ensuring the providers are trained to provide quality post-abortion care services. I am Helen. I have been a midwife at this small clinic for seven years and I have worked with VODA for four years. Unsafe abortion continues and some schoolgirls are raped. They then go to local herbalists and some of them tell me that they are given emilandira [roots] which they insert inside themselves to rupture the membranes. Some of them even try to induce an abortion by using Omo [douching with detergent or bleach]. At the end of the day they get complications then they land here, so we help them. Unsafe abortion is very common. In one month you can get more than five cases. It is a big problem. We help them, they need to go back to school, and we counsel them. If it is less than 12 weeks, we handle them from here. If they are more than 12 weeks along we refer them to the hospital. Most referrals from VODA are related to unwanted pregnancies, HIV testing, family planning, and youth friendly services. A few parents come for services for their children who are at school. So we counsel them that contraception, other than condoms, will only prevent pregnancy, but you can still get HIV and STIs, so take care. I am Josephine and I work as a midwife at a rural health centre. I deal with pregnant mothers, postnatal mothers, and there are girls who come with problems like unwanted pregnancy. I used to have a negative attitude towards abortion. But then VODA helped us understand the importance of helping someone with the problem because many people were dying in the villages because of unsafe abortion. According to my religion, helping someone to have an abortion was not allowed. But again when you look into it, it’s not good to leave someone to die. So I decided to change my attitude to help people. Post-abortion care has helped many people because these days we don’t have many people in the villages dying because of unsafe abortion. These days I’m proud of what we are doing because before I didn’t know the importance of helping someone with a problem. But these days, since people no longer die, people no longer get problems and I’m proud and happy because we help so many people. My name is Jonathan. I am married with three children. I have a Bachelor of Social Work and Social Administration. I have worked with VODA as a project officer since 2008. Due to the training that we have done about abortion many people have changed their attitudes and we have helped people to talk about the issue. Most people were against abortion before but they are now realising that if it’s done safely it is important because otherwise many people die from unsafe abortion. I have talked to religious leaders, I have talked to local leaders; I have talked to people of different categories. At first when you approach them, they have a different perception. The health workers were difficult to work with at first. However they knew people were approaching them with the problems of unsafe abortion. Due to religion, communities can be hard against this issue. But after some time we have seen that they have changed their perception toward the issue of safe and unsafe abortion. And now many of them know that in some instances, abortion is inevitable but it should be done in a safe way. I’m Stevens and I am nurse. We have some clients who come when they have already attempted an unsafe abortion. You find that it is often inevitable. The only solution you have to help those clients is to provide treatment of incomplete abortion as part of post-abortion care. Because of the VODA project there is a very remarkable change in the community. Now, those people who used to have unsafe abortions locally, know where to go for post-abortion care - unlike in the past. I remember a schoolgirl, she was in a very sorry state because she had tried some local remedies to abort. I attended to her and things went well. She went back to school. I feel so proud because that was a big life rescue. A girl like that could have died but now she is alive and I see her carrying on with her studies, I feel so proud. I praise VODA for that encouragement. This service should be legalised because whether they restrict it or not, there is abortion and it is going on. And if it’s not out in the open, so that our people know where to go for such services, it leads to more deaths. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
Working to stop unsafe abortion for school girls
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Unsafe abortion is a huge problem in Uganda with an estimated 400,000 women having an unsafe abortion per year. The law is confusing and unclear, with abortion permitted only under certain circumstances. Post-abortion care is permitted to treat women who have undergone an unsafe abortion, however lack of awareness of the law and stigma surrounding abortion mean that service providers are not always willing to treat patients who arrive seeking care. The VODA project aims to ensure that young women in Uganda are able to lead healthier lives free from unsafe abortion related deaths or complications through reducing abortion stigma in the community, increasing access to abortion-related services and ensuring the providers are trained to provide quality post-abortion care services. I am Helen. I have been a midwife at this small clinic for seven years and I have worked with VODA for four years. Unsafe abortion continues and some schoolgirls are raped. They then go to local herbalists and some of them tell me that they are given emilandira [roots] which they insert inside themselves to rupture the membranes. Some of them even try to induce an abortion by using Omo [douching with detergent or bleach]. At the end of the day they get complications then they land here, so we help them. Unsafe abortion is very common. In one month you can get more than five cases. It is a big problem. We help them, they need to go back to school, and we counsel them. If it is less than 12 weeks, we handle them from here. If they are more than 12 weeks along we refer them to the hospital. Most referrals from VODA are related to unwanted pregnancies, HIV testing, family planning, and youth friendly services. A few parents come for services for their children who are at school. So we counsel them that contraception, other than condoms, will only prevent pregnancy, but you can still get HIV and STIs, so take care. I am Josephine and I work as a midwife at a rural health centre. I deal with pregnant mothers, postnatal mothers, and there are girls who come with problems like unwanted pregnancy. I used to have a negative attitude towards abortion. But then VODA helped us understand the importance of helping someone with the problem because many people were dying in the villages because of unsafe abortion. According to my religion, helping someone to have an abortion was not allowed. But again when you look into it, it’s not good to leave someone to die. So I decided to change my attitude to help people. Post-abortion care has helped many people because these days we don’t have many people in the villages dying because of unsafe abortion. These days I’m proud of what we are doing because before I didn’t know the importance of helping someone with a problem. But these days, since people no longer die, people no longer get problems and I’m proud and happy because we help so many people. My name is Jonathan. I am married with three children. I have a Bachelor of Social Work and Social Administration. I have worked with VODA as a project officer since 2008. Due to the training that we have done about abortion many people have changed their attitudes and we have helped people to talk about the issue. Most people were against abortion before but they are now realising that if it’s done safely it is important because otherwise many people die from unsafe abortion. I have talked to religious leaders, I have talked to local leaders; I have talked to people of different categories. At first when you approach them, they have a different perception. The health workers were difficult to work with at first. However they knew people were approaching them with the problems of unsafe abortion. Due to religion, communities can be hard against this issue. But after some time we have seen that they have changed their perception toward the issue of safe and unsafe abortion. And now many of them know that in some instances, abortion is inevitable but it should be done in a safe way. I’m Stevens and I am nurse. We have some clients who come when they have already attempted an unsafe abortion. You find that it is often inevitable. The only solution you have to help those clients is to provide treatment of incomplete abortion as part of post-abortion care. Because of the VODA project there is a very remarkable change in the community. Now, those people who used to have unsafe abortions locally, know where to go for post-abortion care - unlike in the past. I remember a schoolgirl, she was in a very sorry state because she had tried some local remedies to abort. I attended to her and things went well. She went back to school. I feel so proud because that was a big life rescue. A girl like that could have died but now she is alive and I see her carrying on with her studies, I feel so proud. I praise VODA for that encouragement. This service should be legalised because whether they restrict it or not, there is abortion and it is going on. And if it’s not out in the open, so that our people know where to go for such services, it leads to more deaths. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 20 May 2017
A mother's heart break after losing teen daughter to unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Margaret's daughter, Gladys, was raped by a relative as a teenager and became pregnant. She did not tell her mother what had happened and not wanting to have a child at such a young age conceived through incest, Gladys tried to terminate the pregnancy herself using local herbs but got an infection and died. "My name is Margaret and I am a widow." "I lost my daughter in 2011. She was called Gladys and she was 16. I didn’t know that she was pregnant. She tried to use local herbs to abort. I only found out about it three days later when she was bleeding very heavily. I tried to take her to the hospital but unfortunately she died on the way." Despite being the cause of many deaths in the region, the stigma surrounding abortion means that most people do not mention the cause of death publically. However at Gladys' funeral one of her school friends spoke out and said that she had died due to unsafe abortion. This prompted VODA to start working on the issue and when the project started they included Margaret in their training on how to prevent unsafe abortion. "The training made me stronger to talk about it. Now, I continue to tell my remaining two girls about the dangers of unsafe abortion, sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies. VODA has really helped us. I think my girl wouldn’t have died if VODA was active then like it is now." "I have used VODA's information to carry on with my parental work. That information has been helpful because we are noticing change. I keep on reminding them, 'didn’t you see what happened to your friend here?'. So they have really changed especially with the ongoing help of the people from VODA." "Unsafe abortion was rampant in the past. We had tried to speak to the students, as parents, but it seemed that our information was not enough. But now we have another helping hand from VODA, especially with those seminars targeting the girls." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
A mother's heart break after losing teen daughter to unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grass-roots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Margaret's daughter, Gladys, was raped by a relative as a teenager and became pregnant. She did not tell her mother what had happened and not wanting to have a child at such a young age conceived through incest, Gladys tried to terminate the pregnancy herself using local herbs but got an infection and died. "My name is Margaret and I am a widow." "I lost my daughter in 2011. She was called Gladys and she was 16. I didn’t know that she was pregnant. She tried to use local herbs to abort. I only found out about it three days later when she was bleeding very heavily. I tried to take her to the hospital but unfortunately she died on the way." Despite being the cause of many deaths in the region, the stigma surrounding abortion means that most people do not mention the cause of death publically. However at Gladys' funeral one of her school friends spoke out and said that she had died due to unsafe abortion. This prompted VODA to start working on the issue and when the project started they included Margaret in their training on how to prevent unsafe abortion. "The training made me stronger to talk about it. Now, I continue to tell my remaining two girls about the dangers of unsafe abortion, sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancies. VODA has really helped us. I think my girl wouldn’t have died if VODA was active then like it is now." "I have used VODA's information to carry on with my parental work. That information has been helpful because we are noticing change. I keep on reminding them, 'didn’t you see what happened to your friend here?'. So they have really changed especially with the ongoing help of the people from VODA." "Unsafe abortion was rampant in the past. We had tried to speak to the students, as parents, but it seemed that our information was not enough. But now we have another helping hand from VODA, especially with those seminars targeting the girls." Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 20 May 2017
Educating their peers about unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grassroots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Peer educators in schools provide counselling and advice to other students, who otherwise would have no one to turn to in times of crisis. Today, we have the largest generation of young people ever, each one with their own unique needs. Peer educators are critical in gaining the trust and confidence of hundreds of young girls each term, and together they help each other gain more knowledge about their sexual and reproductive health. Peer educators themselves also gain a great deal from the training and experience and VODA has been successful in empowering many of these young girls to feel confident and be able to talk out in public, something that they were not able to do before. Poverty, gender inequality, lack of knowledge about sex and relationships and lack of access to sanitary protection mean that girls in rural Uganda are at high risk of sexual exploitation and abuse. All of this coupled with very little access to contraception means that Uganda has high rates of unintended pregnancies among young girls. Despite abortion being legal in Uganda in cases of rape and incest, most girls are not aware of the law and resort to unsafe abortion often using local herbs or washing liquid. The peer educators trained by VODA are able to listen to other young people's issues and provide support and information a range of issues including safe abortion as well as how to access contraception. My name is Mabel. I am in my final year of O'Levels and I am a peer counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I was selected with two others by VODA and my head teacher, and then trained to be a peer counsellor. We were trained to help our colleagues at school to handle various problems. Girls used to get pregnant and some were dropping out of school. So we counselled many of our colleagues about unwanted pregnancies. We have seen a change because we get free condoms from VODA. We could preach abstinence from sex. For those that could not manage abstinence, we could give them male condoms. Unsafe abortion has been a big problem. Girls were using local herbs and sharp instruments like metallic hangers for abortion. Many would get injured and some would die. I remember last year there was a girl who aborted using those local methods but she died and was buried in Seeta. If VODA wasn't here I think things would be very bad because as students, we did not have access to most of the information that we needed. We would have seen a big number of girls out of school because of unwanted pregnancies or unsafe abortion. I have benefited a lot. I have acquired information which I have used to keep myself safe in terms of unwanted pregnancies. I don’t think I could ever be lured to perform unsafe abortion because I know the risks. In the past, I wasn't able to speak in public but now I can stand and talk freely. I’m Sharon and I’m a student counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I counsel fellow students, young people in communities and even adults. Before I was selected for VODA training I thought it was just an organisation to promote abortion. But then I realised they were addressing a big problem that was happening at our school and our villages. I have learnt that when someone gets pregnant I don’t have to force her to abort and I don’t encourage her to go for unsafe abortion. If we hear that a certain girl has a boyfriend, we approach her and counsel her on issues like unwanted pregnancy. Many young girls have been lured into early sex because they need money, which is why we end up with unwanted pregnancies. In a bid to fulfil those needs, they get boyfriends or other guys who use them for money, impregnate them and then leave. The girls know about contraceptives like the pill and we have given some of them referral cards for them to access the contraceptives from the health centres. But there has been debate against giving young girls contraceptives. There are restrictions that the government puts in place but that does not mean that girls are not getting pregnant. I remember the girls who died after aborting through unsafe abortion methods and I think about the lives that would have been saved if they had knowledge about contraceptives. I’m Rita and I’m 15-years-old. I was twelve when I was selected to be a VODA counsellor in my primary school. I was lucky because many people wanted to be counsellors but I was chosen. My parents were very happy and they got interested. When I joined this school, I introduced myself to other students because I wanted to continue with my work as a counsellor. I told my colleagues to feel free to share with me their issues. We are lucky here because there are many counsellors. Girls are having unwanted pregnancies because they are lured by men who give them presents and things such as money for sanitary pads that they cannot get from their parents. Before I joined this school, there were many cases of girls terminating pregnancies with unsafe abortions. It was common to hear of or see someone who had aborted. Many would abort so that they would return to school. When I joined this school last year and we intensified the counselling sessions, many came and shared their problems with us. We have learnt that two girls at school gave birth and have since returned to school but we have not had cases of unsafe abortions here since I joined. I wasn’t as serious with studies before I became a counsellor but because I want to maintain my status, I have improved in my studies because I don’t want to feel ashamed in front of my fellow students. VODA gave us T-shirts for identification purposes which has made people in the community respect me as well. In terms of preventing unwanted pregnancies in schools, most of what we see here originates from the girls' homes. Many parents don’t provide for the girls’ necessities (like sanitary towels) so that makes them vulnerable to be lured by men. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda

| 16 May 2025
Educating their peers about unsafe abortion
The Safe Abortion Action Fund (SAAF) which is hosted by IPPF was set up in 2006 in order to support grassroots organisations to increase access to safe abortion. One such organisation which received support under the last round of funding is called Volunteers for Development Association Uganda (VODA). Peer educators in schools provide counselling and advice to other students, who otherwise would have no one to turn to in times of crisis. Today, we have the largest generation of young people ever, each one with their own unique needs. Peer educators are critical in gaining the trust and confidence of hundreds of young girls each term, and together they help each other gain more knowledge about their sexual and reproductive health. Peer educators themselves also gain a great deal from the training and experience and VODA has been successful in empowering many of these young girls to feel confident and be able to talk out in public, something that they were not able to do before. Poverty, gender inequality, lack of knowledge about sex and relationships and lack of access to sanitary protection mean that girls in rural Uganda are at high risk of sexual exploitation and abuse. All of this coupled with very little access to contraception means that Uganda has high rates of unintended pregnancies among young girls. Despite abortion being legal in Uganda in cases of rape and incest, most girls are not aware of the law and resort to unsafe abortion often using local herbs or washing liquid. The peer educators trained by VODA are able to listen to other young people's issues and provide support and information a range of issues including safe abortion as well as how to access contraception. My name is Mabel. I am in my final year of O'Levels and I am a peer counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I was selected with two others by VODA and my head teacher, and then trained to be a peer counsellor. We were trained to help our colleagues at school to handle various problems. Girls used to get pregnant and some were dropping out of school. So we counselled many of our colleagues about unwanted pregnancies. We have seen a change because we get free condoms from VODA. We could preach abstinence from sex. For those that could not manage abstinence, we could give them male condoms. Unsafe abortion has been a big problem. Girls were using local herbs and sharp instruments like metallic hangers for abortion. Many would get injured and some would die. I remember last year there was a girl who aborted using those local methods but she died and was buried in Seeta. If VODA wasn't here I think things would be very bad because as students, we did not have access to most of the information that we needed. We would have seen a big number of girls out of school because of unwanted pregnancies or unsafe abortion. I have benefited a lot. I have acquired information which I have used to keep myself safe in terms of unwanted pregnancies. I don’t think I could ever be lured to perform unsafe abortion because I know the risks. In the past, I wasn't able to speak in public but now I can stand and talk freely. I’m Sharon and I’m a student counsellor at a Secondary School in Namuganga. I counsel fellow students, young people in communities and even adults. Before I was selected for VODA training I thought it was just an organisation to promote abortion. But then I realised they were addressing a big problem that was happening at our school and our villages. I have learnt that when someone gets pregnant I don’t have to force her to abort and I don’t encourage her to go for unsafe abortion. If we hear that a certain girl has a boyfriend, we approach her and counsel her on issues like unwanted pregnancy. Many young girls have been lured into early sex because they need money, which is why we end up with unwanted pregnancies. In a bid to fulfil those needs, they get boyfriends or other guys who use them for money, impregnate them and then leave. The girls know about contraceptives like the pill and we have given some of them referral cards for them to access the contraceptives from the health centres. But there has been debate against giving young girls contraceptives. There are restrictions that the government puts in place but that does not mean that girls are not getting pregnant. I remember the girls who died after aborting through unsafe abortion methods and I think about the lives that would have been saved if they had knowledge about contraceptives. I’m Rita and I’m 15-years-old. I was twelve when I was selected to be a VODA counsellor in my primary school. I was lucky because many people wanted to be counsellors but I was chosen. My parents were very happy and they got interested. When I joined this school, I introduced myself to other students because I wanted to continue with my work as a counsellor. I told my colleagues to feel free to share with me their issues. We are lucky here because there are many counsellors. Girls are having unwanted pregnancies because they are lured by men who give them presents and things such as money for sanitary pads that they cannot get from their parents. Before I joined this school, there were many cases of girls terminating pregnancies with unsafe abortions. It was common to hear of or see someone who had aborted. Many would abort so that they would return to school. When I joined this school last year and we intensified the counselling sessions, many came and shared their problems with us. We have learnt that two girls at school gave birth and have since returned to school but we have not had cases of unsafe abortions here since I joined. I wasn’t as serious with studies before I became a counsellor but because I want to maintain my status, I have improved in my studies because I don’t want to feel ashamed in front of my fellow students. VODA gave us T-shirts for identification purposes which has made people in the community respect me as well. In terms of preventing unwanted pregnancies in schools, most of what we see here originates from the girls' homes. Many parents don’t provide for the girls’ necessities (like sanitary towels) so that makes them vulnerable to be lured by men. Stories Read more stories about the amazing success of SAAF in Uganda








